String源码分析
类结构
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence

String类实现了Serializable可以被序列化
String类实现了Comparable可以进行比较
String类实现了CharSequence可以按下标进行相关操作
并且String类使用final进行修饰,不可以被继承
属性
//用来存储字符串的每一个字符
private final char value[];
//hash值
private int hash; // Default to 0
//序列化版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;
//从变量名大致可以看出和序列化有关,具体的不明白
private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields =
new ObjectStreamField[0];
构造方法
//无参,直接使用空字符串赋值,hash为0
public String() {
this.value = "".value;
}
//使用已有字符串初始化
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
//使用char数组初始化,hash为0
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}
//使用字符数组,并指定偏移、字符个数初始化
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= value.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}
//使用unicode编码数组并指定偏移和数量进行初始化
public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= codePoints.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > codePoints.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
final int end = offset + count;
// Pass 1: Compute precise size of char[] 计算char数组大小
int n = count;
for (int i = offset; i < end; i++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))//判断编码是不是BMP(Basic Mutilingual Plane)
continue;
else if (Character.isValidCodePoint(c))//验证编码是否在unicode编码范围内
n++;
else throw new IllegalArgumentException(Integer.toString(c));
}
// Pass 2: Allocate and fill in char[] 申明char数组并填入编码对应char
final char[] v = new char[n];
for (int i = offset, j = 0; i < end; i++, j++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))//如果编码是BMP直接一个字符就是接受
v[j] = (char)c;
else
Character.toSurrogates(c, v, j++);//转换成两个字符存储
}
this.value = v;
}
//使用ascii码数组进行初始化
@Deprecated
public String(byte ascii[], int hibyte, int offset, int count) {
checkBounds(ascii, offset, count);
char value[] = new char[count];
if (hibyte == 0) {
for (int i = count; i-- > 0;) {
value[i] = (char)(ascii[i + offset] & 0xff);
}
} else {
hibyte <<= 8;
for (int i = count; i-- > 0;) {
value[i] = (char)(hibyte | (ascii[i + offset] & 0xff));
}
}
this.value = value;
}
@Deprecated
public String(byte ascii[], int hibyte) {
this(ascii, hibyte, 0, ascii.length);
}
//使用字节数组+字符集名初始化
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
if (charsetName == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charsetName");
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(charsetName, bytes, offset, length);
}
//使用字节数组+字符集名初始化
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, Charset charset) {
if (charset == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charset");
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(charset, bytes, offset, length);
}
//使用字节数组+字符集名初始化
public String(byte bytes[], String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
this(bytes, 0, bytes.length, charsetName);
}
//使用字节数组+字符集名初始化
public String(byte bytes[], Charset charset) {
this(bytes, 0, bytes.length, charset);
}
//使用字节数组初始化
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) {
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(bytes, offset, length);
}
public String(byte bytes[]) {
this(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
}
//使用StringBuffer初始化
public String(StringBuffer buffer) {
synchronized(buffer) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(buffer.getValue(), buffer.length());
}
}
//使用StringBuilder初始化
public String(StringBuilder builder) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(builder.getValue(), builder.length());
}
方法
静态方法
join(CharSequence,CharSequence...)使用分隔符拼接字符串
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements) {
Objects.requireNonNull(delimiter);
Objects.requireNonNull(elements);
// Number of elements not likely worth Arrays.stream overhead.
StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(delimiter);
for (CharSequence cs: elements) {
joiner.add(cs);
}
return joiner.toString();
}
join(CharSequence,Iterable<? extends CharSequence>)使用分隔符拼接字符串
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter,
Iterable<? extends CharSequence> elements) {
Objects.requireNonNull(delimiter);
Objects.requireNonNull(elements);
StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(delimiter);
for (CharSequence cs: elements) {
joiner.add(cs);
}
return joiner.toString();
}
format(String,Object...)使用字符串格式指定参数进行格式化生成字符串
public static String format(String format, Object... args) {
return new Formatter().format(format, args).toString();
}
format(Local,String,Object...)根据环境使用字符串格式指定参数进行格式化生成字符串
public static String format(Locale l, String format, Object... args) {
return new Formatter(l).format(format, args).toString();
}
valueOf(Object)对象转换成字符串,如果对象为null转为为字符串“null”
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
valueOf(char[])char数组转换成字符串
public static String valueOf(char data[]) {
return new String(data);
}
valueOf(xxx)xxx数据类型转换为字符串
public static String valueOf(boolean b) {
return b ? "true" : "false";
}
public static String valueOf(char c) {
char data[] = {c};
return new String(data, true);
}
public static String valueOf(int i) {
return Integer.toString(i);
}
public static String valueOf(long l) {
return Long.toString(l);
}
public static String valueOf(float f) {
return Float.toString(f);
}
public static String valueOf(double d) {
return Double.toString(d);
}
valueOf(char[],int,int)char数组按照偏移个指定字符格式转换为字符串
public static String valueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
return new String(data, offset, count);
}
copyValueOf(char,int,int)使用指定字符数组根据偏移和字符个数拷贝一个新字符串,同valueOf
public static String copyValueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
return new String(data, offset, count);
}
copyValueOf(char[])使用指定字符数组拷贝新字符串
public static String copyValueOf(char data[]) {
return new String(data);
}
成员方法
char charAt(int index)获取指定下标的字符
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index];
}
void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin)把当前字符串的char数组的指定范围拷贝到目标char数组的指定位置
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) {
if (srcBegin < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
}
if (srcEnd > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
}
if (srcBegin > srcEnd) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
//System.arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos,int length)
//src:要拷贝的源数组
//srcPos:源数组拷贝的起始位置
//dest:目标数组
//destPost:拷贝到目标数组的起始位置
//length:要拷贝元素的个数
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
byte[] getBytes(String charsetName)根据字符集获取字符串的编码后的字节数组
public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
if (charsetName == null) throw new NullPointerException();
return StringCoding.encode(charsetName, value, 0, value.length);
}
boolean equals(Object anObject)方法比较两个字符串,重写的Object方法
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {//地址相等两对象equals为true
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {//判断两字符串的字符个数
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])//有一个字符不相等最直接为false
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
contentEquals(CharSequence cs)判断当前String与其他字符序列是否相等,与equals不同的是,equals只有当两个对象都是String时equals才为true,contentEquals可以用来同其他StringBuffer、StringBuilder和其他字符序列进行比较
public boolean contentEquals(CharSequence cs) {
// Argument is a StringBuffer, StringBuilder
if (cs instanceof AbstractStringBuilder) {
if (cs instanceof StringBuffer) {
synchronized(cs) {//如果是StringBuffer那么进行上锁操作
return nonSyncContentEquals((AbstractStringBuilder)cs);
}
} else {//StringBuilder不上锁
return nonSyncContentEquals((AbstractStringBuilder)cs);
}
}
// Argument is a String
if (cs instanceof String) {
return equals(cs);
}
// Argument is a generic CharSequence
char v1[] = value;
int n = v1.length;
if (n != cs.length()) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//其他字符序列,一个一个字符进行比较
if (v1[i] != cs.charAt(i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)两个字符串忽略大小写进行比较是否相等
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) {
return (this == anotherString) ? true
: (anotherString != null)//不为空
&& (anotherString.value.length == value.length)//字符个数相等
&& regionMatches(true, 0, anotherString, 0, value.length);//忽略大小写比较
}
public boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset,
String other, int ooffset, int len) {
char ta[] = value;
int to = toffset;
char pa[] = other.value;
int po = ooffset;
// Note: toffset, ooffset, or len might be near -1>>>1.
if ((ooffset < 0) || (toffset < 0)
|| (toffset > (long)value.length - len)
|| (ooffset > (long)other.value.length - len)) {
return false;
}
while (len-- > 0) {
char c1 = ta[to++];
char c2 = pa[po++];
if (c1 == c2) {
continue;
}
if (ignoreCase) {
// If characters don't match but case may be ignored,
// try converting both characters to uppercase.
// If the results match, then the comparison scan should
// continue.
//把两个字符转换成大写的
char u1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
char u2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
if (u1 == u2) {
continue;
}
// Unfortunately, conversion to uppercase does not work properly
// for the Georgian alphabet, which has strange rules about case
// conversion. So we need to make one last check before
// exiting.
//转换成大写的不相等,在转换成小写的判断
if (Character.toLowerCase(u1) == Character.toLowerCase(u2)) {
continue;
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
int compareTo(String anotherString)进行字符串的比较
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {//如果当前字符串的字符比参数的大返回正数,否则返回负数
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
//如果两个字符串,长度小的字符串与长度大的前部分每个字符都相等,如果两字符串长度相等返回0,当前字符串长度大于参数字符串返回整数,当前字符串长度小于参数字符串返回负数
return len1 - len2;
}
compareToIgnoreCase(String str)字符串忽略大小写进行比较
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) {
return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this, str);
}
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
int n1 = s1.length();
int n2 = s2.length();
int min = Math.min(n1, n2);
for (int i = 0; i < min; i++) {
char c1 = s1.charAt(i);
char c2 = s2.charAt(i);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toLowerCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toLowerCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
//如果两字符不相等,最后是转换成小写的进行比较
return c1 - c2;
}
}
}
}
return n1 - n2;
}
startsWith(String prefix)判断字符串是否以指定字符串开头
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return startsWith(prefix, 0);
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) {
char ta[] = value;
int to = toffset;
char pa[] = prefix.value;
int po = 0;
int pc = prefix.value.length;
// Note: toffset might be near -1>>>1.
if ((toffset < 0) || (toffset > value.length - pc)) {
return false;
}
while (--pc >= 0) {//循环给定前缀字符串长度
if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {//前缀字符串字符和当前字符串字符比较
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
boolean endsWith(String suffix)判断字符串是否以指定字符串结尾
public boolean endsWith(String suffix) {
return startsWith(suffix, value.length - suffix.value.length);
}
int hashCode()获取字符串的hashCode
public int hashCode() {
//默认字符串hash为0,如果是用另一个字符串就等于另一个字符串的hash
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {//一个一个字符的变量
//前面字符的hash*31+当前字符的ascii码
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
int indexOf(int ch)根据unicode编码获取下标
public int indexOf(int ch) {
return indexOf(ch, 0);
}
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
final int max = value.length;
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
} else if (fromIndex >= max) {//如果查找的起始位置超过了数组下标
// Note: fromIndex might be near -1>>>1.
return -1;
}
if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
//编码是一个基本多语言编码
// handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
// negative value (invalid code point))
final char[] value = this.value;
for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {
if (value[i] == ch) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
} else {
//获取需要使用两个char存储的编码的下标
return indexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex);
}
}
private int indexOfSupplementary(int ch, int fromIndex) {
if (Character.isValidCodePoint(ch)) {//是一个合法的unicode编码
final char[] value = this.value;
final char hi = Character.highSurrogate(ch);
final char lo = Character.lowSurrogate(ch);
final int max = value.length - 1;
for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {
if (value[i] == hi && value[i + 1] == lo) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int lastIndexOf(int ch)获取指定编码从后往前搜索的第一个下标
public int lastIndexOf(int ch) {
return lastIndexOf(ch, value.length - 1);
}
public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {//编码是一个基本多语言unicode编码,使用一个char存储
// handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
// negative value (invalid code point))
final char[] value = this.value;
int i = Math.min(fromIndex, value.length - 1);
for (; i >= 0; i--) {
if (value[i] == ch) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
} else {
//编码使用两个char存储
return lastIndexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex);
}
}
private int lastIndexOfSupplementary(int ch, int fromIndex) {
if (Character.isValidCodePoint(ch)) {
final char[] value = this.value;
char hi = Character.highSurrogate(ch);
char lo = Character.lowSurrogate(ch);
int i = Math.min(fromIndex, value.length - 2);
for (; i >= 0; i--) {
if (value[i] == hi && value[i + 1] == lo) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int indexOf(String str)获取指定字符串的的第一个字符在当前字符串的下标
public int indexOf(String str) {
return indexOf(str, 0);
}
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return indexOf(value, 0, value.length,
str.value, 0, str.value.length, fromIndex);
}
static int indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
int fromIndex) {
if (fromIndex >= sourceCount) {
return (targetCount == 0 ? sourceCount : -1);
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
}
if (targetCount == 0) {
return fromIndex;
}
char first = target[targetOffset];
int max = sourceOffset + (sourceCount - targetCount);
for (int i = sourceOffset + fromIndex; i <= max; i++) {
/* Look for first character. */
if (source[i] != first) {
while (++i <= max && source[i] != first);
}
/* Found first character, now look at the rest of v2 */
if (i <= max) {
int j = i + 1;
//计算终止下标
int end = j + targetCount - 1;
for (int k = targetOffset + 1; j < end && source[j]
== target[k]; j++, k++);
if (j == end) {
/* Found whole string. */
return i - sourceOffset;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
String substring(int beginIndex)获取指定下标到最末下标的字符串
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
//计算长度
int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)根据起始下标和结束下标获取字符串,包含起始下标字符,不包含结束下标字符
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
//计算字符个数
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this
: new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
String concat(String str)把参数字符串拼接到当前字符串
public String concat(String str) {
int otherLen = str.length();
if (otherLen == 0) {
return this;
}
//获取拼接字符串的长度
int len = value.length;
//把原字符串的字符拷贝到一个大小为原字符串大小+参数字符串大小的新数组中
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
//把拼接字符串的字符拷贝到数组中
str.getChars(buf, len);
return new String(buf, true);
}
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)把指定字符替换为新字符
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) {
if (oldChar != newChar) {
int len = value.length;
int i = -1;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while (++i < len) {
if (val[i] == oldChar) {//找到需要替换字符的位置
break;
}
}
if (i < len) {
char buf[] = new char[len];
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
buf[j] = val[j];
}
while (i < len) {
char c = val[i];
buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c;//把原字符替换为新字符
i++;
}
return new String(buf, true);
}
}
return this;
}
boolean matches(String regex)判断正则表达式是否比配当前字符串
public boolean matches(String regex) {
return Pattern.matches(regex, this);
}
boolean contains(CharSequence s)判断当前字符串是否包含另一个字符序列
public boolean contains(CharSequence s) {
return indexOf(s.toString()) > -1;
}
String trim()去掉字符串前后的空格
public String trim() {
int len = value.length;
int st = 0;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
//找到字符串由前往后第一个不是空格的位置
while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) {
st++;
}
//找到字符串由后往前第一个不是空格的位置
while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) {
len--;
}
return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this;
}
char[] toCharArray()把字符串转换成字符数组
public char[] toCharArray() {
// Cannot use Arrays.copyOf because of class initialization order issues
char result[] = new char[value.length];
//使用System.arraycopy方法拷贝
System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, value.length);
return result;
}
本地方法
native String intern();获取字符串所指向的字符串常量池中对象的地址
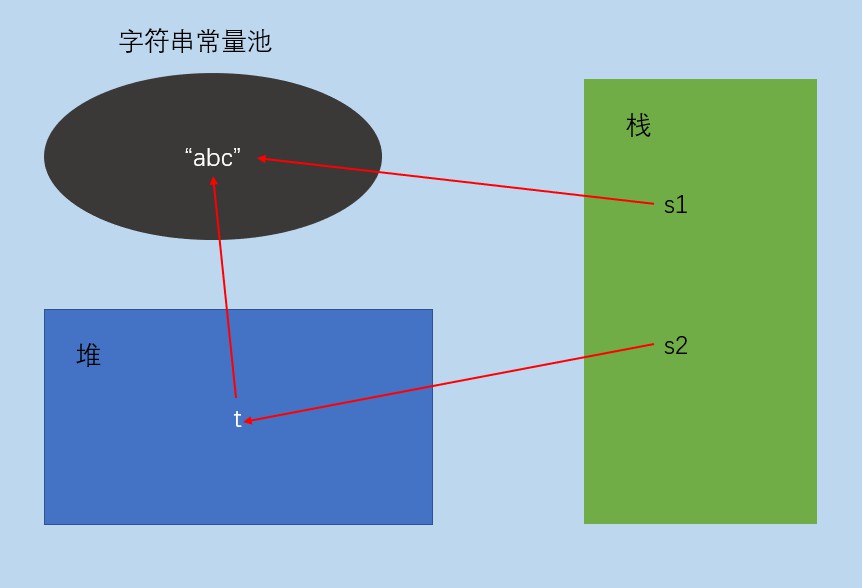
@Test
public void test8() {
String s1="abc";
String s2=new String("abc");
System.out.println(s1==s2);//false
System.out.println(s1==s2.intern());//true
}
使用s1="abc"这种方式栈中变量s1直接指向字符串常量池中的常量“abc”,而s2=new String("abc")这种方式,栈中变量s2指向的是对中一个变量t,t指向字符串常量池中的“abc”,所以s1和s2指向的地址不相同
s2.intern()获取的是字符串的常量池中的地址,也就是如果变量直接指向常量池,那么就是变量的地址,如果变量指向堆,那么会获取堆所指向字符串常量池中的地址