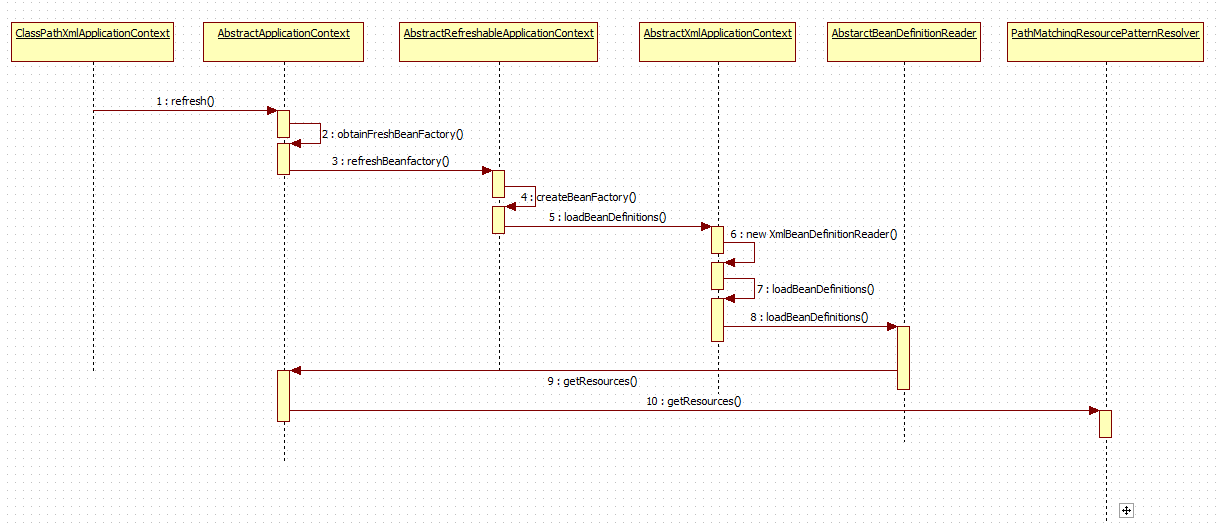
IOC容器的初始化过程主要包括BeanDefinition的Resource定位、载入和注册。在实际项目中我们基本上操作的都是ApplicationContex的实现,我们比较熟悉的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext、XmlWebapplicationContext等。ApplicationContext的具体继承体系如下图所示:

其实,不管是XmlWebApplicationContext还是ClasspathXmlApplicationContext 他们的区别只是Bean的资源信息来源不一样而已,最终都会解析为统一数据结构BeanDefinition。
下面我们源码的解析就从高富帅的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext开始。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:test.xml");
构造方法:
/** * Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions * from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context. * @param configLocation resource location * @throws BeansException if context creation failed */ public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null); }
最终调用构造方法:
/** * Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext with the given parent, * loading the definitions from the given XML files. * @param configLocations array of resource locations * @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context, * loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons. * Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context. * @param parent the parent context * @throws BeansException if context creation failed * @see #refresh() */ public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); } }
1.设置父级上下文,最终是给AbstractApplicationContext的parent属性赋值,AbstractApplicationContext是ApplicationContext最顶层的实现类。
2.设置XML文件的位置,调用了AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext的setConfigLocations方法
/** * Set the config locations for this application context. * <p>If not set, the implementation may use a default as appropriate. */ public void setConfigLocations(String[] locations) { if (locations != null) { Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null"); this.configLocations = new String[locations.length]; for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) { this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim(); } } else { this.configLocations = null; } }
3.刷新容器,调用了AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法,这是一个模板方法,具体的操作都是有子类去实现的。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. //刷新容器前的准备工作 prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. //由子类实现容器的刷新(重启) ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. /*容器使用前的准备工作*/ prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. //甚至beanFacotry的后置处理 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. //调用BeanFactory的后置处理器,这些后置处理是在Bean定义中想容器注册的 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. //注册Bean的后置处理器,在Bean的创建过程中调用 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. //对上下文中的消息源进行初始化 initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. //初始化上下文的事件 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. //初始化其他特殊的Bean onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. //向容器注册监听Bean registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. //实例化所有非延迟加载的Bean finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. //发布容器事件,结束refresh过程 finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt", ex); // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } } }
prepareRefresh():主要是设置启动时间、状态等等;
我们着重看一下刷新容器的obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法:
/** * Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. * @return the fresh BeanFactory instance * @see #refreshBeanFactory() * @see #getBeanFactory() */ protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { //销毁已有容器,重新创建容器并加载Bean refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; }
AbstractApplicationConetxt的refreshBeanFactory()方法是一个抽象方法,是由它的子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext实现的,从类的命名上可以看出这个类主要就是进行容器Refresh用的。
/** * This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying * bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and * initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle. */ @Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //如果容器已经存在则销毁容器中的bean并关闭容器 if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //创建beanFacotry DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); //根据bean定义的方式(XML、注解等)不同,由子类选择相应的BeanDefinitionReader去解析 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
第一步: 这个方法会判断如果已存在容器,则先销毁所有的Bean并且关闭容器,这也是为了保证容器的唯一性。
第二步:createBeanFactory()创建了一个DefaultListableBeanFactory,这个类是BeanFacotry最高级的实现,有了它就有个容器最基本的功能了。
/** * Create an internal bean factory for this context. * Called for each {@link #refresh()} attempt. * <p>The default implementation creates a * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory} * with the {@linkplain #getInternalParentBeanFactory() internal bean factory} of this * context's parent as parent bean factory. Can be overridden in subclasses, * for example to customize DefaultListableBeanFactory's settings. * @return the bean factory for this context * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#setAllowEagerClassLoading * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#setAllowCircularReferences * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#setAllowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping */ protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() { //新建一个DefaultListableBeanFactory return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory()); }
DefaultListableBeanFactory的继承关系:
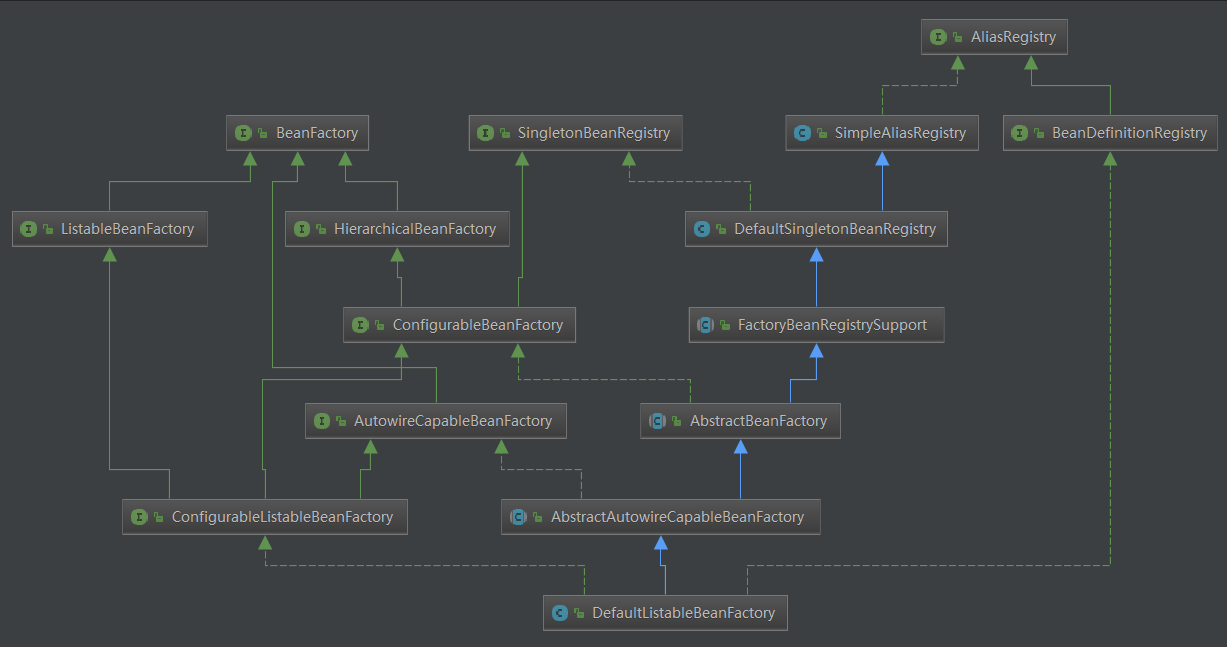
我们看到DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,也就是说最终BeanDefinition的注册工作是由它和它的子类来完成的。
第三步:loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory),这个方法也是一个抽象方法。因为Bean定义方式不同(XML、注解等),会有多个子类分别去实现具体的解析。
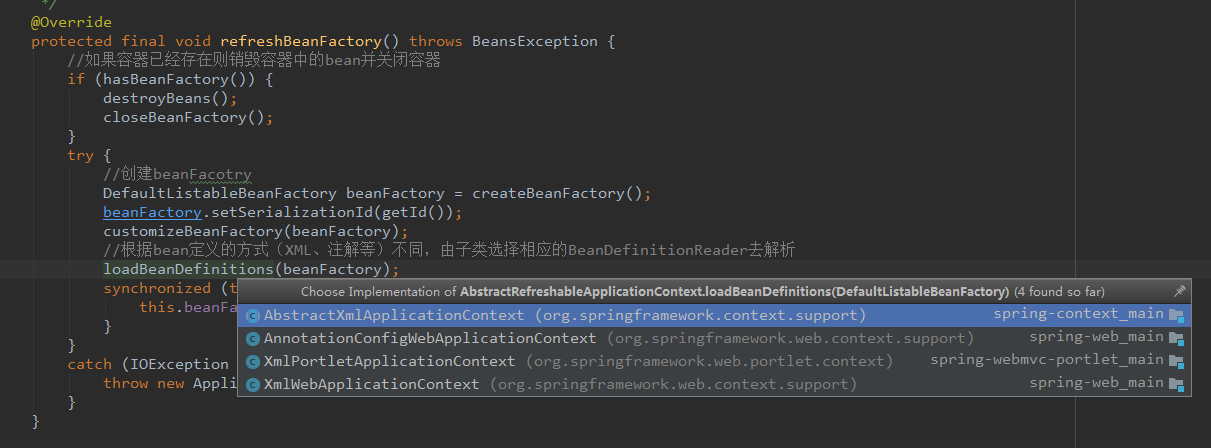
此处,调用的是AbstractXmlApplicationContext的实现:
/** * Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader. * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader * @see #initBeanDefinitionReader * @see #loadBeanDefinitions */ @Override protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); //ApplicationContext继承了ResourceLoader接口,所以this是可以直接使用的 beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); //委派模式,具体事情委派给beanDefinitionReader去做 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
进入loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader):
/** * Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader. * <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory} * method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions. * @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use * @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors * @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found * @see #refreshBeanFactory * @see #getConfigLocations * @see #getResources * @see #getResourcePatternResolver */ protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
该方法调用了XmlBeanDefinitionReader父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法:
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null"); int counter = 0; for (String location : locations) { counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location); } return counter; }
l循环加载location并返回加载个数,最终调用了本类的loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources)方法,actualResources为null:
/** * Load bean definitions from the specified resource location. * <p>The location can also be a location pattern, provided that the * ResourceLoader of this bean definition reader is a ResourcePatternResolver. * @param location the resource location, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader * (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader * @param actualResources a Set to be filled with the actual Resource objects * that have been resolved during the loading process. May be {@code null} * to indicate that the caller is not interested in those Resource objects. * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors * @see #getResourceLoader() * @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource) * @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource[]) */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); if (resourceLoader == null) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available"); } //resourceLoader是ClasspathXmlApplicationContext,ApplicationContext接口本身继承了ResourcePatternResolver接口 if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) { // Resource pattern matching available. try { //location转为Resource完成定位工作 Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location); int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources); if (actualResources != null) { for (Resource resource : resources) { actualResources.add(resource); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]"); } return loadCount; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex); } } else { // Can only load single resources by absolute URL. Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location); int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource); if (actualResources != null) { actualResources.add(resource); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]"); } return loadCount; } }
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location)将location转成了Resource[],这一步完成了资源的定位工作。
它调用了PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver的getResources方法:
1 public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { 2 Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null"); 3 //是否以classpath*:开头 4 if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) { 5 // a class path resource (multiple resources for same name possible) 6 //是否为Ant-style路径 7 //? 匹配任何单字符 8 //* 匹配0或者任意数量的字符 9 //** 匹配0或者更多的目录 10 if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) { 11 // a class path resource pattern 12 return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern); 13 } 14 else { 15 // all class path resources with the given name 16 return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length())); 17 } 18 } 19 else { 20 // Only look for a pattern after a prefix here 21 // (to not get fooled by a pattern symbol in a strange prefix). 22 int prefixEnd = locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1; 23 if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) { 24 // a file pattern 25 return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern); 26 } 27 else { 28 // a single resource with the given name 29 return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)}; 30 } 31 } 32 }
根据location写法,解析方式也不同:
1、前缀为classpath*
1)文件路径路径中包含*和?
调用findPathMatchingResources方法
2)文件路径中不含*和?
调用findAllClassPathResources方法
2.、前缀为classpath
1)文件路径路径中包含*和?
调用findPathMatchingResources方法
2)文件路径中不含*和?
调用DefaultResourceLoader的getResource方法new一个ClasspathResource并返回,如果资源文件根本就不存在,此处也不会校验。
findPathMatchingResources和findAllClassPathResources具体都干了什么呢?
先看一下findAllClassPathResources:
/** * Find all class location resources with the given location via the ClassLoader. * @param location the absolute path within the classpath * @return the result as Resource array * @throws IOException in case of I/O errors * @see java.lang.ClassLoader#getResources * @see #convertClassLoaderURL */ protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException { String path = location; if (path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader(); Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = (cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path)); Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16); while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement(); result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url)); } return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]); }
protected Resource convertClassLoaderURL(URL url) {
return new UrlResource(url);
}
这个方法很简单,根据具体的location通过classLoader的getResources方法返回RUL集合,根据URL创建UrlResource并返回UrlResource的集合。
再来看一下findPathMatchingResources方法:
/** * Find all resources that match the given location pattern via the * Ant-style PathMatcher. Supports resources in jar files and zip files * and in the file system. * @param locationPattern the location pattern to match * @return the result as Resource array * @throws IOException in case of I/O errors * @see #doFindPathMatchingJarResources * @see #doFindPathMatchingFileResources * @see org.springframework.util.PathMatcher */ protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern); String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length()); Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath); Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16); for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) { rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource); if (rootDirResource.getURL().getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) { result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirResource, subPattern, getPathMatcher())); } else if (isJarResource(rootDirResource)) { result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, subPattern)); } else { result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern)); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result); } return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]); }
1.String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern),获取location前缀classpath*/classpath
2.Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath),调用的上面讲到的getResources方法,返回classpath根路径的Resource[],如果是classpath会返回一个Resource,
如果是classpath*会放回所有的classpath路径。
3.遍历根路径Resource[],doFindPathMatchingFileResources方法就是获取给定路径下的所有文件,根据指定的文件名test*.xml去模糊匹配,返回的是FileSystemResource。所以location为classpath:test*.xml可能会找不到文件。