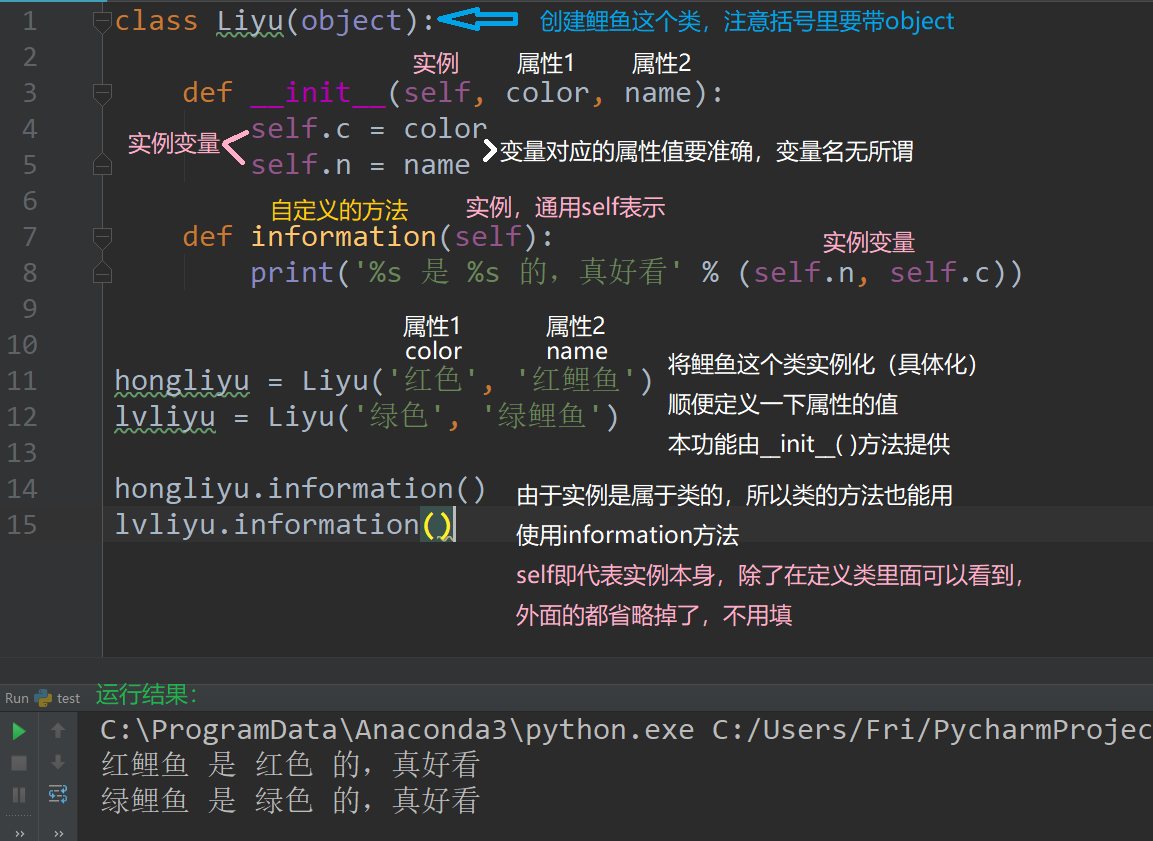
拓展:
更安全的用法,数据封装,通过在实例变量名前面加两个下横线__,使其无法被外部直接访问
测试:
class Student(object): def __init__(self, name, gender): self.name = name self.__gender = gender def get_gender(self): return self.__gender def set_gender(self, gender): self.__gender = gender return self.__gender bart = Student('Bart', 'male') if bart.get_gender() != 'male': print('测试失败!') else: bart.set_gender('female') if bart.get_gender() !='female': print('测试失败!') else: print('测试成功!')
继承:
在定义一个class的时候,可以从现有的class继承
子类会继承父类的全部方法
class Animal(object): #创建一个类叫Animal,注意类一般是首字母大写,其他小写 def run(self): #定义一个run方法 print('animal is running') def run_twice(a): #定义一个函数 a.run() #直接运行是会报错的 a.run() #只有Animal的实例才具有.run方法(其他具有run()方法的对象也可以使用这个函数,a便是"鸭子类型") a = Animal() #创建一个实例 run_twice(a) class Animal2(Animal): pass #子类继承父类的所有方法 class Dog(Animal): #建立一个Dog子类 def run(self): print('dog is running') #同样的方法名会替换掉父类里的 class Cat(Animal): #Cat子类 def run(self): print('cat is running') b = Dog() c = Cat() d = Animal2() run_twice(b) run_twice(c) run_twice(d)
结果:
animal is running animal is running dog is running dog is running cat is running cat is running animal is running animal is running
好处,新增一个子类,任何依赖Animal父类作为参数的函数或方法,都可以不加修改的正常运行。原因就在于多态
只要确保run()方法编写正确即可,不用管调用的细节——开闭原则
定义class的时候,同时定义了一种数据类型,like: str, list, dict 等,可通过 isinstance判断
class Animail(object): pass class Dog(Animail): pass class Puppy(Dog): pass class Cat(Animail): pass a = Animail() b = Dog() c = Puppy() d = Cat() print(isinstance(a,Animail)) print(isinstance(a,Dog)) print(isinstance(b,Animail)) print(isinstance(c,Dog)) print(isinstance(c,Animail)) print(isinstance(c,Cat)) print(isinstance(d,Dog))
结果:
True
False
True
True
True
False
False
子类的数据类型可以是父类,但父类的数据类型不能是子类
同级的子类数据类型不同
类属性
实例属性属于各个实例所有,互不干扰;
类属性属于类所有,所有实例共享一个属性;
不要对实例属性和类属性使用相同的名字,否则将产生难以发现的错误。