线性表
线性表表示一种线性结构的数据结构,顾名思义就是数据排成像一条线一样的结构,每个线性表上的数据只有前和后两个方向。比如:数组、链表、栈和队列都是线性表,今天我们分别来看看这些线性数据结构。

数组
数组是一种线性表数据结构,用一组连续的内存空间来存储一组具有相同类型的数据。
内存分布:

随机访问
连续内存空间存储相同类型的数据,这个特性支持了数组的随机访问特性,相同类型的数据占用的空间是固定的假设为data_size,第n个元素的地址可以根据公式计算出来:
&a[n] = &a[0] + n * data_size
其中:
&a[n]:第n个元素的地址
&a[0]:第0个元素的地址(数组的地址)
data_size:数组存储的元素的类型大小
所以访问数组里指定下标的任何一个元素,都可以直接访问对应的地址,不需要遍历数组,时间复杂度为O(1)。
插入/删除低效
为了保证内存的连续性,插入或删除数据时如果不是在数组末尾操作,就需要做数据的搬移工作,数据搬移会使得数组插入和删除时候效率低下。
向数组里插入一个元素有三种情况:
1、向末尾插入一个元素,此时的时间复杂度为O(1),对应最好时间复杂度。
2、向数组开头插入一个元素,需要将所有元素依次向后挪一个位置,然后将元素插入开头位置,此时时间复杂度为O(n),对应最坏时间复杂度。
3、向数组中间位置插入一个元素,此时每个位置插入元素的概率都是一样的为1/n,平均复杂度为(1+2+3+…+n)/n = O(n)
如果数组元素是没有顺序的(或不需要保证元素顺序),向数组中间位置插入一个元素x,只需要将插入位置的元素放到数组的末尾,然后将x插入,这时候不需要搬移元素,时间复杂度仍为O(1),如:
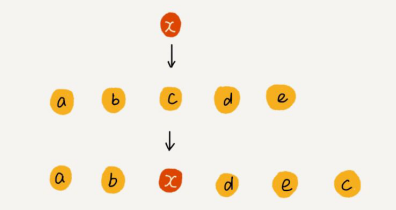
同样地,删除数据的时候,从开头删除,需要将后面n-1个元素往前搬移,对应的时间复杂度为O(n);从末尾删除时间复杂度为O(1);平均时间复杂度也是O(n)。
如果不需要保证数据的连续性,有两种方法:
1、可以将末尾的数据搬移到删除点插入,删除末尾那个元素
2、删除的时候做标记,并不正真删除,等数组空间不够的时候,再进行批量删除搬移操作
Java的ArrayList
很多编程语言都针对数组进行了封装,比如Java的ArrayList,可以将数组的很多操作细节封装起来(插入删除的搬移数据或动态扩容),可以参考ArrayList的扩容数据搬移方法,ArrayList默认size是10,如果空间不够了会先按1.5倍扩容(如果还不够就可能会用到最大容量)。所以在使用的时候如果事先知道数组的大小,可以一次性申请,这样可以免去自动扩容的性能损耗。
什么时候选择使用编程语言帮我们封装的数组,什么时候直接使用数组呢?
1、Java ArrayList不支持基本数据类型,需要封装为Integer、Long类才能使用。Autoboxing、Unboxing有一定的性能消耗。如果比较关注性能可以直接使用数组
2、使用前已经能确认数据大小,并且操作比较简单可以使用数组
链表
比起数组,链表不需要连续内存空间,它通过指针将一组分别独立的内存空间串起来形成一条“链条”。链表有很多种,如:单链表、双向链表、循环链表和双向循环链表。
链表内存分布:
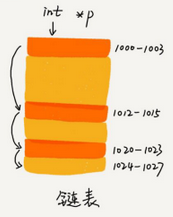
单链表
如下图所示,链表的每一项我们称为结点(node),为了将所有结点连接起来形成链表,结点除了需要记录数据之外,还需要记录下一个结点的地址,记录下一个结点地址的指针我们叫做后继指针(next),第一个结点和最后一个结点比较特殊,第一个结点没有next指针指向它,称为头结点,最后一个结点next指针没有指向任何元素,称为尾结点。头结点用来记录链表的基地址,有了它就可以顺着链子往下搜索每一个元素,如果遇到next指向null表示到达了链表的末尾。

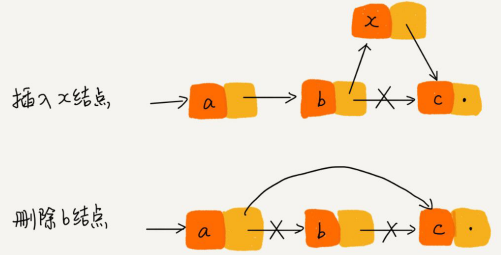
在数组里插入或删除数据需要保证内存空间的连续性,需要做数据的搬移,但是链表里数据内存空间是独立的,插入删除只需要改变指针指向即可,所以链表的插入删除非常高效。如图:
双向链表
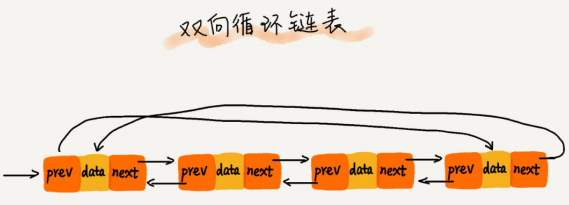
单向链表每个结点只知道自己下一个结点是谁,是一条单向的“链条”,而在双向链表里每个结点既知道下一个结点,还知道前一个结点,相比单链表,双向链表每个结点多了一个前驱指针(prev)指向前一个结点的地址,如下图所示:
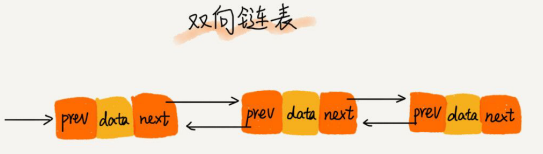
因为每个结点要额外的空间来保存前驱结点的地址,所以相同数据情况下,双向链表比单链表占用的空间更多。双向链表在找前驱结点时间复杂度为O(1),插入删除都比单链表高效,典型的空间换时间的例子。
循环链表
将一个单链表首尾相连就形成了一个环,这就是循环链表,循环链表里尾结点不在是null,而是指向头结点。当数据具有环形结构时候就可以使用循环链表。
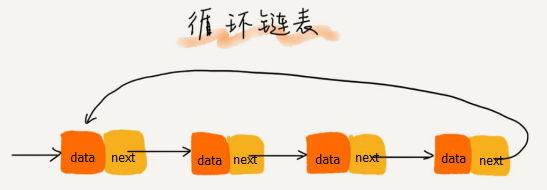
双向循环链表
与循环链表类似,尾结点指向头结点,同时每个结点除了保存自身数据,分别有一个前驱指针和后继指针,就形成了双向循环链表:
插入/删除比较
在链表里插入数据(new_node)
1、在P结点后插入数据
new_node->next = p->next;
p->next = new_node
此时时间复杂度为O(1)
2、在P结点前插入数据
需要找到P结点的前驱结点,然后转化为在P的前驱结点之后插入数据。
- 单链表需要从头遍历,当满足条件 pre->next = p时,转化为再pre结点后插入数据,此时时间复杂度为O(n)遍;
- 双链表只需要通过p->pre即可找到前驱结点,时间复杂度为O(1)
3、在值等于某个值的结点前/后插入数据
需要遍历整个链表,找到这个值,然后在它前/后插入数据,此时时间复杂度为O(n)
在链表里删除数据
1、删除P结点下一个结点
p->next = p->next->next;
直接将p后继结点指针指向p下下一个结点。
2、删除P结点前一个结点
找到P结点前驱结点的前驱结点N,然后转化为删除N的后继结点
- 单链表需要遍历找到结点N,遍历时间复杂度为O(n),然后删除N的一个后继结点,时间复杂度为O(1),所以总的时间复杂度为O(n)
- 双向链表直接找到结点N:p->pre->pre->next = p,时间复杂度为O(1)
3、在值等于某个值的结点前/后删除数据
需要遍历整个链表,找到这个值,然后在它前/后删除数据,此时时间复杂度为O(n)
栈
栈是一种后进者先出,先进者后出的线性数据结构,只允许在一端插入/删除数据。栈可以用数组来实现,也可以用链表来实现,用数组实现的叫顺序栈,用链表来实现是叫链式栈。
栈的数组实现
数组来实现栈,插入和删除都发生在数组的末尾,所以不需要进行数据的搬移,但是如果发生内存不够需要进行扩容的时候,仍然需要进行数据搬移

1 @Test 2 public void testStack() { 3 StringStack stack = new StringStack(10); 4 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 5 stack.push("hello" + i); 6 } 7 System.out.println(stack.push("dd")); 8 9 String item = null; 10 while ((item = stack.pop()) != null) { 11 System.out.println(item); 12 } 13 } 14 15 public class StringStack { 16 private String[] items; 17 private int count; 18 private int size; 19 20 public StringStack(int n) { 21 this.items = new String[n]; 22 this.count = 0; 23 this.size = n; 24 } 25 26 public boolean push(String item) { 27 if (this.count == this.size) { 28 return false; 29 } 30 this.items[count++] = item; 31 return true; 32 } 33 34 public String pop() { 35 if (this.count == 0) { 36 return null; 37 } 38 return this.items[--count]; 39 } 40 41 public int getCount() { 42 return count; 43 } 44 45 public int getSize() { 46 return size; 47 } 48 }
栈的链表实现
链表的实现有个小技巧,倒着创建一个链表来模拟栈结构,最后添加到链表的元素作为链表的头结点,如图:


1 public class LinkStack { 2 private Node top; 3 4 public boolean push(String item) { 5 Node node = new Node(item); 6 if(top == null){ 7 top = node; 8 return true; 9 } 10 node.next = top; 11 top = node; 12 return true; 13 } 14 15 public String pop() { 16 if (top == null) { 17 return null; 18 } 19 String name = top.getName(); 20 top = top.next; 21 return name; 22 } 23 24 private static class Node { 25 private String name; 26 private Node next; 27 28 public Node(String name) { 29 this.name = name; 30 this.next = null; 31 } 32 33 public String getName() { 34 return name; 35 } 36 } 37 }
数组实现的是一个固定大小的栈,当内存不够的时候,可以按照数组扩容方式实现栈的扩容,或是依赖于动态扩容的封装结构来实现栈的动态扩容。出栈的时间复杂度都是O(1),入栈会有不同,如果是数组实现栈需要扩容,最好时间复杂度(不需要扩容的时候)是O(1),最坏时间复杂度是O(n),插入数据的时候,栈刚好满了需要进行扩容,假设扩容为原来的两倍,此时时间复杂度是O(n),每n次时间复杂度为O(1)夹杂着一次时间复杂度为O(n)的扩容,那么均摊时间复杂度就是O(1)。
栈的应用
- 函数调用栈
- java的拦截器
- 表达式求解
队列
队列与栈类似,支持的操作也很相似,不过队列是先进先出的线性数据结构。日常生活中常常需要进行的排队就是队列,排在前面的人优先。队列支持两个操作:入队 enqueue 从队尾添加一个元素;出队 dequeue 从对列头部取一个元素。
和栈一样,队列也有顺序队列和链式队列分别对应数组实现的队列和链表实现的队列。
数组实现队列
数组实现的队列是固定大小的队列,当队列内存不足时候,统一搬移数据整理内存。

1 public class ArrayQueue { 2 private String[] items; 3 private int capacity; 4 private int head = 0; 5 private int tail = 0; 6 7 public ArrayQueue(int n) { 8 this.items = new String[n]; 9 this.capacity = n; 10 } 11 12 /** 13 * 入队列(从队列尾部入) 14 * @param item 15 * @return 16 */ 17 public boolean enqueue(String item) { 18 //队列满了 19 if (this.tail == this.capacity) { 20 //对列头部不在起始位置 21 if (this.head == 0) { 22 return false; 23 } 24 //搬移数据 25 for (int i = head; i < tail; i++) { 26 items[i - head] = items[i]; 27 } 28 this.tail = tail - head; 29 this.head = 0; 30 } 31 items[tail++] = item; 32 return true; 33 } 34 35 /** 36 * 出队列(从队列头部出) 37 * @return 38 */ 39 public String dequeue() { 40 if (this.head == this.tail) { 41 return null; 42 } 43 44 return this.items[head++]; 45 } 46 }
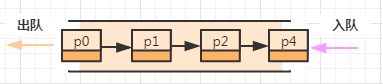
链表实现队列
链表尾部入队,从头部出队,如图:

1 public class LinkQueue { 2 private Node head; 3 private Node tail; 4 5 public LinkQueue() { } 6 7 /** 8 * 入队列 9 * @param item 10 * @return 11 */ 12 public boolean enqueue(String item) { 13 Node node = new Node(item); 14 //队列为空 15 if(this.tail == null) { 16 this.tail = node; 17 this.head = node; 18 return true; 19 } 20 this.tail.next = node; 21 this.tail = node; 22 return true; 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * 出队列 27 * @return 28 */ 29 public String dequeue() { 30 //队列为空 31 if (this.head == null) { 32 return null; 33 } 34 String name = this.head.getName(); 35 this.head = this.head.next; 36 if (this.head == null) { 37 this.tail = null; 38 } 39 return name; 40 } 41 42 private static class Node { 43 private String name; 44 private Node next; 45 46 public Node(String name) { 47 this.name = name; 48 } 49 50 public String getName() { 51 return name; 52 } 53 } 54 }
循环队列
数组实现队列时,当队列满了,头部出队时候,会发生数据搬移,但是如果是一个首尾相连的环形结构,如下图,头部有空间,尾部到达7位置,再添加元素时候,tail到达环形的第一个位置(下标为0)不需要搬移数据。
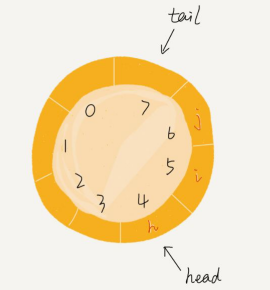
为空的判定条件:
head = tail
队列满了的判定条件:
- 当head = 0,tail = 7
- 当head = 1,tail = 0
- 当head = 4,tail = 3
- head = (tail + 1)% 8

1 public class CircleQueue { 2 private String[] items; 3 private int capacity; 4 private int head = 0; 5 private int tail = 0; 6 7 public CircleQueue(int n) { 8 this.items = new String[n]; 9 this.capacity = n; 10 } 11 12 /** 13 * 入队列(从队列尾部入) 14 * @param item 15 * @return 16 */ 17 public boolean enqueue(String item) { 18 //队列满了 19 if (this.head == (this.tail + 1)% this.capacity) { 20 return false; 21 } 22 items[tail] = item; 23 tail = (tail + 1) % this.capacity; 24 return true; 25 } 26 27 /** 28 * 出队列(从队列头部出) 29 * @return 30 */ 31 public String dequeue() { 32 //队列为空 33 if (this.head == this.tail) { 34 return null; 35 } 36 String item = this.items[head]; 37 head = (head + 1) % this.capacity; 38 return item; 39 } 40 }
1 public class CircleQueue { 2 private String[] items; 3 private int capacity; 4 private int head = 0; 5 private int tail = 0; 6 7 public CircleQueue(int n) { 8 this.items = new String[n]; 9 this.capacity = n; 10 } 11 12 /** 13 * 入队列(从队列尾部入) 14 * @param item 15 * @return 16 */ 17 public boolean enqueue(String item) { 18 //队列满了 19 if (this.head == (this.tail + 1)% this.capacity) { 20 return false; 21 } 22 items[tail++] = item; 23 return true; 24 } 25 26 /** 27 * 出队列(从队列头部出) 28 * @return 29 */ 30 public String dequeue() { 31 //队列为空 32 if (this.head == this.tail) { 33 return null; 34 } 35 36 return this.items[head++]; 37 } 3
链表实现循环队列:
为空的判定条件:
head = tail
队列满了的判定条件:
head = tail.next

1 public class CircleLinkQueue { 2 private Node head = null; 3 private Node tail = null; 4 5 public CircleLinkQueue(int n) { 6 Node tempNode = null; 7 // 初始化一个 n 大小的环形链表 8 while (n >= 0) { 9 Node node = new Node(String.valueOf(n)); 10 if (this.head == null) { 11 this.head = this.tail = node; 12 this.head.next = this.head; 13 tempNode = this.head; 14 } else { 15 tempNode.next = node; 16 tempNode = tempNode.next; 17 tempNode.next = this.head; 18 } 19 n--; 20 } 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * 入队列(从队列尾部入) 25 * 26 * @param item 27 * @return 28 */ 29 public boolean enqueue(String item) { 30 //队列满了 31 if (this.head == this.tail.next) { 32 return false; 33 } 34 this.tail.setValue(item); 35 this.tail = this.tail.next; 36 return true; 37 } 38 39 /** 40 * 出队列(从队列头部出) 41 * 42 * @return 43 */ 44 public String dequeue() { 45 //队列为空 46 if (this.head == this.tail) { 47 return null; 48 } 49 String item = this.head.getValue(); 50 this.head = this.head.next; 51 return item; 52 } 53 54 public Node peek() { 55 //空队列 56 if (this.head == this.tail) { 57 return null; 58 } 59 return this.head; 60 } 61 62 private class Node { 63 private String value; 64 private Node next; 65 66 public Node(String value) { 67 this.value = value; 68 } 69 70 public String getValue() { 71 return value; 72 } 73 public void setValue(String value) { 74 this.value = value; 75 } 76 } 77 }
阻塞队列
阻塞队列是指当头部没有元素的时候(对应队列为空),出队会阻塞直到有元素为止;或者队列满了,尾部不能再插入数据,直到有空闲位置了再插入。
并发队列
线程安全的队列叫并发队列。dequeue和enqueue加锁或者使用CAS实现高效的并发。
附录
后续
首先感谢@李勇888提供建议。然后抽空实现了一下,加一个size来表示循环队列里元素的数量,实现demo参考:ArrayCircleQueue

