什么是遍历?
jQuery 遍历,意为"移动",用于根据其相对于其他元素的关系来"查找"(或选取)HTML 元素。以某项选择开始,并沿着这个选择移动 下图展示了一个家族树。通过 jQuery 遍历,能够从被选(当前的)元素开始,轻松地在家族树中向上移动(祖先),向下移动(子孙),水平移动(同胞)。这种移动被称为对 DOM 进行遍历。
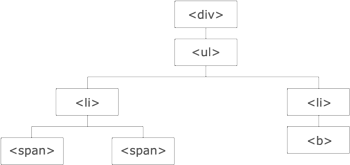
图示解析:
- <div> 元素是 <ul> 的父元素,同时是其中所有内容的祖先。
- <ul> 元素是 <li> 元素的父元素,同时是 <div> 的子元素
- 左边的 <li> 元素是 <span> 的父元素,<ul> 的子元素,同时是 <div> 的后代。
- <span> 元素是 <li> 的子元素,同时是 <ul> 和 <div> 的后代。
- 两个 <li> 元素是同胞(拥有相同的父元素)。
- 右边的 <li> 元素是 <b> 的父元素,<ul> 的子元素,同时是 <div> 的后代。
<b> 元素是右边的 <li> 的子元素,同时是 <ul> 和 <div> 的后代。
- 祖先是父、祖父、曾祖父等等。后代是子、孙、曾孙等等。同胞拥有相同的父。
遍历 DOM
jQuery 提供了多种遍历 DOM 的方法。
遍历方法中最大的种类是树遍历(tree-traversal)。
jQuery parent() 方法
parent() 方法返回被选元素的直接父元素。
该方法只会向上一级对 DOM 树进行遍历。
$(document).ready(function(){
$("span").parent();
});
parents() 方法返回被选元素的所有祖先元素,它一路向上直到文档的根元素 (<html>)。
$(document).ready(function(){
$("span").parents();
});
parentsUntil() 方法返回介于两个给定元素之间的所有祖先元素。
向下遍历 DOM 树
下面是两个用于向下遍历 DOM 树的 jQuery 方法:
- children()
- find()
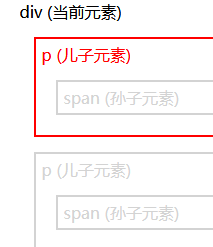
jQuery children() 方法
children() 方法返回被选元素的所有直接子元素。
该方法只会向下一级对 DOM 树进行遍历。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.descendants *
{
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").children().css({"color":"red","border":"2px solid red"});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="descendants" style="500px;">div (当前元素)
<p>p (儿子元素)
<span>span (孙子元素)</span>
</p>
<p>p (儿子元素)
<span>span (孙子元素)</span>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>

可以使用可选参数来过滤对子元素的搜索。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.descendants *
{
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").children("p.1").css({"color":"red","border":"2px solid red"});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="descendants" style="500px;">div (当前元素)
<p class="1">p (儿子元素)
<span>span (孙子元素)</span>
</p>
<p class="2">p (儿子元素)
<span>span (孙子元素)</span>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
jQuery find() 方法
find() 方法返回被选元素的后代元素,一路向下直到最后一个后代。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.descendants *
{
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div").find("span").css({"color":"red","border":"2px solid red"});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="descendants" style="500px;">div (当前元素)
<p>p (儿子元素)
<span>span (孙子元素)</span>
</p>
<p>p (儿子元素)
<span>span (孙子元素)</span>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>

在 DOM 树中水平遍历
有许多有用的方法让我们在 DOM 树进行水平遍历:
- siblings()
- next()
- nextAll()
- nextUntil()
- prev()
- prevAll()
- prevUntil()
siblings() 方法返回被选元素的所有同胞元素。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.siblings *
{
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("h2").siblings().css({"color":"red","border":"2px solid red"});
});
</script>
</head>
<body class="siblings">
<div>div (父元素)
<p>p</p>
<span>span</span>
<h2>h2</h2>
<h3>h3</h3>
<p>p</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
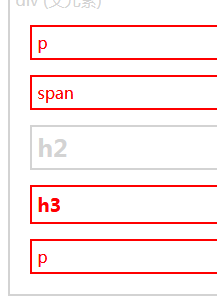
jQuery next() 方法
next() 方法返回被选元素的下一个同胞元素。
该方法只返回一个元素。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.siblings *
{
display: block;
border: 2px solid lightgrey;
color: lightgrey;
padding: 5px;
margin: 15px;
}
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("h2").next().css({"color":"red","border":"2px solid red"});
});
</script>
</head>
<body class="siblings">
<div>div (父元素)
<p>p</p>
<span>span</span>
<h2>h2</h2>
<h3>h3</h3>
<p>p</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>

jQuery nextAll() 方法
nextAll() 方法返回被选元素的所有跟随的同胞元素。
jQuery nextUntil() 方法
nextUntil() 方法返回介于两个给定参数之间的所有跟随的同胞元素。
jQuery first() 方法
first() 方法返回被选元素的首个元素。
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div p").first();
});
jQuery last() 方法
last() 方法返回被选元素的最后一个元素。
$(document).ready(function(){
$("div p").last();
});
jQuery eq() 方法
eq() 方法返回被选元素中带有指定索引号的元素。
索引号从 0 开始,因此首个元素的索引号是 0 而不是 1。下面的例子选取第二个 <p> 元素(索引号 1):
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").eq(1);
});
jQuery filter() 方法
filter() 方法允许您规定一个标准。不匹配这个标准的元素会被从集合中删除,匹配的元素会被返回。
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").filter(".url");
});
jQuery not() 方法
not() 方法返回不匹配标准的所有元素。
$(document).ready(function(){
$("p").not(".url");
});