Ingress
1.Pod与Ingress的关系
- 通过service相关联
- 通过Ingress Controller实现Pod负载均衡
- 支持TCP/UDP 4层和7层
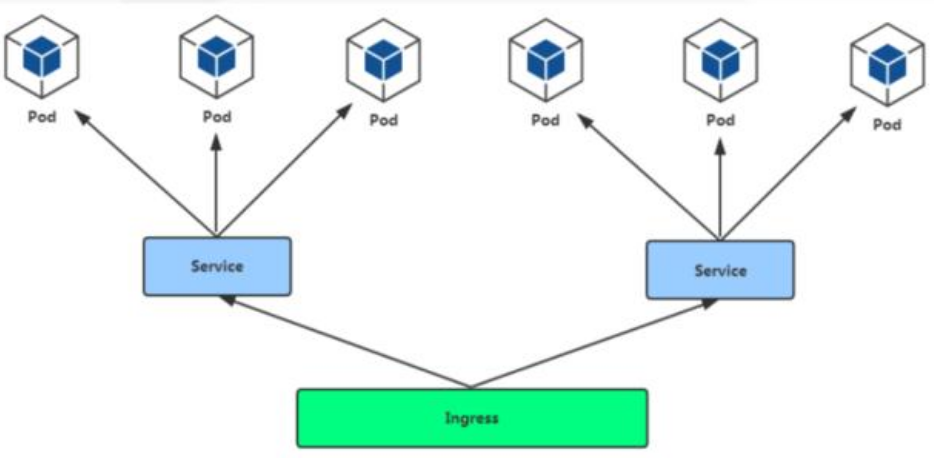
访问流程
用户->Ingress controller->Pod
部署参考文档:https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/blob/master/docs/deploy/index.md
下载ingress-nginx配置文件
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/master/deploy/static/mandatory.yaml
PS:如果无法下载在本机hosts添加一行配置
151.101.108.133 raw.githubusercontent.com
下载后修改
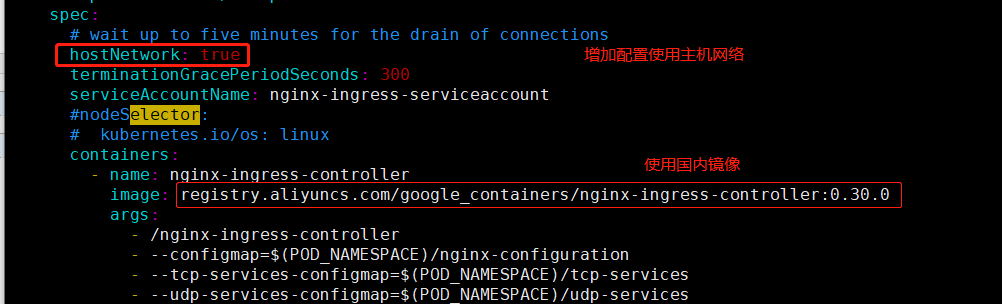
应用
kubectl apply -f mandatory.yaml
拍错:应用以后使用命令查看显示为空 本次拍错参考文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/Dev0ps/p/10778328.html
# kubectl get pod -n ingress-nginx No resources found.
修改kube-controller-manager配置文件记录日志
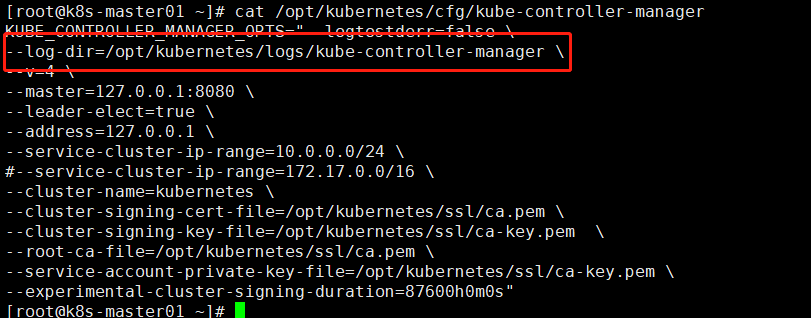
查看错误日志kube-controller-manager.ERROR发现以下报错
E0310 08:55:56.869874 13765 replica_set.go:450] Sync "ingress-nginx/nginx-ingress-controller-5648d4586f" failed with pods "nginx-ingress-controller-5648d4586f-884bb" is forbidden: SecurityContext.RunAsUser is forbidden
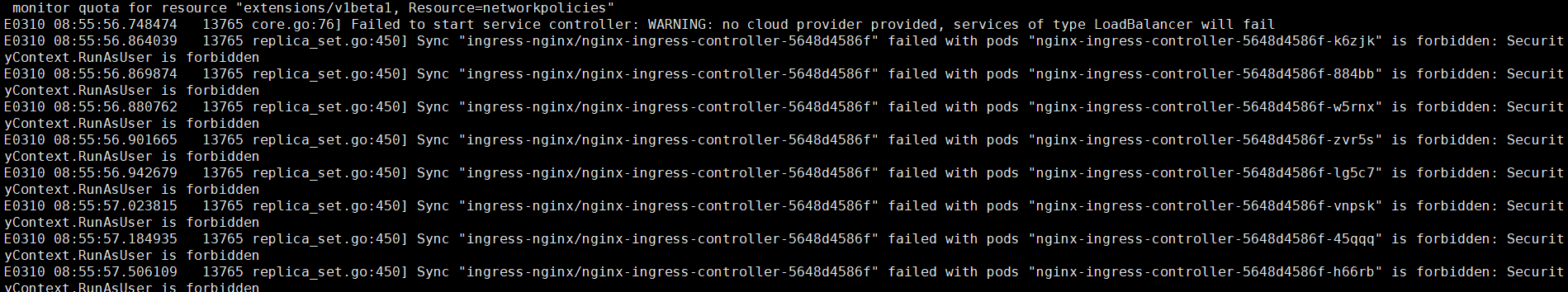
修改kube-apiserver配置文件增加配置
--enable-admission-plugins=NamespaceLifecycle,LimitRanger,ServiceAccount,ResourceQuota,NodeRestriction
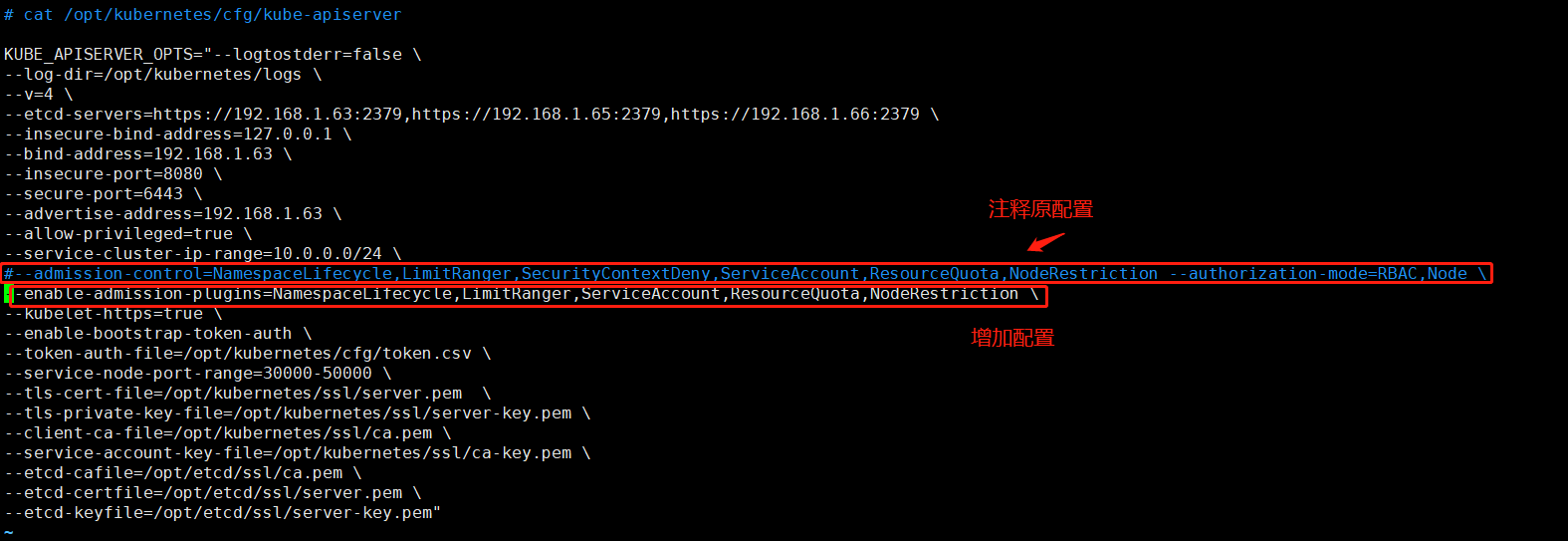
重启kube-apiserver
systemctl restart kube-apiserver
应用以后查看
# kubectl get pod,ns -n ingress-nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/nginx-ingress-controller-5648d4586f-nhzm5 1/1 Running 0 20s NAME STATUS AGE namespace/default Active 15h namespace/ingress-nginx Active 20s namespace/kube-public Active 15h namespace/kube-system Active 15h
查看该pod分配到哪个node节点上

因为配置文件配置hostNetwork=true使用宿主机网络所以在对应节点会监听80和443端口
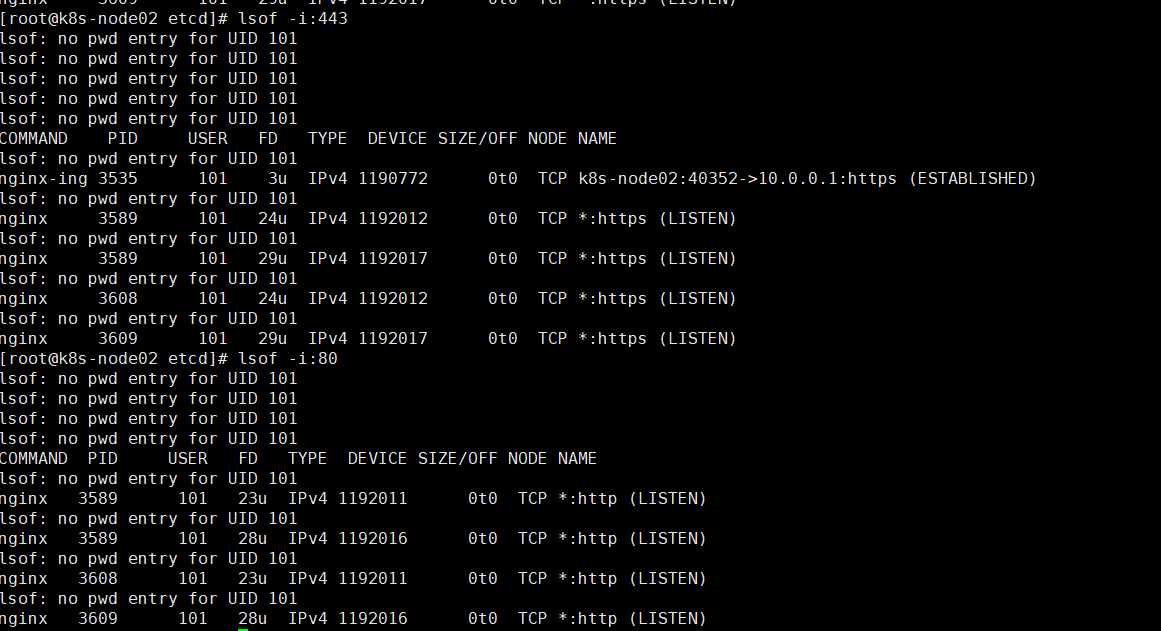
对应节点不要有其他应用程序占用这两个端口
2.Ingress Controller
控制器已经部署好了,需要定义ingress规则定义域名访问
创建测试示例,最小示例可以在官方网站下载https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress/
# cat ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: simple-fanout-example
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
#定义访问域名
- host: foo.bar.com
http:
paths:
#访问根目录
- path: /
backend:
#转发到哪个server下
serviceName: my-service
servicePort: 80
该ingrss对应的service必须存在,如果没有使用以下命令创建,service端口也需要对应80
#创建deployment kubectl run my-service --image=nginx --port=80 #创建service对应刚刚创建的deployment my-service kubectl expose deployment my-service --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort #查看是否创建成功 # kubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 17h my-service NodePort 10.0.0.130 <none> 80:42291/TCP 99s
应用ingress
# kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml ingress.extensions/simple-fanout-example created
查看
# kubectl get ingress NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE simple-fanout-example foo.bar.com 80 62s
对应的name是 simple-fanout-example
对应的域名是 foo.bar.com
对应的ADDRESS为空 是转发到backend对应的后端
在主机设置hosts即可使用域名访问nginx
ingress控制器使用nginx进行负载均衡,进入控制器
kubectl exec -it nginx-ingress-controller-74cf54575-gt9mm bash -n ingress-nginx
ps -ef|grep nginx
查看nginx配置文件
# Configuration checksum: 4424420289189243736
# setup custom paths that do not require root access
pid /tmp/nginx.pid;
daemon off;
worker_processes 2;
worker_rlimit_nofile 523264;
worker_shutdown_timeout 240s ;
events {
multi_accept on;
worker_connections 16384;
use epoll;
}
http {
lua_package_path "/etc/nginx/lua/?.lua;;";
lua_shared_dict balancer_ewma 10M;
lua_shared_dict balancer_ewma_last_touched_at 10M;
lua_shared_dict balancer_ewma_locks 1M;
lua_shared_dict certificate_data 20M;
lua_shared_dict certificate_servers 5M;
lua_shared_dict configuration_data 20M;
init_by_lua_block {
collectgarbage("collect")
-- init modules
local ok, res
ok, res = pcall(require, "lua_ingress")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
lua_ingress = res
lua_ingress.set_config({
use_forwarded_headers = false,
use_proxy_protocol = false,
is_ssl_passthrough_enabled = false,
http_redirect_code = 308,
listen_ports = { ssl_proxy = "442", https = "443" },
hsts = true,
hsts_max_age = 15724800,
hsts_include_subdomains = true,
hsts_preload = false,
})
end
ok, res = pcall(require, "configuration")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
configuration = res
end
ok, res = pcall(require, "balancer")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
balancer = res
end
ok, res = pcall(require, "monitor")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
monitor = res
end
ok, res = pcall(require, "certificate")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
certificate = res
end
ok, res = pcall(require, "plugins")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
plugins = res
end
-- load all plugins that'll be used here
plugins.init({})
}
init_worker_by_lua_block {
lua_ingress.init_worker()
balancer.init_worker()
monitor.init_worker()
plugins.run()
}
geoip_country /etc/nginx/geoip/GeoIP.dat;
geoip_city /etc/nginx/geoip/GeoLiteCity.dat;
geoip_org /etc/nginx/geoip/GeoIPASNum.dat;
geoip_proxy_recursive on;
aio threads;
aio_write on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
log_subrequest on;
reset_timedout_connection on;
keepalive_timeout 75s;
keepalive_requests 100;
client_body_temp_path /tmp/client-body;
fastcgi_temp_path /tmp/fastcgi-temp;
proxy_temp_path /tmp/proxy-temp;
ajp_temp_path /tmp/ajp-temp;
client_header_buffer_size 1k;
client_header_timeout 60s;
large_client_header_buffers 4 8k;
client_body_buffer_size 8k;
client_body_timeout 60s;
http2_max_field_size 4k;
http2_max_header_size 16k;
http2_max_requests 1000;
http2_max_concurrent_streams 128;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
server_names_hash_max_size 1024;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 32;
map_hash_bucket_size 64;
proxy_headers_hash_max_size 512;
proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size 64;
variables_hash_bucket_size 256;
variables_hash_max_size 2048;
underscores_in_headers off;
ignore_invalid_headers on;
limit_req_status 503;
limit_conn_status 503;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type text/html;
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 5;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_types application/atom+xml application/javascript application/x-javascript application/json application/rss+xml application/vnd.ms-fontobject application/x-font-ttf application/x-web-app-manifest+json application/xhtml+xml application/xml font/opentype image/svg+xml image/x-icon text/css text/javascript text/plain text/x-component;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_vary on;
# Custom headers for response
server_tokens on;
# disable warnings
uninitialized_variable_warn off;
# Additional available variables:
# $namespace
# $ingress_name
# $service_name
# $service_port
log_format upstreaminfo '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" $request_length $request_time [$proxy_upstream_name] [$proxy_alternative_upstream_name] $upstream_addr $upstream_response_length $upstream_response_time $upstream_status $req_id';
map $request_uri $loggable {
default 1;
}
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log upstreaminfo if=$loggable;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
resolver 114.114.114.114 8.8.8.8 valid=30s ipv6=off;
# See https://www.nginx.com/blog/websocket-nginx
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_upstream_module.html#keepalive
'' '';
}
# Reverse proxies can detect if a client provides a X-Request-ID header, and pass it on to the backend server.
# If no such header is provided, it can provide a random value.
map $http_x_request_id $req_id {
default $http_x_request_id;
"" $request_id;
}
# Create a variable that contains the literal $ character.
# This works because the geo module will not resolve variables.
geo $literal_dollar {
default "$";
}
server_name_in_redirect off;
port_in_redirect off;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2;
ssl_early_data off;
# turn on session caching to drastically improve performance
ssl_session_cache builtin:1000 shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# allow configuring ssl session tickets
ssl_session_tickets on;
# slightly reduce the time-to-first-byte
ssl_buffer_size 4k;
# allow configuring custom ssl ciphers
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ecdh_curve auto;
# PEM sha: 9f4bba529d99741566ce35e96beba9d3da375481
ssl_certificate /etc/ingress-controller/ssl/default-fake-certificate.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ingress-controller/ssl/default-fake-certificate.pem;
proxy_ssl_session_reuse on;
upstream upstream_balancer {
### Attention!!!
#
# We no longer create "upstream" section for every backend.
# Backends are handled dynamically using Lua. If you would like to debug
# and see what backends ingress-nginx has in its memory you can
# install our kubectl plugin https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/kubectl-plugin.
# Once you have the plugin you can use "kubectl ingress-nginx backends" command to
# inspect current backends.
#
###
server 0.0.0.1; # placeholder
balancer_by_lua_block {
balancer.balance()
}
keepalive 32;
keepalive_timeout 60s;
keepalive_requests 100;
}
# Cache for internal auth checks
proxy_cache_path /tmp/nginx-cache-auth levels=1:2 keys_zone=auth_cache:10m max_size=128m inactive=30m use_temp_path=off;
# Global filters
## start server _
server {
server_name _ ;
listen 80 default_server reuseport backlog=511 ;
listen 443 default_server reuseport backlog=511 ssl http2 ;
set $proxy_upstream_name "-";
ssl_certificate_by_lua_block {
certificate.call()
}
location / {
set $namespace "";
set $ingress_name "";
set $service_name "";
set $service_port "";
set $location_path "/";
rewrite_by_lua_block {
lua_ingress.rewrite({
force_ssl_redirect = false,
ssl_redirect = false,
force_no_ssl_redirect = false,
use_port_in_redirects = false,
})
balancer.rewrite()
plugins.run()
}
# be careful with `access_by_lua_block` and `satisfy any` directives as satisfy any
# will always succeed when there's `access_by_lua_block` that does not have any lua code doing `ngx.exit(ngx.DECLINED)`
# other authentication method such as basic auth or external auth useless - all requests will be allowed.
#access_by_lua_block {
#}
header_filter_by_lua_block {
lua_ingress.header()
plugins.run()
}
body_filter_by_lua_block {
}
log_by_lua_block {
balancer.log()
monitor.call()
plugins.run()
}
access_log off;
port_in_redirect off;
set $balancer_ewma_score -1;
set $proxy_upstream_name "upstream-default-backend";
set $proxy_host $proxy_upstream_name;
set $pass_access_scheme $scheme;
set $pass_server_port $server_port;
set $best_http_host $http_host;
set $pass_port $pass_server_port;
set $proxy_alternative_upstream_name "";
client_max_body_size 1m;
proxy_set_header Host $best_http_host;
# Pass the extracted client certificate to the backend
# Allow websocket connections
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Request-ID $req_id;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $best_http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $pass_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $pass_access_scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $pass_access_scheme;
# Pass the original X-Forwarded-For
proxy_set_header X-Original-Forwarded-For $http_x_forwarded_for;
# mitigate HTTPoxy Vulnerability
# https://www.nginx.com/blog/mitigating-the-httpoxy-vulnerability-with-nginx/
proxy_set_header Proxy "";
# Custom headers to proxied server
proxy_connect_timeout 5s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
proxy_buffers 4 4k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 1024m;
proxy_request_buffering on;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_cookie_domain off;
proxy_cookie_path off;
# In case of errors try the next upstream server before returning an error
proxy_next_upstream error timeout;
proxy_next_upstream_timeout 0;
proxy_next_upstream_tries 3;
proxy_pass http://upstream_balancer;
proxy_redirect off;
}
# health checks in cloud providers require the use of port 80
location /healthz {
access_log off;
return 200;
}
# this is required to avoid error if nginx is being monitored
# with an external software (like sysdig)
location /nginx_status {
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
access_log off;
stub_status on;
}
}
## end server _
## start server foo.bar.com
server {
server_name foo.bar.com ;
listen 80 ;
listen 443 ssl http2 ;
set $proxy_upstream_name "-";
ssl_certificate_by_lua_block {
certificate.call()
}
location / {
set $namespace "default";
set $ingress_name "simple-fanout-example";
set $service_name "my-service";
set $service_port "80";
set $location_path "/";
rewrite_by_lua_block {
lua_ingress.rewrite({
force_ssl_redirect = false,
ssl_redirect = true,
force_no_ssl_redirect = false,
use_port_in_redirects = false,
})
balancer.rewrite()
plugins.run()
}
# be careful with `access_by_lua_block` and `satisfy any` directives as satisfy any
# will always succeed when there's `access_by_lua_block` that does not have any lua code doing `ngx.exit(ngx.DECLINED)`
# other authentication method such as basic auth or external auth useless - all requests will be allowed.
#access_by_lua_block {
#}
header_filter_by_lua_block {
lua_ingress.header()
plugins.run()
}
body_filter_by_lua_block {
}
log_by_lua_block {
balancer.log()
monitor.call()
plugins.run()
}
port_in_redirect off;
set $balancer_ewma_score -1;
set $proxy_upstream_name "default-my-service-80";
set $proxy_host $proxy_upstream_name;
set $pass_access_scheme $scheme;
set $pass_server_port $server_port;
set $best_http_host $http_host;
set $pass_port $pass_server_port;
set $proxy_alternative_upstream_name "";
client_max_body_size 1m;
proxy_set_header Host $best_http_host;
# Pass the extracted client certificate to the backend
# Allow websocket connections
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Request-ID $req_id;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $best_http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $pass_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $pass_access_scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $pass_access_scheme;
# Pass the original X-Forwarded-For
proxy_set_header X-Original-Forwarded-For $http_x_forwarded_for;
# mitigate HTTPoxy Vulnerability
# https://www.nginx.com/blog/mitigating-the-httpoxy-vulnerability-with-nginx/
proxy_set_header Proxy "";
# Custom headers to proxied server
proxy_connect_timeout 5s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
proxy_buffers 4 4k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 1024m;
proxy_request_buffering on;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_cookie_domain off;
proxy_cookie_path off;
# In case of errors try the next upstream server before returning an error
proxy_next_upstream error timeout;
proxy_next_upstream_timeout 0;
proxy_next_upstream_tries 3;
proxy_pass http://upstream_balancer;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
## end server foo.bar.com
# backend for when default-backend-service is not configured or it does not have endpoints
server {
listen 8181 default_server reuseport backlog=511;
set $proxy_upstream_name "internal";
access_log off;
location / {
return 404;
}
}
# default server, used for NGINX healthcheck and access to nginx stats
server {
listen 127.0.0.1:10246;
set $proxy_upstream_name "internal";
keepalive_timeout 0;
gzip off;
access_log off;
location /healthz {
return 200;
}
location /is-dynamic-lb-initialized {
content_by_lua_block {
local configuration = require("configuration")
local backend_data = configuration.get_backends_data()
if not backend_data then
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
return
end
ngx.say("OK")
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK)
}
}
location /nginx_status {
stub_status on;
}
location /configuration {
client_max_body_size 21m;
client_body_buffer_size 21m;
proxy_buffering off;
content_by_lua_block {
configuration.call()
}
}
location / {
content_by_lua_block {
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_NOT_FOUND)
}
}
}
}
stream {
lua_package_path "/etc/nginx/lua/?.lua;/etc/nginx/lua/vendor/?.lua;;";
lua_shared_dict tcp_udp_configuration_data 5M;
init_by_lua_block {
collectgarbage("collect")
-- init modules
local ok, res
ok, res = pcall(require, "configuration")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
configuration = res
end
ok, res = pcall(require, "tcp_udp_configuration")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
tcp_udp_configuration = res
end
ok, res = pcall(require, "tcp_udp_balancer")
if not ok then
error("require failed: " .. tostring(res))
else
tcp_udp_balancer = res
end
}
init_worker_by_lua_block {
tcp_udp_balancer.init_worker()
}
lua_add_variable $proxy_upstream_name;
log_format log_stream '[$remote_addr] [$time_local] $protocol $status $bytes_sent $bytes_received $session_time';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log log_stream ;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
upstream upstream_balancer {
server 0.0.0.1:1234; # placeholder
balancer_by_lua_block {
tcp_udp_balancer.balance()
}
}
server {
listen 127.0.0.1:10247;
access_log off;
content_by_lua_block {
tcp_udp_configuration.call()
}
}
# TCP services
# UDP services
}
3.Ingress(HTTP与HTTPS)
实现基于https需要定义ssl
生成自签名证书
# cat certs.sh
cat > ca-config.json <<EOF
{
"signing": {
"default": {
"expiry": "87600h"
},
"profiles": {
"kubernetes": {
"expiry": "87600h",
"usages": [
"signing",
"key encipherment",
"server auth",
"client auth"
]
}
}
}
}
EOF
cat > ca-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "kubernetes",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "Beijing",
"ST": "Beijing",
"O": "k8s",
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
EOF
cfssl gencert -initca ca-csr.json | cfssljson -bare ca -
#-----------------------
cat > sslexample.foo.com-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "sslexample.foo.com",
"hosts": [],
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "BeiJing",
"ST": "BeiJing",
"O": "k8s",
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
EOF
cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -config=ca-config.json -profile=kubernetes sslexample.foo.com-csr.json | cfssljson -bare sslexample.foo.com
运行脚本生成
sh cert.sh
创建的以下证书
创建证书至k8s
kubectl create secret tls sslexample-foo-com --cert=sslexample.foo.com.pem --key=sslexample.foo.com-key.pem
查看,是在默认命名空间default
# kubectl get secret NAME TYPE DATA AGE default-token-ctcb9 kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 20h sslexample-foo-com kubernetes.io/tls 2 3m20s
创建ingrss配置文件
# cat ingress-https.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: tls-example-ingress
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- sslexample.foo.com
#证书名,需要和刚刚导入的证书名队员
secretName: sslexample-foo-com
rules:
- host: sslexample.foo.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: my-service
servicePort: 80
应用
kubectl apply -f ingress-https.yaml
查看
# kubectl get ingress NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE simple-fanout-example foo.bar.com 80 171m tls-example-ingress sslexample.foo.com 80, 443 4m7s
设置hosts以后使用https://域名 访问,因为是自签名证书不受浏览器信任,需要添加信任
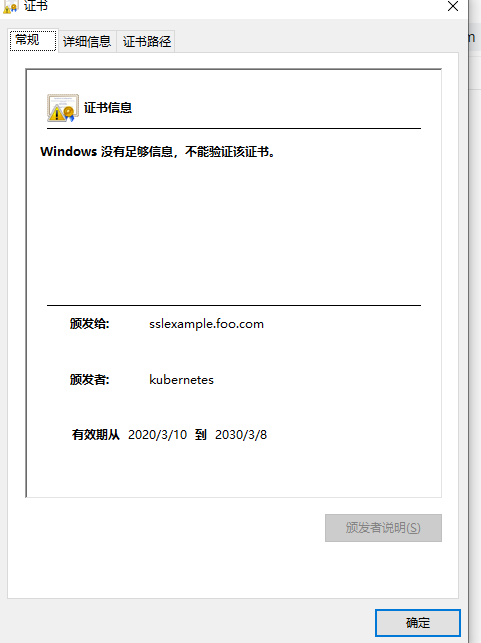
如果指定的证书没有,则k8s会自动颁发一个证书
Ingress高可用
上面配置的副本数为1个那么启动该pod的node只会是集群中的一台node主机,也只会在该主机启动80 443端口,无法实现高可用
我们只是解决了集群对外提供服务的功能,并没有对ingress进行高可用的部署,Ingress高可用,我们可以通过修改deploment的副本数来实现高可用,但是对于ingress承载着整个集群流量的接入,所以在生产环境中,建议把ingres通过DaemonSet的方式部署集群,而且该节点打上污点不允许业务pod进行调度,以避免业务应用于Ingress服务发生资源争抢。然后通过SLB把ingress节点主机添加为后端服务器,进行流量转发。
高可用配置参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/minseo/p/12171687.html
小结
Ingress
1,四层,七层负载均衡
2,支持自定义Serverice访问策略
3,只支持域名的网站访问
4,支持TLS