1. vue-router 在 Vue 中的生命周期:
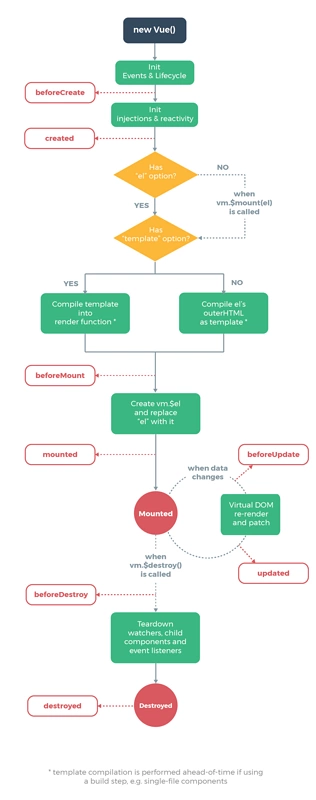
这是 vue 生命周期的图:
在路由中分别定义A页面和B页面
A页面:
<template>
<div>
<router-link to="/test2">去B页面</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
beforeCreate(){
console.log('A页面 beforeCreate');
},
created(){
console.log('A页面 created');
},
mounted(){
console.log('A页面 mounted');
},
beforeDestroy(){
console.log('A页面 beforeDestroy');
},
destroyed(){
console.log('A页面 destroyed');
}
}
</script>
B页面:
<template>
<div>
<router-link to="/test1">去A页面</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
beforeCreate(){
console.log('B页面 beforeCreate');
},
created(){
console.log('B页面 created');
},
mounted(){
console.log('B页面 mounted');
},
beforeDestroy(){
console.log('B页面 beforeDestroy');
},
destroyed(){
console.log('B页面 destroyed');
}
}
</script>
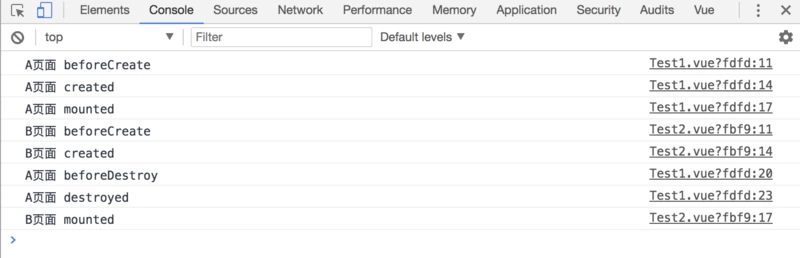
从 A 页面跳到 B 页面:
2. Vue-Router中,导航守卫的执行顺序:

这里存在疑惑的是组件的生命周期到底在导航守卫的哪个阶段执行,测试代码如下:

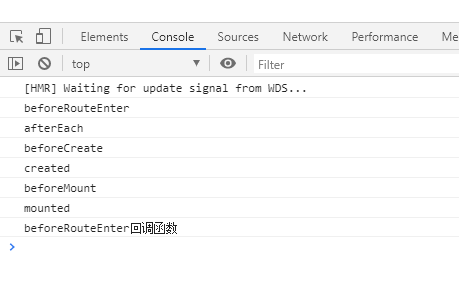
结论:从控制台结果可以看出,组件的生命周期是在Vue-Router导航守卫的DOM更新过程中执行的
- 导航被触发。
- 在失活的组件里调用离开守卫。
- 调用全局的
beforeEach守卫。 - 在重用的组件里调用
beforeRouteUpdate守卫 (2.2+)。 - 在路由配置里调用
beforeEnter。 - 解析异步路由组件。
- 在被激活的组件里调用
beforeRouteEnter。 - 调用全局的
beforeResolve守卫 (2.5+)。 - 导航被确认。
- 调用全局的
afterEach钩子。 - 触发 DOM 更新。(此过程触发组件的生命周期)
- 用创建好的实例调用
beforeRouteEnter守卫中传给next的回调函数。
这也就解释了切换路由时,两个组件生命周期执行的顺序是交叉的。