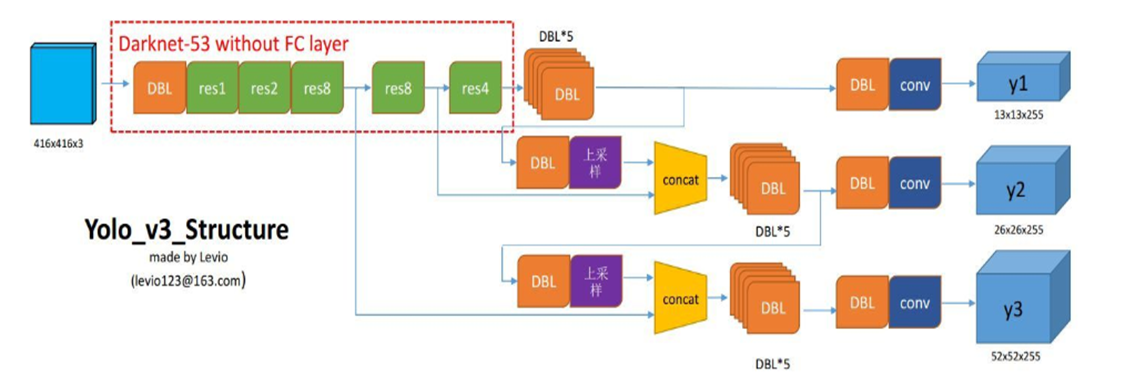
在实际预测的过程中,主要包括两个部分:
- 输入图像的标准化处理
- 从模型输出的y1,y2,y3中进行分类和定位
虽然会先生成yolo的对象,即预测评估的运算过程。
输入图像的处理
1 def detect_img(yolo): 2 path = "VOCdevkit/VOC2007/SegmentationClass/*.jpg" 3 outdir = "./VOCdevkit/VOC2007/SegmentationObject" 4 for jpgfile in glob.glob(path): 5 img = Image.open(jpgfile) 6 img = yolo.detect_image(img) # (731*575) 7 img.save(os.path.join(outdir, os.path.basename(jpgfile))) 8 yolo.close_session()
在代码的第6行yolo.detect_image(img)中对输入的图像进行处理。
1 def detect_image(self, image):
A. 要获得图像数据image_data:
- 判断设置的输入尺寸是不是能够整除32的,
- 将输入的图片等比缩放至设定的model_image_size的大小中(此处为416*416)
-- letterbox_image()中, 过程与y_true的等比缩放的过程相同(详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/monologuesmw/p/12794278.html),放在灰片上也会使图像放置在正中央的位置, 只不过此时没有标定框的事宜。
1 if self.model_image_size != (None, None): # 判断是否设定图像输入模型的尺寸范围 2 assert self.model_image_size[0] % 32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required' # 这个是关于模型设定的尺寸的大小是否符合规范, 3 assert self.model_image_size[1] % 32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required' # 而不是图像的大小(对图像没有要求) 4 boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size))) # 把输入图像缩放至规定的方位内 5 else: 6 new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32), 7 image.height - (image.height % 32)) 8 boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size) 9 image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
B. 图像数据归一化,并将其维度调整至运算过程中可用的维度
扩展数组的形状,在第0维的位置多1维。 即 416*416*3--》1*416*416*3
#通过上述的扩展转换,使得输入的尺寸符合网络输入格式 [batch_size, width, high, channels]
1 image_data /= 255. # 归一化了 2 image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
C. 通过喂数据,获得边框、类别信息
该部分的主干在于yolo初始化的generate过程,这个时候返回的检测每个物体的图像仅有一个。(即已经经过了nms等过滤系统)
1 out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run( 2 [self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes], 3 feed_dict={ 4 self.yolo_model.input: image_data, # 图像的数据 5 self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]], # 原始图像的宽高 6 K.learning_phase(): 0 # 学习模式, 0: 测试模型, 1: 训练模型 7 }) # 该部分的目的在于求解generate的过程,
D. 将获得的边框,类别、类别概率信息绘制在原图上
- 进行字体、厚度的设置
1 font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf', 2 size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32')) # 字体 3 thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300 # 厚度
- 按照输出的类别进行循环,并进行绘制
1 for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
获得框、类等信息
1 predicted_class = self.class_names[c] # 预测的类别 2 box = out_boxes[i] # 框信息 3 score = out_scores[i] # 框的得分(IOU)
获取预测边框的尺寸
1 top, left, bottom, right = box 2 top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32')) 3 left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32')) 4 bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32')) 5 right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
上、左会+0.5 并且向下取整;
下、右会+0.5 并且向下取整,再和原图的宽高对比取最小
1 print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom)) # 边框坐标
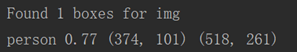
根据预测框的位置,调整文本的位置label_size--》[110, 20]
1 if top - label_size[1] >= 0: # 101-20>=0 2 text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]]) # 3 else: 4 text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
绘制
1 for i in range(thickness): 2 draw.rectangle( 3 [left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i], 4 outline=self.colors[c]) 5 draw.rectangle( 6 [tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)], 7 fill=self.colors[c]) 8 draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
2. 模型预测
始于YOLO()类的初始化。
1 detect_img(YOLO())
关于模型的预测,全系于代码第8行的generate中。
1 def __init__(self, **kwargs): 2 self.__dict__.update(self._defaults) # set up default values 3 self.__dict__.update(kwargs) # and update with user overrides 4 self.class_names = self._get_class() # 通过路径获取class_names的值 5 self.anchors = self._get_anchors() # 获取边界的宽高, 并将原始数据转化为两列 6 self.sess = K.get_session() 7 self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
generate内部包含处理的函数如下思维导图所示:
- yolo_head: 将模型最后一层的输出转化为中心点坐标、宽、高、框置信度、类别概率。即那些公式的计算。
- yolo_correct_boxes: 转换成真实图像上的坐标
- yolo_boxes_and_scores:中除了包含两个函数以外,还会进行框的得分的计算:
框的得分=框的置信度*类别置信度
并且返回框的信息和框的得分
- yolo_eval:中除了包含上述的函数,还会根据框的得分和阈值进行过滤,并进行NMS抑制被标定多次的框。

接下来将从最底层往顶层扒~
A. yolo_head()
1 def yolo_head(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=False): 2 """Convert final layer features to bounding box parameters."""
获得anchors的个数,并初始化一个相关的张量
1 num_anchors = len(anchors) 2 # Reshape to batch, height, width, num_anchors, box_params. 3 anchors_tensor = K.reshape(K.constant(anchors), [1, 1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
创建网格
这个网格用于后续将偏移量转化为每个中心点的坐标。
- 会包含x轴的网格和y轴的网格 两部分
- 每部分每行都是从0到12的网格数
- 最后将其合并在一起,组成了一个13*13*1*2的矩阵
1 grid_shape = K.shape(feats)[1:3] # height, width 获取网格的尺寸 eg:13*13 2 grid_y = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]), 3 [1, grid_shape[1], 1, 1]) # 0~12的 从代码上看,只有grid_shape[1]能够体现reshape的这个功能 一个像素一个格子? 4 grid_x = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]), 5 [grid_shape[0], 1, 1, 1]) # 用于生成网格grid 6 grid = K.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y]) 7 grid = K.cast(grid, K.dtype(feats)) # -》(13,13,1,2)
将最后一位展开,网格info与其它分离
1 feats = K.reshape( 2 feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
进行计算
- 中心点坐标
- 宽高
- 框的置信度
- 类别概率
1 box_xy = (K.sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid) / K.cast(grid_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats)) 2 box_wh = K.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor / K.cast(input_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats)) 3 box_confidence = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 4:5]) # 框置信度 4 box_class_probs = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 5:]) # 类别置信度 # 可以一次性的把所有网格包含的内容都算出来
中心点的坐标是相对于网格尺寸的位置
宽高是相对于416*416尺寸的位置
B. yolo_correct_boxes()
1 def yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape): 2 '''转化成真实的坐标'''
进行坐标的翻转
1 box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1] 2 box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
获得图像经过等比缩放以后的尺寸(没有灰边的)--- new_shape
1 input_shape = K.cast(input_shape, K.dtype(box_yx)) 2 image_shape = K.cast(image_shape, K.dtype(box_yx)) 3 new_shape = K.round(image_shape * K.min(input_shape/image_shape))
将box的中心点、宽高调整至原图尺寸
1 offset = (input_shape-new_shape)/2./input_shape 2 scale = input_shape/new_shape 3 box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale 4 box_hw *= scale
将中心点、宽高信息转化为四个坐标点 xmin ymin xmax ymax
1 box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.) 2 box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.) 3 boxes = K.concatenate([ 4 box_mins[..., 0:1], # y_min 5 box_mins[..., 1:2], # x_min 6 box_maxes[..., 0:1], # y_max 7 box_maxes[..., 1:2] # x_max 8 ])# 即转化为真实坐标 9 return boxes ---- 此处的boxes已经是原图上的了
C. yolo_boxes_and_scores()
1 def yolo_boxes_and_scores(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape): 2 '''Process Conv layer output''' 处理卷积层输出的结果
执行A.和B
1 box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs = yolo_head(feats, 2 anchors, num_classes, input_shape) 3 boxes = yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape) 4 boxes = K.reshape(boxes, [-1, 4])
计算框的得分
框的得分=框的置信度*类别概率
1 box_scores = box_confidence * box_class_probs # 框的得分=框的置信度*类别置信度 2 box_scores = K.reshape(box_scores, [-1, num_classes]) 3 return boxes, box_scores --- 原图上的boxes 而且是四坐标
D. yolo_eval()
1 def yolo_eval(yolo_outputs, # 网络神经元输出的feature map(last layer) 2 anchors, 3 num_classes, 4 image_shape, 5 max_boxes=20, 6 score_threshold=.6, 7 iou_threshold=.5): 8 """Evaluate YOLO model on given input and return filtered boxes."""
相关使用的信息初始化:
1 num_layers = len(yolo_outputs) 2 anchor_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]] if num_layers==3 else [[3,4,5], [1,2,3]] # default setting 3 input_shape = K.shape(yolo_outputs[0])[1:3] * 32 # 模型最后一层有三个神经元---> (32,16,8)13-26-52 (下采样的时候的尺度缩放) 4 boxes = [] # 每个神经元会有3个anchor_box 5 box_scores = []
input_shape 为 416*416的;
逐层获得的边框信息和框的分的信息:
1 for l in range(num_layers): 2 _boxes, _box_scores = yolo_boxes_and_scores(yolo_outputs[l], 3 anchors[anchor_mask[l]], num_classes, input_shape, image_shape) # 处理卷积层的输出 内含yolo_head 4 boxes.append(_boxes) 5 box_scores.append(_box_scores) #
将boxes 和 box_scores的数据展平:
1 boxes = K.concatenate(boxes, axis=0) # 将数据展平 (?,4)---四坐标(与标定一样) 2 box_scores = K.concatenate(box_scores, axis=0)
获得了一个边界框的得分是否大于阈值的布尔向量,用于将低于阈值的边界框过滤掉
1 mask = box_scores >= score_threshold # 对三种尺度的得分进行筛选(阈值) 得到一堆符合条件的布尔值
初始化:
1 max_boxes_tensor = K.constant(max_boxes, dtype='int32') 2 boxes_ = [] 3 scores_ = [] 4 classes_ = []
按类进行进一步的框框筛选:
1 for c in range(num_classes):
过滤掉一些得分小于阈值的边框:
1 class_boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, mask[:, c]) # 过滤掉一些得分小于阈值的边界框 2 class_box_scores = tf.boolean_mask(box_scores[:, c], mask[:, c])
进行NMS处理(处理掉标定同一物体的多个标定的框)
1 nms_index = tf.image.non_max_suppression( 2 class_boxes, class_box_scores, max_boxes_tensor, iou_threshold=iou_threshold) # 运行非最大抑止—用于排出同一目标被标注多次的框
1 class_boxes = K.gather(class_boxes, nms_index) # 在class_boxes中搜寻nms_index下表的向量 2 class_box_scores = K.gather(class_box_scores, nms_index) 3 classes = K.ones_like(class_box_scores, 'int32') * c 4 boxes_.append(class_boxes) 5 scores_.append(class_box_scores) 6 classes_.append(classes)
从此结束循环
1 boxes_ = K.concatenate(boxes_, axis=0) 2 scores_ = K.concatenate(scores_, axis=0) 3 classes_ = K.concatenate(classes_, axis=0) 4 return boxes_, scores_, classes_
generate中包含导入模型以及给不同的类分配一种颜色的框,然后就是yolo_eval().