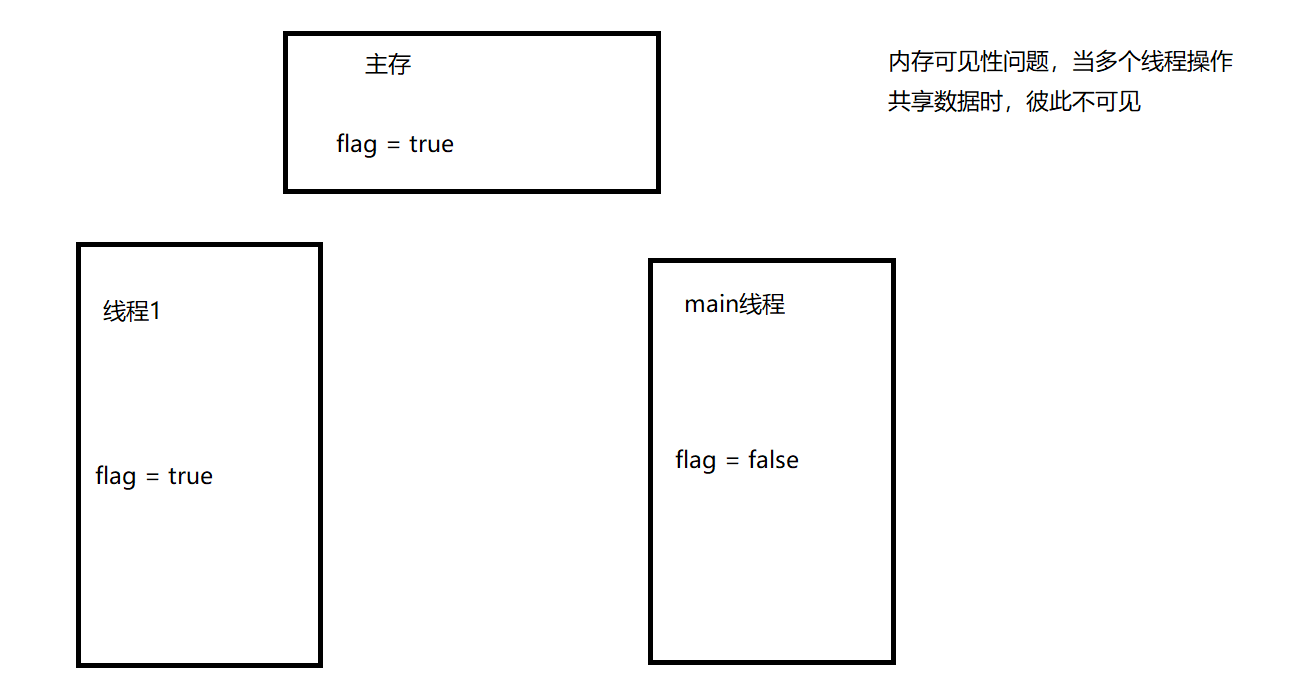
内存可见性问题
//同步锁每次都能刷新缓存
volatile关键字,多线程访问主存(共享数据) 是可见的(保证多线程访问的数据可见性)
相较于线程锁synchronized 是一种较为轻量级的同步策略。
//注意:1.volatile 不具备互斥性 2.volatile 不能保证 变量的“原子性”
原子变量
原子变变量:jdk1.5之后java.util.concurrent.atomic 包下提供了常用的原子变量 1.volatile 保存内存可见性 2.CAS() 算法保证数据的原子性 (硬件对于并发操作共享数据的支持)
JUC包下提供,多线程代替方案
ConcurrentHashMap 优于同步的hashmap,
ConcurrentSkipListMap优于TreeMap
CopyOnWriteArrayList 优于 ArrayList
闭锁 final CountDownLatch latch=new CountDownLatch(5);
public static void main(String[] args) { // 闭锁 一个线程执行完,执行下一个 final CountDownLatch latch=new CountDownLatch(5); LatchDemo latchDemo = new LatchDemo(latch); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { new Thread(latchDemo).start(); } try { latch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗费时间:"+(end - start)); } } class LatchDemo implements Runnable{ private CountDownLatch latch; public LatchDemo(CountDownLatch latch) { this.latch = latch; } @Override public void run() { synchronized (this){ try { for (int i = 0; i <50000 ; i++) { if(i % 2 == 0){ System.out.println(i); } } }finally { latch.countDown(); } } }
创建执行线程的方式三:时间Callable接口,相较于实现Runnable接口,可有返回值,并进行 异常抛出
public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadDemo threadDemo = new ThreadDemo(); //执行Callable 方式, 需要 FutureTask 实现类的支持,运用于接受运算结果。 //FutureTask ————> Future的实现类 FutureTask<Integer> result= new FutureTask<>(threadDemo); new Thread(result).start(); //接受的对象 Integer integer = null; try { integer = result.get(); System.out.println(integer); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } class ThreadDemo implements Callable<Integer>{ @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int sum =0; for (int i = 0; i <10000 ; i++) { sum += i; } return sum; } }
Lock (ReentrantLock 同步锁)
/** * * @author Qianxy * @date * @param synchronized : 隐式锁、 * 同步锁Lock * 注意:是一个显示锁,需要通过lock()方法上锁,必须通过unlock()方法进行释放锁 * * @return */ public static void main(String[] args) { Ticket ticket = new Ticket(); new Thread(ticket,"one:").start(); new Thread(ticket,"two").start(); new Thread(ticket,"three").start(); } } class Ticket implements Runnable{ private int tick = 100; private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run() { while (tick != 0){ lock.lock(); try{ if(tick > 0 ){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "完成售票, 余票为:" + --tick); } }finally { //释放锁 lock.unlock(); } } }
//优势 ReentrantLock提供了多样化的同步,比如有时间限制的同步,可以被Interrupt的同步(synchronized的同步是不能Interrupt的)等。在资源竞争不激烈的情形下,性能稍微比synchronized差点点。但是当同步非常激烈的时候,synchronized的性能一下子能下降好几十倍。而ReentrantLock确还能维持常态。 //Synchronized 同步 资源竞争不是很激烈的情况下,偶尔会有同步的情形下,synchronized是很合适的。原因在于,编译程序通常会尽可能的进行优化synchronize,另外可读性非常好 ReentrantLock实现原理: CAS(Compare and Swap) + CLH CAS:内存值V、预期值A、要修改的新值B。当且仅当预期值A和内存值V相同时,将内存值V修改为B,否则什么都不做。改操作是一个原子操作。 CLH:带头结点的双向非循环链表
Condition 线程通讯
Condition提供三种 await、signal、signalAll方法 对应wait、notify、notifyAll
生产者、消费者和店员案例,
//主函数 public static void main(String[] args) { Clerk clerk = new Clerk(); Productor productor = new Productor(clerk); Consumer consumer = new Consumer(clerk); new Thread(productor,"生产者").start(); new Thread(consumer,";消费者:").start(); } //店员 class Clerk{ private int product = 0; private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); //获得 condtion 对象 private Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); //进货 public void get(){//循环次数:0 lock.lock(); try{ while(product >= 1){//为了避免虚假唤醒问题,应该总是使用在循环中 System.out.println("产品已满!"); try { condition.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + ++product); condition.signalAll(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } //卖货 public void sale(){//product = 0; 循环次数:0 lock.lock(); try { while(product <= 0){ System.out.println("缺货!"); try { condition.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + --product); condition.signalAll(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } } //生产者 class Productor implements Runnable{ private Clerk clerk; public Productor(Clerk clerk) { this.clerk = clerk; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } clerk.get(); } } } //消费者 class Consumer implements Runnable{ private Clerk clerk; public Consumer(Clerk clerk) { this.clerk = clerk; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { clerk.sale(); } } }