编译原理实验-LL1语法分析器(自动生成First、Follow)java
博主在做实验时,参考众多他人代码,发现bug众多,在@moni_mm代码基础上,与伙伴把能看到的BUG都做出修正,同时增添了一个GUI展示。再次我将代码做出讲解。完整代码最下方贴出。
一、数据结构
下文程序运行的文法为:
static String[] grammarStr = {"E->TG" ,"G->+TG|-TG" ,"G->ε" ,"T->FS" ,"S->*FS|/FS" ,"S->ε" ,"F->(E)" ,"F->i"};//相关文法
处理的输入串为:
static inStr="i+i*i#";//输入串
-----首先要考虑FOLLOW、FIRST、终结符、非终结符、预测分析表、栈、各个产生式的存储的数据结构设计:
static HashMap<Character, HashSet<Character>> FirstSet = new HashMap<>();//构造FIRST集合
static HashMap<String, HashSet<Character>> FirstSetX = new HashMap<>();//生成任何符号串的first
static HashMap<Character, HashSet<Character>> FollowSet = new HashMap<>();//构造FOLLOW集合
static String[][] table;//预测分析表
static HashSet<Character> VnSet = new HashSet<>();//非终结符Vn集合
static HashSet<Character> VtSet = new HashSet<>();//终结符Vt集合
static Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>(); //符号栈
static HashMap<Character,ArrayList<String>> production = new HashMap<>();//产生式
二、运行效果
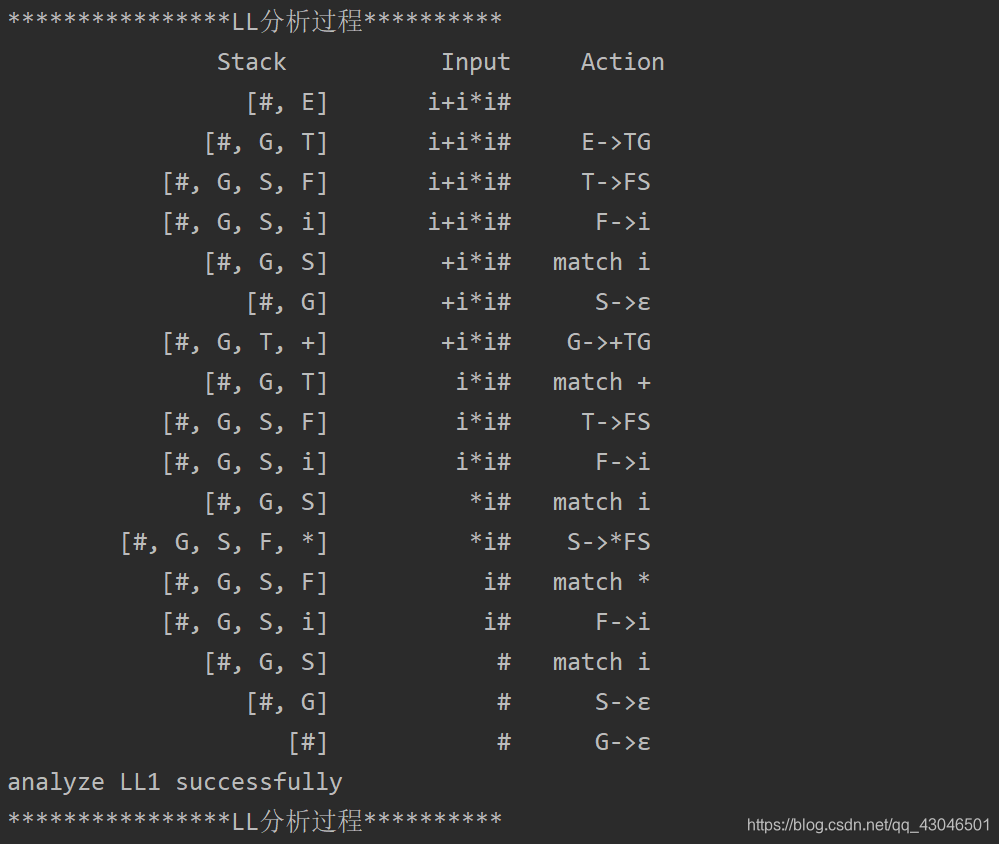
LL(1)预测分析的实现均在类LL1中得到实现,类GUI仅仅将结果在桌面程序得到展示,LL1也可单独运行,结果输出控制台:
运行GUI(注释掉LL1的main即可,反之亦然):
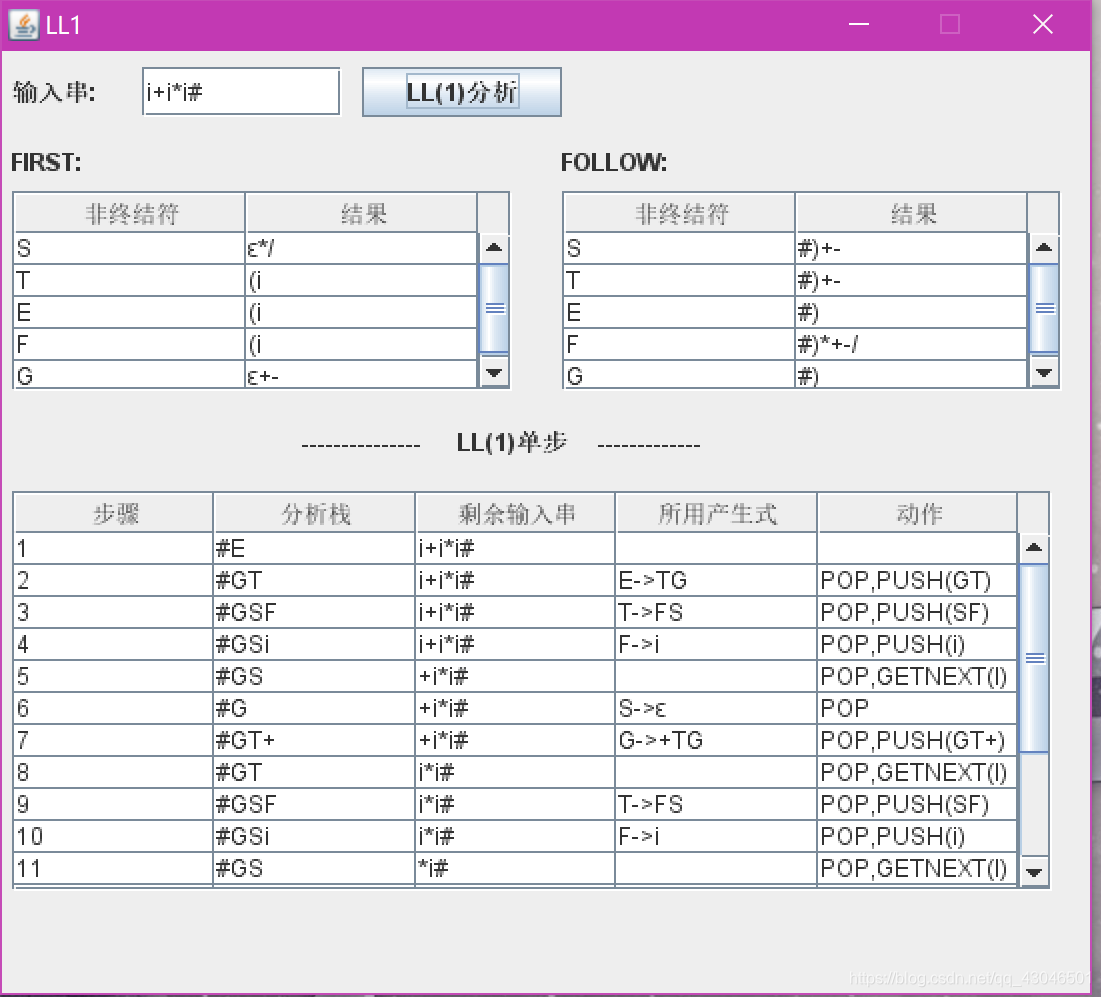
运行LL1: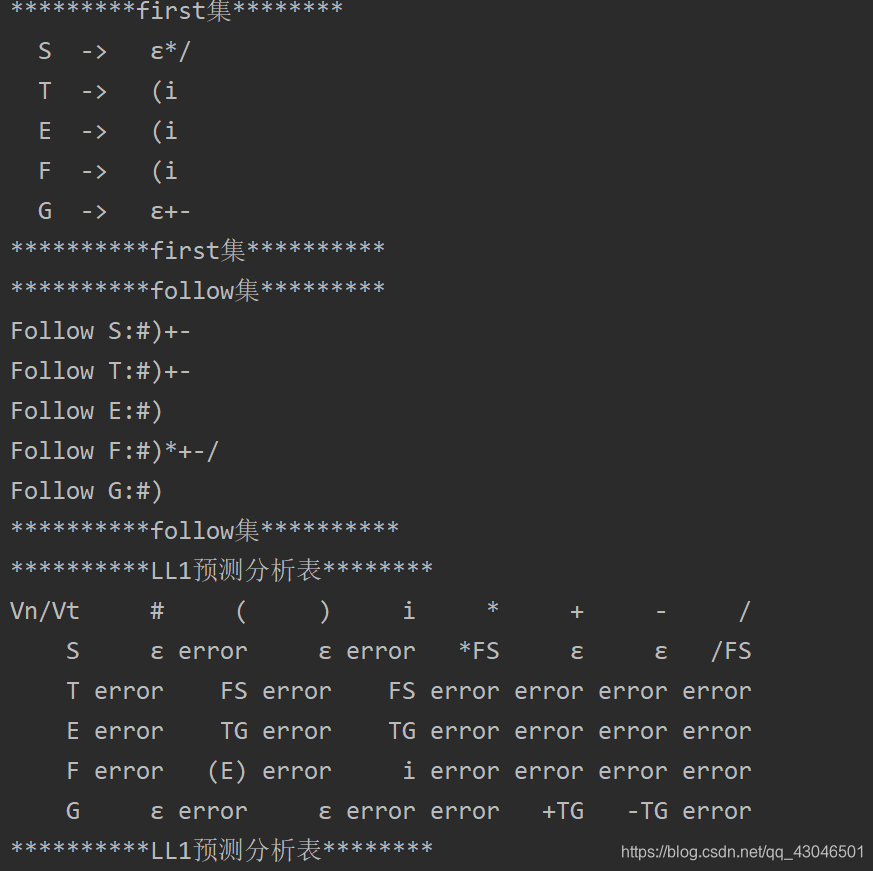
三、类的设计
-
class: LL1(打印相关不与介绍)
- dividechar() 将产生式填充进production,划分终结符(vt)与非终结符(vn) - First() 生成FIRST集(非终结符的) - getFirstX() 生成FIRST集(任意字符串的),Follow()需要调用 - Follow() 生成FOLLOW集 - insert() 将生成式插入表中 - creatTable() 创建预测分析表 - find(char X, char a) 寻找预测分析表中对应内容,X非终结符,a终结符 - processLL1() 执行LL1栈分析 -
class:GUI(可专注于LL1即可,本处简略)
- Gui(String title) 添加组件,创建面板
- class Listener implements ActionListener 时间监听器(添加具体执行语句,展示LL1.stepList、LL1.FirstSet、LL1.FollowSet的数据)
三、核心算法(求firstfollow)
- 求First集:
first集叫做首终结符集下面是博主自己的理解,用的列子讲的。在博主自己学的时候,不会的时候,死磕概念是看不懂的。额,博主菜ji.
基本就两种情况:(终结符的first即它本身)- 1.直接遇到终结符
A->aBCd | ε
若a,e为终结符,first(A)= {a,ε}。 - 2.第一个为非终结符
A->BC
此时first(A)=first(B);值得注意的是,若first(B)包含空ε,需要继续求first(C )加入first(A)中。若first(c)仍旧包含空ε,将空字符ε加入first(A)。
- 1.直接遇到终结符
- 程序实现:
/** * 生成非终结符的FIRST集的递归入口 */ static void First(){ //遍历求每一个非终结符vn的first集 for (Character vn: VnSet ) { getfisrst(vn); } } /** * 生成非终结符FIRST集的递归程序 */ static void getfisrst(Character ch){ ArrayList<String> ch_production = production.get(ch); HashSet<Character> set = FirstSet.containsKey(ch) ? FirstSet.get(ch) : new HashSet<>(); // 当ch为终结符vt if(VtSet.contains(ch)){ set.add(ch); FirstSet.put(ch,set); return; } //ch为非终结符vn for (String str:ch_production ) { int i = 0; while (i < str.length()) { char tn = str.charAt(i); //递归 getfisrst(tn); HashSet<Character> tvSet = FirstSet.get(tn); // 将其first集加入左部 for (Character tmp : tvSet) { if (tmp != 'ε') set.add(tmp); } // 若包含空串 处理下一个符号 if (tvSet.contains('ε')) i++; // 否则退出 处理下一个产生式 else break; } //此处处理产生式如A ->BC,B、C的first集都有ε if(i==str.length()) set.add('ε'); } FirstSet.put(ch,set); }- 求follow集:
课本上规则如下:
- 求follow集:
-
将放到follow(S)中,其中S是开始符号,#将放到follow(S)中,其中S是开始符号,而#是输入右端的结束标记。
-
如果存在一个产生式A→αBβ,那么first(β)中除ε之外的所有符号都在follow(B)中。
-
如果存在一个产生式A→αB,或存在产生式A→αBβ(β可以是单个非终结符,或数个非终结符的组合,β或许是CD)且first(β)包含ε,那么follow(A)中的所有符号都在follow(B)中。
举例说明:
①E→TE’
②E’→+TE’ | ε
③T→FT’
④T’→*FT’ | ε
⑤F→(E)| id
各个规则的展现:
规则一:E是文法的开始符号,第一步,follow(E).add(’#’)
规则二:对于产生式①E→TE’,follow(T).add(first(E’))
规则三:对于产生式①E→TE’,E’后面为空,故follow(E’).add(follow(E));又first(E’)包含空ε,follow(T).add(follow(E))
对每条产生式套用上述规则,循环至各个follow集都不增加。
因为:例如对于产生式①E→TE’,first(E’)包含空ε,follow(T).add(follow(E)),而此时follow(E)并未求完整。需要第二遍。
- 程序实现:
/**
* 生成FOLLOW集
*/
static void Follow(){
//此处我多循环了几次,合理的方法应该是看每一个非终结符的follow集师傅增加,不增加即可停止循环。
for (int i = 0; i <3 ; i++) {
for (Character ch:VnSet
) {
getFollow(ch);
}
}
}
/**
* 求单个字符的FOLLOW集
*/
static void getFollow(char c){
ArrayList<String> list = production.get(c);
HashSet<Character> setA = FollowSet.containsKey(c) ? FollowSet.get(c) : new HashSet<Character>();
//如果是开始符 添加 #
if (c == start) {
setA.add('#');
}
//查找输入的所有产生式,确定c的后跟 终结符
for (Character ch : VnSet) {
ArrayList<String> l = production.get(ch);
for (String s : l)
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
if (s.charAt(i) == c && i + 1 < s.length() && VtSet.contains(s.charAt(i + 1)))
setA.add(s.charAt(i + 1));
}
FollowSet.put(c, setA);
//处理c的每一条产生式,从右向左分析,A->aBβ,
for (String s : list) {
int i = s.length() - 1;
while (i >= 0 ) {
char tn = s.charAt(i);
//只处理非终结符
if(VnSet.contains(tn)){
// 都按 A->αBβ 形式处理
//若β不存在 followA 加入 followB
//若β存在,把β的非空first集 加入followB
//若β存在 且 first(β)包含空串 followA 加入 followB
//若β存在
if (s.length() - i - 1 > 0) {
String right = s.substring(i + 1);
//非空first集 加入 followB
HashSet<Character> setF = null;
if( right.length() == 1){
if(!FirstSet.containsKey(right.charAt(0)))
getfisrst(right.charAt(0));
setF = FirstSet.get(right.charAt(0));
}
else{
//先找出右部的first集
if(!FirstSetX.containsKey(right))
getFirstX(right);
setF =FirstSetX.get(right);
}
HashSet<Character> setX = FollowSet.containsKey(tn) ? FollowSet.get(tn) : new HashSet<Character>();
for (Character var : setF)
if (var != 'ε')
setX.add(var);
FollowSet.put(tn, setX);
// 若first(β)包含空串 followA 加入 followB
if(setF.contains('ε')){
if(tn != c){
HashSet<Character> setB =FollowSet.containsKey(tn) ? FollowSet.get(tn) : new HashSet<Character>();
for (Character var : setA)
setB.add(var);
FollowSet.put(tn, setB);
}
}
}
//若β不存在 followA 加入 followB
else{
// A和B相同不添加
if(tn != c){
HashSet<Character> setB = FollowSet.containsKey(tn) ? FollowSet.get(tn) : new HashSet<Character>();
for (Character var : setA)
setB.add(var);
FollowSet.put(tn, setB);
}
}
i--;
}
//如果是终结符往前看 如 A->aaaBCDaaaa 此时β为 CDaaaa
else i--;
}
}
}
四、完整代码
IDEA 工程文件放在github上:https://github.com/mhl222/BiYiYuanLi_2
大家可直接git clone下来运行
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.DefaultTableModel;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.*;
/**
* class:
* --LL1:
* 实现LL(1)分析,构造分析预测程序(FIRST集-->FOLLOW集-->分析预测表-->stack预测分析)
* --Gui:
* 读取输入串,桌面程序展示分析预测步骤
*/
public class LL1 {
static String[] grammarStr = {"E->TG" ,"G->+TG|-TG" ,"G->ε" ,"T->FS" ,"S->*FS|/FS" ,"S->ε" ,"F->(E)" ,"F->i"};//相关文法
static HashMap<Character,ArrayList<String>> production = new HashMap<>();//产生式
static HashMap<Character, HashSet<Character>> FirstSet = new HashMap<>();//构造FIRST集合
static HashMap<String, HashSet<Character>> FirstSetX = new HashMap<>();//生成任何符号串的first
static HashMap<Character, HashSet<Character>> FollowSet = new HashMap<>();//构造FOLLOW集合
static String[][] table;//预测分析表
static HashSet<Character> VnSet = new HashSet<>();//非终结符Vn集合
static HashSet<Character> VtSet = new HashSet<>();//终结符Vt集合
static Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>(); //符号栈
static String inStr="i+i*i#";//输入串
static Character start = 'E';
static int index = 0;//输入字符指针
static String action ="";
static ArrayList<Vector> stepList = new ArrayList<>();//与LL(1)无关,可不关心,为GUI记录了stack每一步的变化
public static void main(String[] args) {
dividechar();
First();
for (Character c : VnSet) {
ArrayList<String> l = production.get(c);
for (String s : l)
getFirstX(s);
}
Follow();
creatTable();
ouput();
processLL1();
}
/**
* 生成产生式Map(production),划分终结符(vt)与非终结符(vn)
*/
static void dividechar(){
//生成产生式Map(production)
for (String str:grammarStr
) {
//将“|”相连的产生式分开
String[] strings = str.split("->")[1].split("\|");
//非终结符
char Vch = str.charAt(0);
ArrayList<String> list = production.containsKey(Vch) ? production.get(Vch) : new ArrayList<String>();
for (String S:strings
) {
list.add(S);
}
production.put(str.charAt(0),list);
VnSet.add(Vch);
}
//寻找终结符
for (Character ch:VnSet
){
for (String str : production.get(ch)
) {
for (Character c: str.toCharArray()
) {
if( !VnSet.contains(c) )
VtSet.add(c);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 生成非终结符的FIRST集的递归入口
*/
static void First(){
//遍历求每一个非终结符vn的first集
for (Character vn: VnSet
) {
getfisrst(vn);
}
}
/**
* 生成非终结符FIRST集的递归程序
*/
static void getfisrst(Character ch){
ArrayList<String> ch_production = production.get(ch);
HashSet<Character> set = FirstSet.containsKey(ch) ? FirstSet.get(ch) : new HashSet<>();
// 当ch为终结符
if(VtSet.contains(ch)){
set.add(ch);
FirstSet.put(ch,set);
return;
}
//ch为vn
for (String str:ch_production
) {
int i = 0;
while (i < str.length()) {
char tn = str.charAt(i);
//递归
getfisrst(tn);
HashSet<Character> tvSet = FirstSet.get(tn);
// 将其first集加入左部
for (Character tmp : tvSet) {
if (tmp != 'ε')
set.add(tmp);
}
// 若包含空串 处理下一个符号
if (tvSet.contains('ε'))
i++;
// 否则退出 处理下一个产生式
else
break;
}
if(i==str.length())
set.add('ε');
}
FirstSet.put(ch,set);
}
/**
* 生成任何符号串的first
*/
static void getFirstX( String s) {
HashSet<Character> set = (FirstSetX.containsKey(s))? FirstSetX.get(s) : new HashSet<Character>();
// 从左往右扫描该式
int i = 0;
while (i < s.length()) {
char tn = s.charAt(i);
if(!FirstSet.containsKey(tn))
getfisrst(tn);
HashSet<Character> tvSet = FirstSet.get(tn);
// 将其非空 first集加入左部
for (Character tmp : tvSet)
if(tmp != 'ε')
set.add(tmp);
// 若包含空串 处理下一个符号
if (tvSet.contains('ε'))
i++;
// 否则结束
else
break;
// 到了尾部 即所有符号的first集都包含空串 把空串加入
if (i == s.length()) {
set.add('ε');
}
}
FirstSetX.put(s, set);
}
/**
* 生成FOLLOW集
*/
static void Follow(){
//此处我多循环了几次,合理的方法应该是看每一个非终结符的follow集师傅增加,不增加即可停止循环。
for (int i = 0; i <3 ; i++) {
for (Character ch:VnSet
) {
getFollow(ch);
}
}
}
static void getFollow(char c){
ArrayList<String> list = production.get(c);
HashSet<Character> setA = FollowSet.containsKey(c) ? FollowSet.get(c) : new HashSet<Character>();
//如果是开始符 添加 #
if (c == start) {
setA.add('#');
}
//查找输入的所有产生式,确定c的后跟 终结符
for (Character ch : VnSet) {
ArrayList<String> l = production.get(ch);
for (String s : l)
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
if (s.charAt(i) == c && i + 1 < s.length() && VtSet.contains(s.charAt(i + 1)))
setA.add(s.charAt(i + 1));
}
FollowSet.put(c, setA);
//处理c的每一条产生式
for (String s : list) {
int i = s.length() - 1;
while (i >= 0 ) {
char tn = s.charAt(i);
//只处理非终结符
if(VnSet.contains(tn)){
// 都按 A->αBβ 形式处理
//若β不存在 followA 加入 followB
//若β存在,把β的非空first集 加入followB
//若β存在 且 first(β)包含空串 followA 加入 followB
//若β存在
if (s.length() - i - 1 > 0) {
String right = s.substring(i + 1);
//非空first集 加入 followB
HashSet<Character> setF = null;
if( right.length() == 1){
if(!FirstSet.containsKey(right.charAt(0)))
getfisrst(right.charAt(0));
setF = FirstSet.get(right.charAt(0));
}
else{
//先找出右部的first集
if(!FirstSetX.containsKey(right))
getFirstX(right);
setF =FirstSetX.get(right);
}
HashSet<Character> setX = FollowSet.containsKey(tn) ? FollowSet.get(tn) : new HashSet<Character>();
for (Character var : setF)
if (var != 'ε')
setX.add(var);
FollowSet.put(tn, setX);
// 若first(β)包含空串 followA 加入 followB
if(setF.contains('ε')){
if(tn != c){
HashSet<Character> setB =FollowSet.containsKey(tn) ? FollowSet.get(tn) : new HashSet<Character>();
for (Character var : setA)
setB.add(var);
FollowSet.put(tn, setB);
}
}
}
//若β不存在 followA 加入 followB
else{
// A和B相同不添加
if(tn != c){
HashSet<Character> setB = FollowSet.containsKey(tn) ? FollowSet.get(tn) : new HashSet<Character>();
for (Character var : setA)
setB.add(var);
FollowSet.put(tn, setB);
}
}
i--;
}
//如果是终结符往前看 如 A->aaaBCDaaaa 此时β为 CDaaaa
else i--;
}
}
}
/**
* 生成预测分析表
*/
static void creatTable(){
Object[] VtArray = VtSet.toArray();
Object[] VnArray = VnSet.toArray();
// 预测分析表初始化
table = new String[VnArray.length + 1][VtArray.length + 1];
table[0][0] = "Vn/Vt";
//初始化首行首列
for (int i = 0; i < VtArray.length; i++)
table[0][i + 1] = (VtArray[i].toString().charAt(0) == 'ε') ? "#" : VtArray[i].toString();
for (int i = 0; i < VnArray.length; i++)
table[i + 1][0] = VnArray[i] + "";
//全部置error
for (int i = 0; i < VnArray.length; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < VtArray.length; j++)
table[i + 1][j + 1] = "error";
//插入生成式
for (char A : VnSet) {
ArrayList<String> l = production.get(A);
for(String s : l){
HashSet<Character> set = FirstSetX.get(s);
for (char a : set)
insert(A, a, s);
if(set.contains('ε')) {
HashSet<Character> setFollow = FollowSet.get(A);
if(setFollow.contains('#'))
insert(A, '#', s);
for (char b : setFollow)
insert(A, b, s);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 将生成式插入表中
*/
static void insert(char X, char a,String s) {
if(a == 'ε') a = '#';
for (int i = 0; i < VnSet.size() + 1; i++) {
if (table[i][0].charAt(0) == X)
for (int j = 0; j < VtSet.size() + 1; j++) {
if (table[0][j].charAt(0) == a){
table[i][j] = s;
return;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 返回当前栈内容的字符串,与LL(1)无关,为GUI提供字符串
*
*/
static String getStack(){
String str ="";
for (Character ch : stack
) {
str+=ch;
}
return str;
}
/**
* 与LL(1)无关,为GUI的表格所需的setpList,提供一行数据
*/
static void addRowToList(String production,String action){
Vector v = new Vector();
v.add(stepList.size()+1);
v.add(getStack());
v.add(inStr.substring(index));
v.add(production);
v.add(action);
stepList.add(v);
}
/**
* 执行LL1栈分析
*/
static void processLL1(){
System.out.println("****************LL分析过程**********");
System.out.println(" Stack Input Action");
stack.push('#');
stack.push('E');
addRowToList("","");//GUI数据,可不关心
displayLL();
char X = stack.peek();
while (X != '#') {
char a = inStr.charAt(index);
if (X == a) {
action = "match " + stack.peek();
stack.pop();
index++;
addRowToList("","POP,GETNEXT(I)");//GUI数据,可不关心
}
// }else if (VtSet.contains(X))
// return;
else if (find(X, a).equals("error")){
boolean flag = false;
if(FirstSet.get(X).contains('ε')){
addRowToList(X+"->ε","POP");//GUI数据,可不关心
action = X+"->ε";
stack.pop();
flag = true;
}
if(!flag){
action="error";
addRowToList("","ERROR");//GUI数据,可不关心
displayLL();
return;
}
}
else if (find(X, a).equals("ε")) {
stack.pop();
action = X + "->ε";
addRowToList(action,"POP");//GUI数据,可不关心
}
else {
String str = find(X, a);
if (str != "") {
action = X + "->" + str;
stack.pop();
int len = str.length();
String pushStr="";
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--){
stack.push(str.charAt(i));
pushStr+=str.charAt(i);
}
addRowToList(action,"POP,PUSH("+pushStr+")");//GUI数据,可不关心
}
else {
System.out.println("error at '" + inStr.charAt(index) + " in " + index);
return;
}
}
X = stack.peek();
displayLL();
}
System.out.println("analyze LL1 successfully");
System.out.println("****************LL分析过程**********");
}
/**
*
* @param X 非终结符
* @param a 终结符
* @return 预测分析表中对应内容
*/
static String find(char X, char a) {
for (int i = 0; i < VnSet.size() + 1; i++) {
if (table[i][0].charAt(0) == X)
for (int j = 0; j < VtSet.size() + 1; j++) {
if (table[0][j].charAt(0) == a)
return table[i][j];
}
}
return "";
}
static void displayLL() {
// 输出 LL1单步处理
Stack<Character> s = stack;
System.out.printf("%23s", s);
System.out.printf("%13s", inStr.substring(index));
System.out.printf("%10s", action);
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 打印first.follow集,预测分析表
*/
static void ouput() {
System.out.println("*********first集********");
for (Character c : VnSet) {
HashSet<Character> set = FirstSet.get(c);
System.out.printf("%10s",c + " -> ");
for (Character var : set)
System.out.print(var);
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("**********first集**********");
System.out.println("**********follow集*********");
for (Character c : VnSet) {
HashSet<Character> set =FollowSet.get(c);
System.out.print("Follow " + c + ":");
for (Character var : set)
System.out.print(var);
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("**********follow集**********");
System.out.println("**********LL1预测分析表********");
for (int i = 0; i < VnSet.size() + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < VtSet.size() + 1; j++) {
System.out.printf("%6s", table[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("**********LL1预测分析表********");
}
}
class Gui extends JFrame {
static JButton btnLL1 = new JButton("LL(1)分析");
static JTextField input = new JTextField("i+i*i#",8);
static JLabel label = new JLabel("输入串:");
static JLabel first = new JLabel("FIRST:");
static JLabel follow = new JLabel("FOLLOW:");
static JLabel tit = new JLabel("--------------- LL(1)单步 -------------");
static JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel();
static Vector row= new Vector();;
static Vector row2= new Vector();
static Vector row3= new Vector();
static Vector columnNames2 = new Vector() ;
static Vector columnNames1 = new Vector() ;
static JTable table3;
static JTable table2;
static JTable table;
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// new Gui("LL1");
// }
public Gui(String title) throws HeadlessException {
super(title);
setSize(550,500);
setResizable(false);
contentPanel.setLayout(null);
columnNames1.add("步骤");
columnNames1.add("分析栈");
columnNames1.add( "剩余输入串");
columnNames1.add("所用产生式");
columnNames1.add("动作");
table = new JTable(row,columnNames1);
JScrollPane scrollPane1 = new JScrollPane(table);
columnNames2.add("非终结符");
columnNames2.add("结果");
table2 = new JTable(row2,columnNames2);
JScrollPane scrollPane2 = new JScrollPane(table2);
table3 = new JTable(row3,columnNames2);
JScrollPane scrollPane3 = new JScrollPane(table3);
contentPanel.add(btnLL1);
contentPanel.add(input);
contentPanel.add(label);
contentPanel.add(first);
contentPanel.add(follow);
contentPanel.add(scrollPane1);
contentPanel.add(scrollPane2);
contentPanel.add(scrollPane3);
contentPanel.add(tit);
label.setBounds(5,5,110,30);
input.setBounds(70,8,100,25);
btnLL1.setBounds(180,8,100,25);
first.setBounds(5,40,110,30);
follow.setBounds(280,40,110,30);
tit.setBounds(150,180,300,30);
scrollPane1.setBounds(5,220,520,200);
scrollPane2.setBounds(5,70,250,100);
scrollPane3.setBounds(280,70,250,100);
btnLL1.addActionListener(new Listener());
this.add(contentPanel);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
class Listener implements ActionListener {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent actionEvent) {
if(actionEvent.getSource()==btnLL1){
String in = input.getText();
LL1.inStr = in;
LL1.dividechar();
LL1.First();
for (Character ch:LL1.VnSet
) {
HashSet<Character> firset = LL1.FirstSet.get(ch);
String token = "";
for (Character c:firset
) {
token+=c;
}
Vector vc = new Vector();
vc.add(ch);
vc.add(token);
((DefaultTableModel)Gui.table2.getModel()).addRow(vc);
}
for (Character c : LL1.VnSet) {
ArrayList<String> l = LL1.production.get(c);
for (String s : l)
LL1.getFirstX(s);
}
LL1.Follow();
for (Character chr:LL1.VnSet
) {
HashSet<Character> firset = LL1.FollowSet.get(chr);
String token1 = "";
for (Character c:firset
) {
token1+=c;
}
Vector vc1 = new Vector();
vc1.add(chr);
vc1.add(token1);
((DefaultTableModel)Gui.table3.getModel()).addRow(vc1);
}
LL1.creatTable();
LL1.processLL1();
for (Vector vc2: LL1.stepList
) {
((DefaultTableModel)Gui.table.getModel()).addRow(vc2);
}
}
}
}
}