从提交来一步一步分析,本文源码基于Apache社区 1.8-release 版本
REST提交作业流程:
1.集群启动后 通过 /jars/upload 向集群提交可执行jar文件
2.通过 /jars/:jarid/run 来启动一个job
1.构建并提交JobGraph
我们直接找到WebSubmissionExtension这个类,在StandaloneSession 集群模式下集群初始化DispatcherRestEndpoint的时候会从WebSubmissionExtension里加载所有的Handlers(webSubmissionHandlers)
在WebSubmissionExtension中可以找到 /jars/:jarid/run 对应的Headers是JarRunHeaders,而接受http请求的是jarRunHandler。
Flink的rest服务是基于netty实现的,在jarRunHandler接受http请求后会调用handleRequest()方法来处理请求。
在handleRequest()方法的第一行如下,会从request中构造一个JarHandlerContext对象,而jobId就是JarHandlerContext对象的一个属性。在之后的getJobGraphAsync()传入的第一个参数就是context
在getJobGraphAsync()方法中调用context的toJobGraph()方法获取jobGraph
protected CompletableFuture<JarRunResponseBody> handleRequest(
@Nonnull final HandlerRequest<JarRunRequestBody, JarRunMessageParameters> request,
@Nonnull final DispatcherGateway gateway) throws RestHandlerException {
final JarHandlerContext context = JarHandlerContext.fromRequest(request, jarDir, log);
...
final CompletableFuture<JobGraph> jobGraphFuture = getJobGraphAsync(context, savepointRestoreSettings, jobName, streamGraphPlan, userLibJars);
...
}
private CompletableFuture<JobGraph> getJobGraphAsync(
JarHandlerContext context,
final SavepointRestoreSettings savepointRestoreSettings,
final String jobName,
final String plan,
final List<URL> userLibJars) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
final JobGraph jobGraph = context.toJobGraph(configuration, jobName, plan, userLibJars);
jobGraph.setSavepointRestoreSettings(savepointRestoreSettings);
return jobGraph;
}, executor);
}
内部版本当前判断streamGraphPlan是否存在来执行不同的createJobGraph方法,区别在于是否传入jobId。
社区版调用PackagedProgramUtils的createJobGraph()方法的时候会把JarHandlerContext的jobId属性传过去,随后通过steamPlan(streamGraph)的getJobGraph()方法把jobId传进去,之后调用StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph()方法传入this(streamGraph)和jobId,在new jobGraph时传入jobId和jobName。
JobGraph的构造方法判断jobId和jobName是否为空,如果为空新生成一个jobId实例,jobName则使用默认值"(unnamed job)"
JobGraph的构造方法:
public JobGraph(JobID jobId, String jobName) {
this.jobID = jobId == null ? new JobID() : jobId;
this.jobName = jobName == null ? "(unnamed job)" : jobName;
try {
setExecutionConfig(new ExecutionConfig());
} catch (IOException e) {
// this should never happen, since an empty execution config is always serializable
throw new RuntimeException("bug, empty execution config is not serializable");
}
}
在拿到jobGraph后进行一些后续处理然后向集群提交job
CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> jobSubmissionFuture = jarUploadFuture.thenCompose(jobGraph -> {
// we have to enable queued scheduling because slots will be allocated lazily
jobGraph.setAllowQueuedScheduling(true);
return gateway.submitJob(jobGraph, timeout);
});
集群在接受jobGraph后,有如下的代码:
private CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> internalSubmitJob(JobGraph jobGraph) {
log.info("Submitting job {} ({}).", jobGraph.getJobID(), jobGraph.getName());
final CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> persistAndRunFuture = waitForTerminatingJobManager(jobGraph.getJobID(), jobGraph, this::persistAndRunJob)
.thenApply(ignored -> Acknowledge.get());
return persistAndRunFuture.handleAsync((acknowledge, throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
cleanUpJobData(jobGraph.getJobID(), true);
final Throwable strippedThrowable = ExceptionUtils.stripCompletionException(throwable);
log.error("Failed to submit job {}.", jobGraph.getJobID(), strippedThrowable);
throw new CompletionException(
new JobSubmissionException(jobGraph.getJobID(), "Failed to submit job.", strippedThrowable));
} else {
return acknowledge;
}
}, getRpcService().getExecutor());
}
在internalSubmitJob()方法中调用waitForTerminatingJobManager()第一个参数就是jobId,随后在异步执行完成后判断时候有异常,在没有异常即提交成功的情况下,调用cleanUpJobData()清理client在提交过程中的数据,清理的标识也是jobId
接着看waitForTerminatingJobManager()方法
private CompletableFuture<Void> waitForTerminatingJobManager(JobID jobId, JobGraph jobGraph, FunctionWithException<JobGraph, CompletableFuture<Void>, ?> action) {
final CompletableFuture<Void> jobManagerTerminationFuture = getJobTerminationFuture(jobId)
.exceptionally((Throwable throwable) -> {
throw new CompletionException(
new DispatcherException(
String.format("Termination of previous JobManager for job %s failed. Cannot submit job under the same job id.", jobId),
throwable)); });
return jobManagerTerminationFuture.thenComposeAsync(
FunctionUtils.uncheckedFunction((ignored) -> {
jobManagerTerminationFutures.remove(jobId);
return action.apply(jobGraph);
}),
getMainThreadExecutor());
}
CompletableFuture<Void> getJobTerminationFuture(JobID jobId) {
if (jobManagerRunnerFutures.containsKey(jobId)) {
return FutureUtils.completedExceptionally(new DispatcherException(String.format("Job with job id %s is still running.", jobId)));
} else {
return jobManagerTerminationFutures.getOrDefault(jobId, CompletableFuture.completedFuture(null));
}
}
其中getJobTerminationFuture()来判断当前的jobId对应的job是否已在运行中,看方法名是在wait任务终止,实际在getJobTerminationFuture(),方法中并没有终止任务的操作,只是判断jobManagerRunnerFutures这个map中是否存在当前jobId。
private final Map<JobID, CompletableFuture<JobManagerRunner>> jobManagerRunnerFutures;
jobManagerRunnerFutures看定义就可以了解,是持有运行中job的以jobId为key,CompletableFuture<JobManagerRunner>为value的映射关系。
继续回到internalSubmitJob()方法,在waitForTerminatingJobManager()用::(jdk1.8特性)传入了方法persistAndRunJob(),在该方法中先把jobGraph包装成SubmittedJobGraph写到zk中,然后调用runJob()方法,runJob()方法会先根据jobId判断当前job是否已经提交,然后创建一个jobManagerRunner,接着把CompletableFuture<JobManagerRunner>放到名为jobManagerRunnerFutures的Map里,其中key就是jobId。
private CompletableFuture<Void> persistAndRunJob(JobGraph jobGraph) throws Exception {
//包装jobGraph 写入zk
submittedJobGraphStore.putJobGraph(new SubmittedJobGraph(jobGraph));
final CompletableFuture<Void> runJobFuture = runJob(jobGraph);
return runJobFuture.whenComplete(BiConsumerWithException.unchecked((Object ignored, Throwable throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
submittedJobGraphStore.removeJobGraph(jobGraph.getJobID());
}
}));
}
private CompletableFuture<Void> runJob(JobGraph jobGraph) {
//判断当前job是否已经提交
Preconditions.checkState(!jobManagerRunnerFutures.containsKey(jobGraph.getJobID()));
final CompletableFuture<JobManagerRunner> jobManagerRunnerFuture = createJobManagerRunner(jobGraph);
jobManagerRunnerFutures.put(jobGraph.getJobID(), jobManagerRunnerFuture);
return jobManagerRunnerFuture
.thenApply(FunctionUtils.nullFn())
.whenCompleteAsync(
(ignored, throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
jobManagerRunnerFutures.remove(jobGraph.getJobID());
}
},
getMainThreadExecutor());
}
继续看createJobManagerRunner()方法,先异步的创建jobManagerRunner,然后执行startJobManagerRunner()方法,在确认jobManagerRunner后,执行start方法启动jobManagerRunner。
在jobManagerRunner的start方法中,启动zk选举服务,让自身(this)参与选举获得执行权,在zk确认后会回调grantLeadership()方法,jobManagerRunner实现了LeaderContender接口。
public void start() throws Exception {
try {
leaderElectionService.start(this);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Could not start the JobManager because the leader election service did not start.", e);
throw new Exception("Could not start the leader election service.", e);
}
}
@Override
public void grantLeadership(final UUID leaderSessionID) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (shutdown) {
log.info("JobManagerRunner already shutdown.");
return;
}
leadershipOperation = leadershipOperation.thenCompose(
(ignored) -> {
synchronized (lock) {
return verifyJobSchedulingStatusAndStartJobManager(leaderSessionID);
}
});
handleException(leadershipOperation, "Could not start the job manager.");
}
}
获得执行权限后调用verifyJobSchedulingStatusAndStartJobManager()方法,先判断job状态,如果是DONE(finished),则已经finished,否则执行startJobMaster(),在startJobMaster()方法中先把job状态设为running,
把job和对应的状态写到zk。
如果需要实时的获取job状态可以用zk watch这个路径
private CompletableFuture<Void> verifyJobSchedulingStatusAndStartJobManager(UUID leaderSessionId) {
final CompletableFuture<JobSchedulingStatus> jobSchedulingStatusFuture = getJobSchedulingStatus();
return jobSchedulingStatusFuture.thenCompose(
jobSchedulingStatus -> {
if (jobSchedulingStatus == JobSchedulingStatus.DONE) {
return jobAlreadyDone();
} else {
return startJobMaster(leaderSessionId);
}
});
}
private CompletionStage<Void> startJobMaster(UUID leaderSessionId) {
log.info("JobManager runner for job {} ({}) was granted leadership with session id {} at {}.",
jobGraph.getName(), jobGraph.getJobID(), leaderSessionId, getAddress());
try {
runningJobsRegistry.setJobRunning(jobGraph.getJobID());
} catch (IOException e) {
return FutureUtils.completedExceptionally(
new FlinkException(
String.format("Failed to set the job %s to running in the running jobs registry.", jobGraph.getJobID()),
e));
}
final CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> startFuture;
try {
startFuture = jobMasterService.start(new JobMasterId(leaderSessionId));
} catch (Exception e) {
return FutureUtils.completedExceptionally(new FlinkException("Failed to start the JobMaster.", e));
}
final CompletableFuture<JobMasterGateway> currentLeaderGatewayFuture = leaderGatewayFuture;
return startFuture.thenAcceptAsync(
(Acknowledge ack) -> confirmLeaderSessionIdIfStillLeader(leaderSessionId, currentLeaderGatewayFuture),
executor);
}
然后执行jobMasterService.start(),在jobMaster中 start()方法启动RPC服务,然后startJobExecution来调度作业。
public CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> start(final JobMasterId newJobMasterId) throws Exception {
// make sure we receive RPC and async calls
start();
return callAsyncWithoutFencing(() -> startJobExecution(newJobMasterId), RpcUtils.INF_TIMEOUT);
}
startJobExecution()方法如下:
private Acknowledge startJobExecution(JobMasterId newJobMasterId) throws Exception {
validateRunsInMainThread();
checkNotNull(newJobMasterId, "The new JobMasterId must not be null.");
if (Objects.equals(getFencingToken(), newJobMasterId)) {
log.info("Already started the job execution with JobMasterId {}.", newJobMasterId);
return Acknowledge.get();
}
setNewFencingToken(newJobMasterId);
startJobMasterServices();
log.info("Starting execution of job {} ({}) under job master id {}.", jobGraph.getName(), jobGraph.getJobID(), newJobMasterId);
resetAndScheduleExecutionGraph();
return Acknowledge.get();
}
其中validateRunsInMainThread()使用断言来确认调用是否发生在RPC endpoint 的主线程中,正常不会执行。然后判断jobMasterId,并且确认当前jobMaster没有调度过其他的job。接着到startJobMasterServices()方法,这个方法的主要作用是在调度作业之前启动jobMaster相关的组件:
- 启动心跳服务
- 启动taskManager的slotPool RPC服务,确保接受当前jobMaster的调用和分配请求
- 启动schedule
- 连接到resourceManager
在这些步骤执行完成之后,执行resetAndScheduleExecutionGraph()来开始调度executionGraph。
private void resetAndScheduleExecutionGraph() throws Exception {
validateRunsInMainThread();
final CompletableFuture<Void> executionGraphAssignedFuture;
if (executionGraph.getState() == JobStatus.CREATED) {
executionGraphAssignedFuture = CompletableFuture.completedFuture(null);
executionGraph.start(getMainThreadExecutor());
} else {
suspendAndClearExecutionGraphFields(new FlinkException("ExecutionGraph is being reset in order to be rescheduled."));
final JobManagerJobMetricGroup newJobManagerJobMetricGroup = jobMetricGroupFactory.create(jobGraph);
final ExecutionGraph newExecutionGraph = createAndRestoreExecutionGraph(newJobManagerJobMetricGroup);
executionGraphAssignedFuture = executionGraph.getTerminationFuture().handle(
(JobStatus ignored, Throwable throwable) -> {
newExecutionGraph.start(getMainThreadExecutor());
assignExecutionGraph(newExecutionGraph, newJobManagerJobMetricGroup);
return null;
});
}
executionGraphAssignedFuture.thenRun(this::scheduleExecutionGraph);
}
首先判断executionGraph的状态是否为create,如果不为create会根据jobGraph创建新的executionGraph来代替当前的executionGraph,然后执行scheduleExecutionGraph(),
private void scheduleExecutionGraph() {
checkState(jobStatusListener == null);
// register self as job status change listener
jobStatusListener = new JobManagerJobStatusListener();
executionGraph.registerJobStatusListener(jobStatusListener);
try {
executionGraph.scheduleForExecution();
}
catch (Throwable t) {
executionGraph.failGlobal(t);
}
}
注册想executionGraph作业状态变更监听器,执行executionGraph.scheduleForExecution(),先更新状态从created到running,然后判断调度模式,目前有两种调度模式:
- LAZY_FROM_SOURCES
- EAGER
Eager 调度如其名子所示,它会在作业启动时申请资源将所有的 Task 调度起来。这种调度算法主要用来调度可能没有终止的流作业。与之对应,Lazy From Source 则是从 Source 开始,按拓扑顺序来进行调度。简单来说,Lazy From Source 会先调度没有上游任务的 Source 任务,当这些任务执行完成时,它会将输出数据缓存到内存或者写入到磁盘中。然后,对于后续的任务,当它的前驱任务全部执行完成后,Flink 就会将这些任务调度起来。这些任务会从读取上游缓存的输出数据进行自己的计算。这一过程继续进行直到所有的任务完成计算。

我们占时可以先不考虑批程序,从流程序scheduleEager()继续往下看,scheduleEager()方法有点长,我们先把这个方法贴出来一步一步来看。
private CompletableFuture<Void> scheduleEager(SlotProvider slotProvider, final Time timeout) {
assertRunningInJobMasterMainThread();
checkState(state == JobStatus.RUNNING, "job is not running currently");
// Important: reserve all the space we need up front.
// that way we do not have any operation that can fail between allocating the slots
// and adding them to the list. If we had a failure in between there, that would
// cause the slots to get lost
final boolean queued = allowQueuedScheduling;
// collecting all the slots may resize and fail in that operation without slots getting lost
final ArrayList<CompletableFuture<Execution>> allAllocationFutures = new ArrayList<>(getNumberOfExecutionJobVertices());
final Set<AllocationID> allPreviousAllocationIds =
Collections.unmodifiableSet(computeAllPriorAllocationIdsIfRequiredByScheduling());
// allocate the slots (obtain all their futures
for (ExecutionJobVertex ejv : getVerticesTopologically()) {
// these calls are not blocking, they only return futures
Collection<CompletableFuture<Execution>> allocationFutures = ejv.allocateResourcesForAll(
slotProvider,
queued,
LocationPreferenceConstraint.ALL,
allPreviousAllocationIds,
timeout);
allAllocationFutures.addAll(allocationFutures);
}
// this future is complete once all slot futures are complete.
// the future fails once one slot future fails.
final ConjunctFuture<Collection<Execution>> allAllocationsFuture = FutureUtils.combineAll(allAllocationFutures);
return allAllocationsFuture.thenAccept(
(Collection<Execution> executionsToDeploy) -> {
for (Execution execution : executionsToDeploy) {
try {
execution.deploy();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new CompletionException(
new FlinkException(
String.format("Could not deploy execution %s.", execution),
t));
}
}
})
// Generate a more specific failure message for the eager scheduling
.exceptionally(
(Throwable throwable) -> {
final Throwable strippedThrowable = ExceptionUtils.stripCompletionException(throwable);
final Throwable resultThrowable;
if (strippedThrowable instanceof TimeoutException) {
int numTotal = allAllocationsFuture.getNumFuturesTotal();
int numComplete = allAllocationsFuture.getNumFuturesCompleted();
String message = "Could not allocate all requires slots within timeout of " +
timeout + ". Slots required: " + numTotal + ", slots allocated: " + numComplete +
", previous allocation IDs: " + allPreviousAllocationIds;
StringBuilder executionMessageBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < allAllocationFutures.size(); i++) {
CompletableFuture<Execution> executionFuture = allAllocationFutures.get(i);
try {
Execution execution = executionFuture.getNow(null);
if (execution != null) {
executionMessageBuilder.append("completed: " + execution);
} else {
executionMessageBuilder.append("incomplete: " + executionFuture);
}
} catch (CompletionException completionException) {
executionMessageBuilder.append("completed exceptionally: " + completionException + "/" + executionFuture);
}
if (i < allAllocationFutures.size() - 1) {
executionMessageBuilder.append(", ");
}
}
message += ", execution status: " + executionMessageBuilder.toString();
resultThrowable = new NoResourceAvailableException(message);
} else {
resultThrowable = strippedThrowable;
}
throw new CompletionException(resultThrowable);
});
}
首先后验证当前job的状态,确认当前的job state确实为running,否者抛出异常,job状态先设置为running然后才开始调度的。接着从ExecutionJobVertex(以后简称ejv)开始遍历分配slot,在ejv的allocateResourcesForAll()方法中其实又把ejv的ExecutionVertex(简称ev)遍历一遍,然后取ev对应的Execution然后调用Execution的allocateAndAssignSlotForExecution()方法分配slot,具体分配算法之后单独介绍。
在分配完slot之后,调用execution.deploy()方法来启动部署。
streamGraph,jobGraph,executionGraph,ExecutionJobVertex,ExecutionVertex,Execution 的关系可以参考下图:
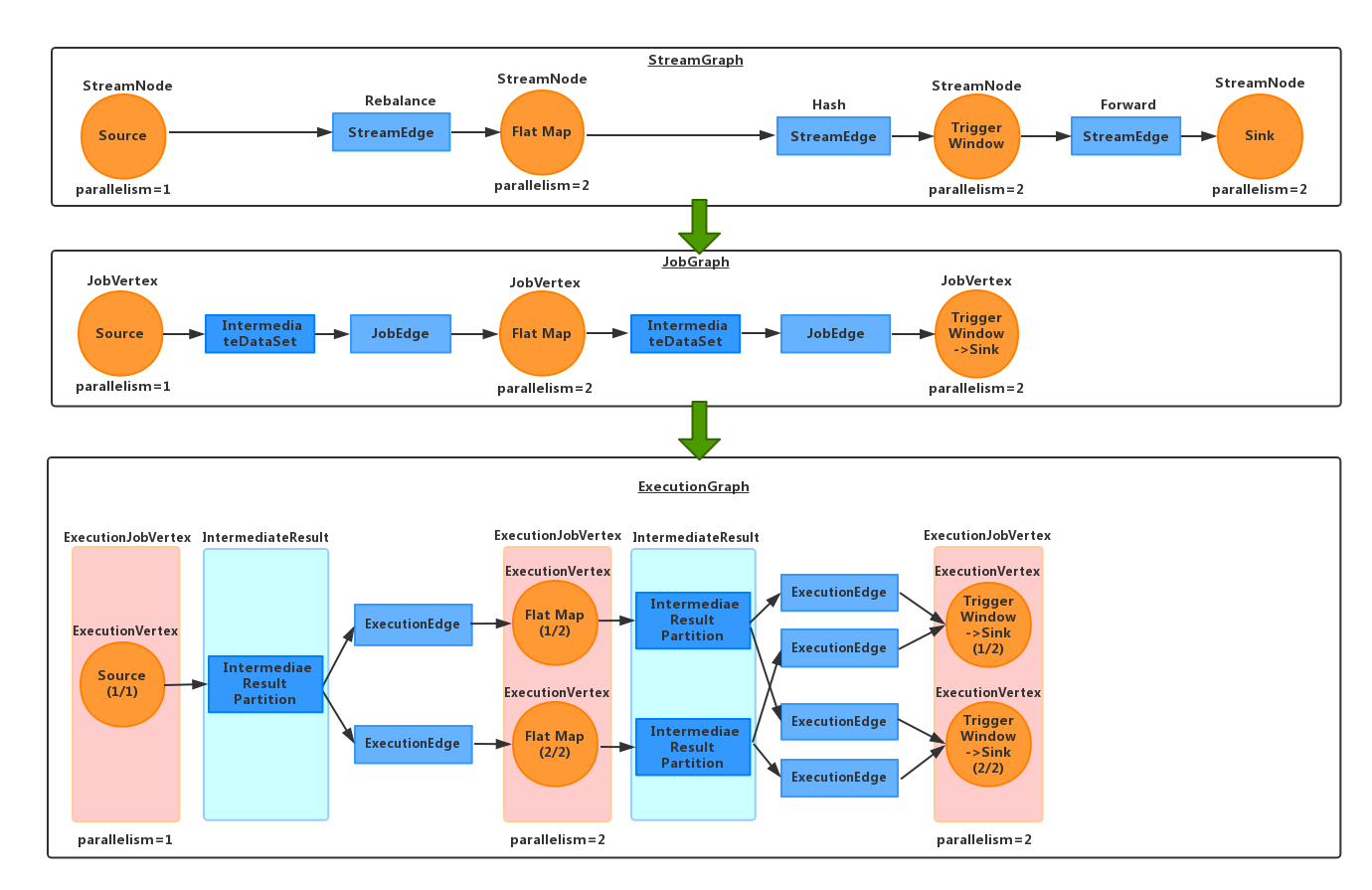
解析