How To List Users and Groups on Linux
On Linux, as a system administrator, you often want to have a complete list of all the users and all the groups on your host.
It is quite crucial for security purposes to make sure that you have the correct amount of users and that you didn’t forget to delete some.
There are several ways to list users and groups on Linux.
First, you can read the passwd and the group file on your system, with cut commands to extract useful information.
A more effective way is to use the getent command that relies on the Name Service Switch, a Unix-based facility to define custom databases on your host.
Here is how you can list users and groups on Linux.
Table of Contents
List Users on Linux
In order to list users on Linux, you have to execute the “cat” command on the “/etc/passwd” file. When executing this command, you will be presented with the list of users currently available on your system.
Alternatively, you can use the “less” or the “more” command in order to navigate within the username list.
$ cat /etc/passwd
$ less /etc/passwd
$ more /etc/passwdYou will be presented with a list of users currently available on your system.
Note : it does not mean that users are connected right now!
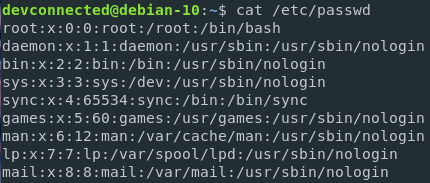
But what do the columns of the passwd file even mean?
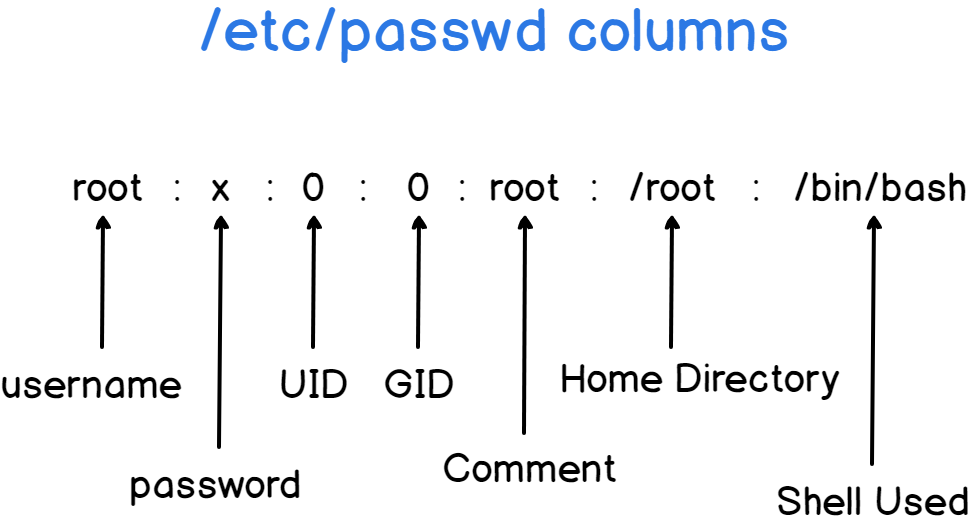
As a quick side note, an “x” in the password column means that the password is encrypted and it is to be found in the /etc/shadow file.
Now that you know how to list users on your Linux host, let’s see how you can effectively isolate a list of usernames.
List Usernames using the /etc/passwd file
As you probably noticed, the /etc/passwd file is made of lines separated by colons.
a – List Usernames using cut
In order to list usernames on Linux, use the “cat” command and pipe it to the “cut” command in order to isolate usernames available in the first column of your file.
To achieve that, run the following command
$ cat /etc/passwd | cut -d: -f1First, you are printing a list of all records in the passwd file. Next, those results are piped (using Linux pipes and redirection) to the cut command.
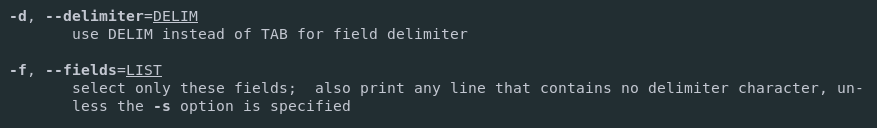
The cut command defines a custom separator (with the d option) that is equal to the colon character.
Finally, we are isolating the first field of the results we are getting. In this case, this is equal to the usernames as defined by our schema on the passwd columns.
b – List Usernames using awk
In order to list usernames on Linux, you can also use the “cat” command piped with the “awk” command that is similar to the “cut” command that we have seen before.
As a reminder, the awk command (or mawk) is an interpreter for the AWK programming language.
AWK is a programming language designed to ease data extract and manipulation for data streams.
It is widely used on Unix-based systems when text structures are quite complicated and cannot be separated with a single command.
To list usernames on Linux using the awk interpreter, run the following command
$ cat /etc/passwd | awk -F: '{print $1}'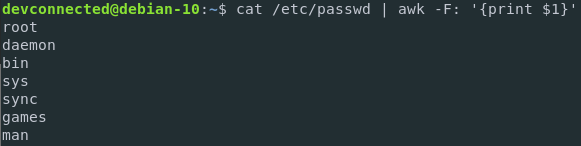
List Users on Linux using getent
The easiest way to list users on Linux is to use the “getent” command with the “passwd” argument and specify an optional user that you want to list on your system.
getent passwd <optional_user>As a reminder, the getent command retrieves entries from Name Service Switch databases.
The Name Service Switch is a Unix utility that retrieves entries from a set of different datasources such as files, LDAP, a DNS server or a Network Information Service.
The list of all the datasources available can be read from the nsswitch.conf file located at /etc.
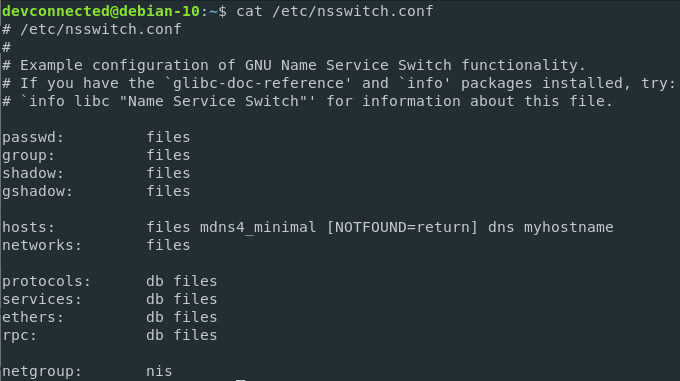
In our case, it can be used in order to list users and groups easily on our Linux host.
To list users using the getent function, run the following command
$ getent passwd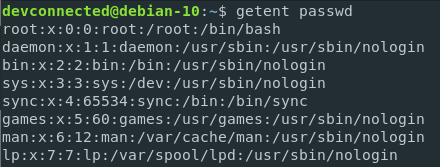
a – List Usernames with getent
Similarly to the previous section, it is possible to list only usernames when interacting with the getent command.
To achieve that, you can alternatively execute the cut command or the awk command in the following way.
$ getent passwd | cut -d: -f1Or with AWK
$ getent passwd | awk -F: '{print $1}'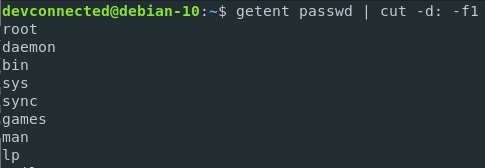
List Connected Users on your Linux host
As mentionned previously, inspecting the passwd file, either with less or with getent, does not provide you with a list of all the connected users on your host.
To achieve that, you are going to use the who command.
$ who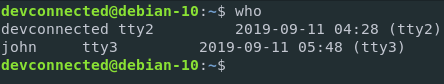
As you can see, you are provided with a list of users currently connected on your host along with the shell they are using and when they connected.
Alternatively, you can use the users command to achieve the same result with less details.
$ users
devconnected johnPretty handy!
Now that we have seen how we can list users on a Linux host, let’s see how we can apply the same knowledge to list groups on your system.
List Groups on Linux using the /etc/group file
In order to list groups on Linux, you have to execute the “cat” command on the “/etc/group” file. When executing this command, you will be presented with the list of groups available on your system.
Use one of the following commands to list groups on your system.
$ cat /etc/group
$ less /etc/group
$ more /etc/group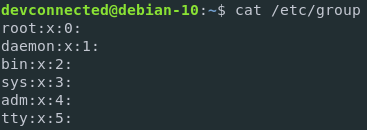
But what do the columns of the group file even represent?
Let’s take a complete line on the group file to inspect it.
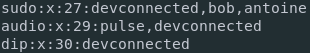
As you can see, similarly to the passwd file, the entries are separated by colons. They are fairly easy to understand.
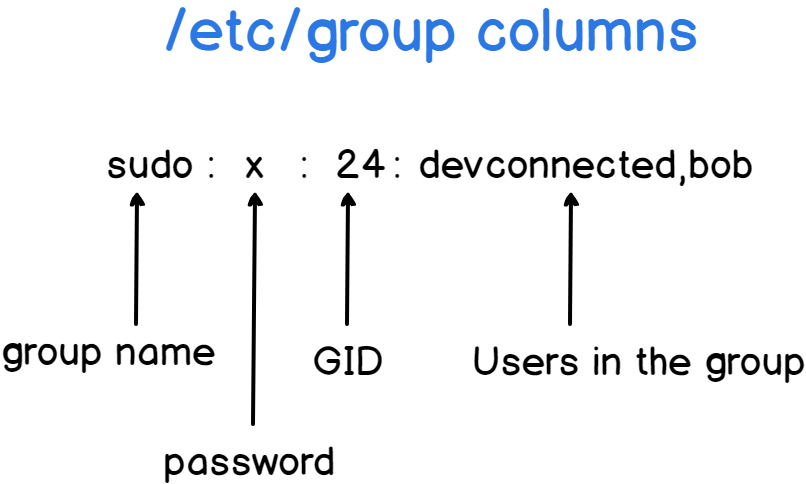
Note : the password field is not used most of the time, it is reserved to create privileged groups on your system.
List Groupnames using the /etc/group
As you can see, inspecting the /etc/group gives you a complete and sometimes too detailed listing of all the groups on your system.
However, you sometimes want to isolate the groupnames on your group file.
To achieve that, you can either use the cut command or the AWK command.
$ cat /etc/group | cut -d: -f1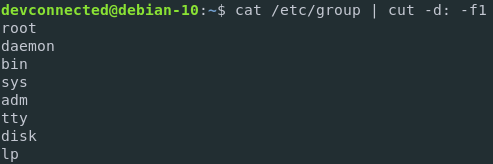
$ cat /etc/group | awk -F: '{print $1}'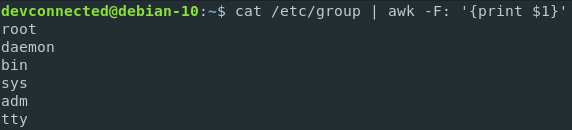
You can of course choose to isolate one group if you want to see which users belong to the group you are targeting.
$ cat /etc/group | grep <group>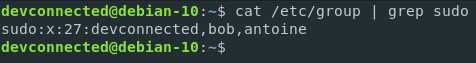
List Groups using getent
Again, you can choose to list groups on Linux by using the getent command.
$ getent <database> <key>Here, we are interested in the “group” database.
If you choose not to provide a key, you will be provided with the entire group file.
$ getent group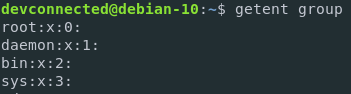
Similarly to the passwd database, you can choose to “target” one specific group by providing a key to the getent function.
$ getent group sudo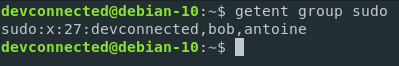
List Groups for the current user
The groups commands is used to get a list of groups a specific user is in.
$ groups <username>If provided with no arguments, it will return the groups for the user that launched the command.
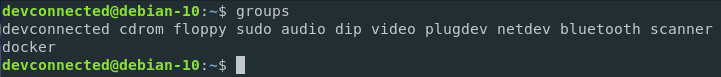
To prove that it provides the groups for the user that launched the command, try to launch the command with sudo privileges.
$ sudo groups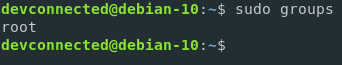
The result is.. root! Because the command is executed as root and root only belongs to one group which is the root group.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learnt how you can list users and groups on any Linux based system.
You learnt more about specific configuration file like passwd and group, as well as the getent command for Name Service Switch facilities.
Again, if you are interested in Linux system administration, we have tons of tutorials on the subject in our Linux System Administration category.
Click the image below to check them.

Also, for those who want to dig deeper in the Name Service Switch and the nsswitch configuration file, here is a detailed video to understand it better.
