这是用Python实现的Neural Networks, 基于Python 2.7.9, numpy, matplotlib。
代码来源于斯坦福大学的课程: http://cs231n.github.io/neural-networks-case-study/
基本是照搬过来,通过这个程序有助于了解python语法,以及Neural Networks 的原理。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
N = 200 # number of points per class
D = 2 # dimensionality
K = 3 # number of classes
X = np.zeros((N*K,D)) # data matrix (each row = single example)
y = np.zeros(N*K, dtype='uint8') # class labels
for j in xrange(K):
ix = range(N*j,N*(j+1))
r = np.linspace(0.0,1,N) # radius
t = np.linspace(j*4,(j+1)*4,N) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # theta
X[ix] = np.c_[r*np.sin(t), r*np.cos(t)]
y[ix] = j
# print y
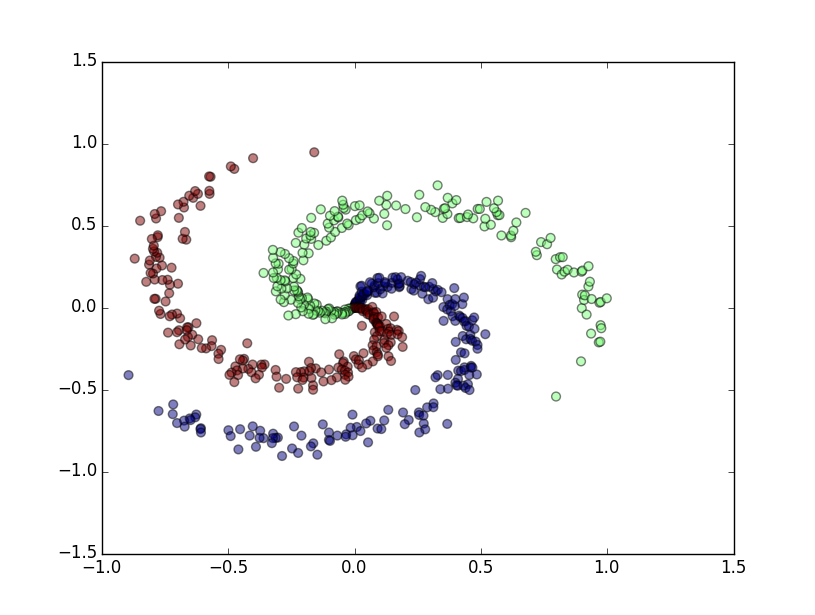
# lets visualize the data:
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], s=40, c=y, alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
# Train a Linear Classifier
# initialize parameters randomly
h = 20 # size of hidden layer
W = 0.01 * np.random.randn(D,h)
b = np.zeros((1,h))
W2 = 0.01 * np.random.randn(h,K)
b2 = np.zeros((1,K))
# define some hyperparameters
step_size = 1e-0
reg = 1e-3 # regularization strength
# gradient descent loop
num_examples = X.shape[0]
for i in xrange(1):
# evaluate class scores, [N x K]
hidden_layer = np.maximum(0, np.dot(X, W) + b) # note, ReLU activation
# print np.size(hidden_layer,1)
scores = np.dot(hidden_layer, W2) + b2
# compute the class probabilities
exp_scores = np.exp(scores)
probs = exp_scores / np.sum(exp_scores, axis=1, keepdims=True) # [N x K]
# compute the loss: average cross-entropy loss and regularization
corect_logprobs = -np.log(probs[range(num_examples),y])
data_loss = np.sum(corect_logprobs)/num_examples
reg_loss = 0.5*reg*np.sum(W*W) + 0.5*reg*np.sum(W2*W2)
loss = data_loss + reg_loss
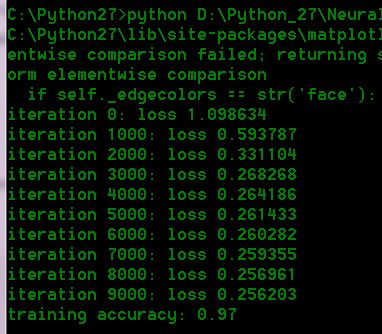
if i % 1000 == 0:
print "iteration %d: loss %f" % (i, loss)
# compute the gradient on scores
dscores = probs
dscores[range(num_examples),y] -= 1
dscores /= num_examples
# backpropate the gradient to the parameters
# first backprop into parameters W2 and b2
dW2 = np.dot(hidden_layer.T, dscores)
db2 = np.sum(dscores, axis=0, keepdims=True)
# next backprop into hidden layer
dhidden = np.dot(dscores, W2.T)
# backprop the ReLU non-linearity
dhidden[hidden_layer <= 0] = 0
# finally into W,b
dW = np.dot(X.T, dhidden)
db = np.sum(dhidden, axis=0, keepdims=True)
# add regularization gradient contribution
dW2 += reg * W2
dW += reg * W
# perform a parameter update
W += -step_size * dW
b += -step_size * db
W2 += -step_size * dW2
b2 += -step_size * db2
# evaluate training set accuracy
hidden_layer = np.maximum(0, np.dot(X, W) + b)
scores = np.dot(hidden_layer, W2) + b2
predicted_class = np.argmax(scores, axis=1)
print 'training accuracy: %.2f' % (np.mean(predicted_class == y))
随机生成的数据
运行结果