承接上一篇文章Android Inline Hook,接下来我们看一下android系统中基于异常的hook方式,这种方式与inline hook相比实现较为简单,但执行效率是它的短板。
exception hook的执行流程大致如下:
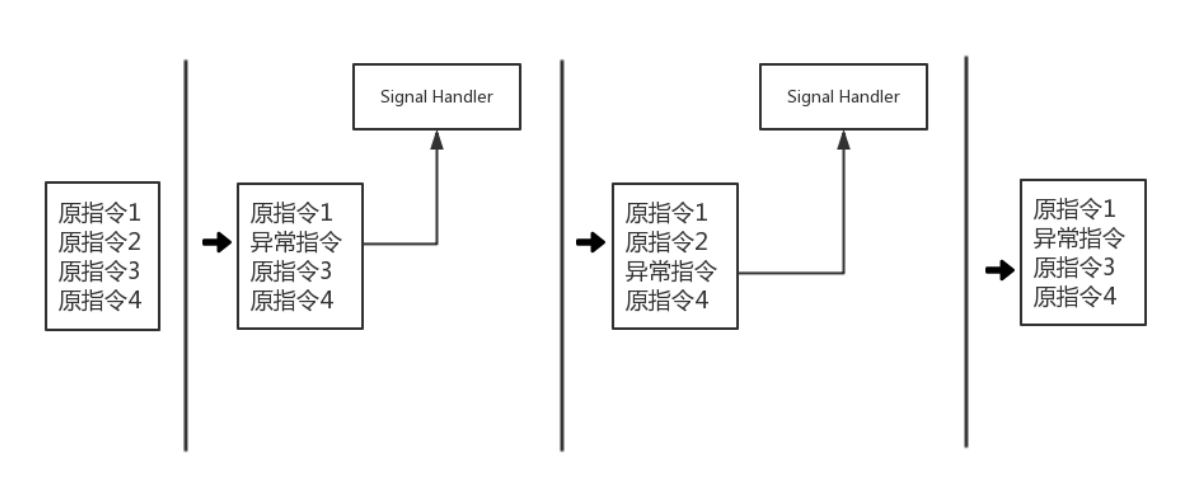
如图所示,在hook过程中需要多次对hook点指令和hook点的下一条指令进行修改,由此造成在执行效率上的损耗。
首先我们需要将hook点指令替换为一条不合法的异常指令,当程序执行到该位置时进程会接收到信号SIGILL(illegal instruction),然后进入到我们注册的SIgnal Handler中,在信号处理函里我们需要做两件事,一是执行我们的hook逻辑(如修改寄存器的值),二是恢复hook点指令并将hook点指令的下一条指令替换为异常指令,再恢复程序的运行。当程序运行到hook点的下一条指令时会再次触发异常进入信号处理函数,这一次我们需要在信号处理函数中将hook点指令再次替换为异常指令,然后恢复hook点的下一条指令,最后恢复程序运行。
由此可见,我们在信号处理函数中需要对异常的发生位置进行判断,对hook点跟hook点的下一条指令进行区分。当然最重要的是理解Linux系统中的信号机制。
void signal_handler(int signum, siginfo_t *Ssiginfo, void *context) { //信号处理函数
ucontext_t *uc = context;
struct sigcontext *sigc = &uc->uc_mcontext; } struct sigaction sig; //initialize the signal set sigemptyset(&sig.sa_mask); //make sigaction.sa_sigaction specifies the //signal-handling function for signum sig.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO; //attach our handler sig.sa_sigaction = signal_handler; sigaction(SIGILL, &sig, NULL);
通过sigaction函数对信号进行注册后我们便可以在信号处理函数中对其进行处理。Linux用户手册中对该函数进行了详细的说明,可参阅:Linux Programmer's Manual SIGACTION(2)
在信号处理函数中我们可以通过结构体sigcontext获取异常发生时各个寄存器的信息,其定义如下:
struct sigcontext { unsigned long trap_no; unsigned long error_code; unsigned long oldmask; unsigned long arm_r0; unsigned long arm_r1; unsigned long arm_r2; unsigned long arm_r3; unsigned long arm_r4; unsigned long arm_r5; unsigned long arm_r6; unsigned long arm_r7; unsigned long arm_r8; unsigned long arm_r9; unsigned long arm_r10; unsigned long arm_fp; unsigned long arm_ip; unsigned long arm_sp; unsigned long arm_lr; unsigned long arm_pc; unsigned long arm_cpsr;unsigned long fault_address; };
例如我们可以通过pc寄存器的值确定程序执行的位置。
完整程序如下:
1 #include <assert.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 #include <signal.h> 6 #include <ucontext.h> 7 #include <sys/mman.h> 8 9 int g_code_type; 10 long g_code_address; 11 uint32_t g_code_origin; 12 uint32_t g_code_next; 13 14 long get_module_addr(pid_t pid, const char *module_name) 15 { 16 FILE *fp; 17 char file_path[256]; 18 char file_line[512]; 19 if (pid < 0) { 20 snprintf(file_path, sizeof(file_path), "/proc/self/maps"); 21 } else { 22 snprintf(file_path, sizeof(file_path), "/proc/%d/maps", pid); 23 } 24 fp = fopen(file_path, "r"); 25 if (fp == NULL) { 26 return -1; 27 } 28 long addr_start = -1, addr_end = 0; 29 while (fgets(file_line, sizeof(file_line), fp)) { 30 if (strstr(file_line, module_name)) { 31 if (2 == sscanf(file_line, "%8lx-%8lx", &addr_start, &addr_end)) { 32 break; 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 fclose(fp); 37 return addr_start; 38 } 39 40 bool change_addr_attr(long address, bool writable) { 41 //根据内存页大小对齐 42 long page_size = sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE); 43 long page_start = address & (~(page_size - 1)); 44 if (writable == true) { 45 return mprotect((void*)page_start, page_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE | PROT_EXEC) != -1; 46 } else { 47 return mprotect((void*)page_start, page_size, PROT_READ | PROT_EXEC) != -1; 48 } 49 } 50 51 bool write_code(long address, uint32_t data) 52 { 53 if (change_addr_attr(address, true) == false) { 54 return false; 55 } 56 if (g_code_type == IS_THUMB) { 57 *((uint16_t*)address) = (uint16_t)data; 58 } else { 59 *((uint32_t*)address) = data; 60 } 61 return change_addr_attr(address, false); 62 } 63 64 bool write_ill_instruction(long address, uint32_t *save) 65 { 66 if (g_code_type == IS_THUMB) { 67 *save = *((uint16_t*)address); 68 } else if (g_code_type == IS_ARM) { 69 *save = *((uint32_t*)address); 70 } 71 return write_code(address, 0xFFFFFFFF); 72 } 73 74 static void signal_handler(int signum, siginfo_t *Ssiginfo, void *context) 75 { 76 ucontext_t *uc = context; 77 struct sigcontext *sigc = &uc->uc_mcontext; 78 79 long next_address = g_code_address + (IS_ARM ? 4 : 2); 80 81 if (sigc->arm_pc == g_code_address) { 82 //恢复hook点指令 83 write_code(g_code_address, g_code_origin); 84 //将hook点下一条指令改为异常指令 85 write_ill_instruction(next_address, &g_code_next); 86 } else if (sigc->arm_pc == next_address){ 87 //恢复hook点下一条指令 88 write_code(next_address, g_code_next); 89 //将hook点指令改为异常指令 90 write_ill_instruction(g_code_address, &g_code_origin); 91 } else { 92 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 93 } 94 } 95 96 bool hook_exception_make(const char *library, long address, enum code_type type) 97 { 98 g_code_type = type; 99 100 struct sigaction sig; 101 sigemptyset(&sig.sa_mask); 102 sig.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO; 103 sig.sa_sigaction = signal_handler; 104 sigaction(SIGILL, &sig, NULL); 105 106 long target_address = get_module_addr(-1, library); 107 g_code_address = target_address + address; 108 return write_ill_instruction(g_code_address, &g_code_origin); 109 }