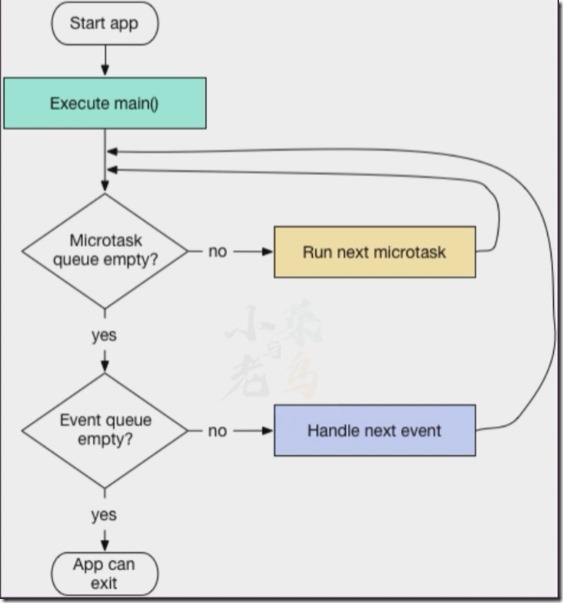
参考
https://dart.cn/guides/language/language-tour#asynchrony-support
https://dart.cn/guides/libraries/library-tour#dartasync---asynchronous-programming
https://dart.cn/codelabs/async-await
异步编程
在dart中是没有线程的概念的,取而代之的是异步编程。
可以使用两种方式创建异步函数:
- 通过async和await关键字
- 通过Future api来链式创建
async和await的操作和Future是分不开的,只是async和await更简化了逻辑,看起来像是同步代码一样。
在直接使用 Future API 前,首先应该考虑 await 来替代。代码中使用 await 表达式会比直接使用 Future API 更容易理解。
async和await
声明一个异步函数,在方法名后边添加上关键字async即可,同时返回值要修改成用Future<T>,T是函数体要返回的值,如下例:
Future<void> main() async { var future = getName(); future.then((value) => print('getName:$value')); print("after get name"); } Future<String> getName() async { print("getName start"); return "wz"; }
输出结果是:
getName start
after get name
getName:wz
上边的代码其实并不会异步执行,因为异步执行是在遇到第一await时会挂起函数,并直接返回Future<T>,同时函数会等待await指定的操作完成后才继续方法后边的代码。
修改一下上边的getName的代码:
Future<String> getName() async { print("getName start"); await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2)); print("after delay"); return "wz"; }
输出结果是:
getName start
after get name
after delay
getName:wz
await使用说明:
- await只能用在async中。
- await后可以跟普通函数(但没有意义的),也可以跟异步函数(返回值是Future<T>的函数)。
- await等待的操作结果是可以赋值给一个变量的,此时会把后边的Future<T>的T取出来,这样我们就可以用同步的方式编写异步调用,
var entrypoint = await findEntrypoint(); var exitCode = await runExecutable(entrypoint, args); await flushThenExit(exitCode);
处理异常
使用 try、catch 以及 finally 来处理使用 await 导致的异常:
try { version = await lookUpVersion(); 。。。 } catch (e) { // 无法找到版本时做出的反应 }
如果有异常发生的话,lookUpVersion下边的代码就不会执行了,会直接跳到catch中。
Future
https://api.dart.cn/stable/2.10.4/dart-async/Future-class.html
从 Dart 2.1 开始,使用 Future 和 Stream 不需要导入 dart:async ,因为 dart:core 库 export 了这些类。
上边通过async和await返回了一个Future对象,可以通过此对象注册一些监听,比如执行完后再去执行其他,异常处理等。
Future<int> future = getFuture(); future.then((value) => handleValue(value)) .catchError((error) => handleError(error));
FutureOr<T>
先说一下这个类,因为Future中有很多方法都有此类,
此类表示的是一个值,这个值可以是Future<T>或T。
此类声明是内部future或value泛型类型的公共代理。对此类的引用被解析为内部类型。
任何类extend、mixin或implement 此类都是一个编译时错误。
Future的构造函数
- Future(FutureOr<T> computation())
创建一个Future,其中包含Timer.run异步调用computation()的结果。
- Future.delayed(Duration duration, [FutureOr<T> computation()])
创建一个Future,会在指定的延时后执行computation()
- Future.microtask(FutureOr<T> computation())
其中包含scheduleMicrotask异步调用computation()的结果。
microtask是比普通的事件(比如Timer事件)更先执行的一种任务。
- Future.sync(FutureOr<T> computation())
包含立即调用computation()的结果。
If calling computation throws, the returned future is completed with the error.
If calling computation returns a Future<T>, that future is returned.
If calling computation returns a non-future value, a future is returned which has been completed with that value.
- Future.error(Object error, [StackTrace? stackTrace])
创建一个Future,此Future有一个error的结果。
- Future.value([FutureOr<T>? value])
如果value是一个Future,那么会创建一个等待value的future执行完成的Future。
如果value是一个值,那么就相当于new Future<T>.sync(() => value)
Future的成员方法
- asStream() → Stream<T>
Creates a Stream containing the result of this future.
- catchError(Function onError, {bootest(Object error)}) → Future<T>
Handles errors emitted by this Future.
确保调用 catchError() 方式在 then() 的结果上,而不是在原来的 Future 对象上调用。否则的话,catchError() 就只能处理原来 Future 对象抛出的异常,而无法处理 then() 代码里面的异常。
- then<R>(FutureOr<R> onValue(T value), {Function? onError}) → Future<R>
Register callbacks to be called when this future completes.
- timeout(Duration timeLimit, {FutureOr<T> onTimeout()}) → Future<T>
Time-out the future computation after timeLimit has passed.
- whenComplete(FutureOr<void> action()) → Future<T>
Registers a function to be called when this future completes.
Future的static方法
- any<T>(Iterable<Future<T>> futures) → Future<T>
Returns the result of the first future in futures to complete.
- doWhile(FutureOr<bool> action()) → Future
Performs an operation repeatedly untiit returns false.
- forEach<T>(Iterable<T> elements, FutureOr action(T element)) → Future
Performs an action for each element of the iterable, in turn.
- wait<T>(Iterable<Future<T>> futures, {booeagerError: false, void cleanUp(T successValue)}) → Future<List<T>>
Waits for multiple futures to complete and collects their results.
Stream
在 Dart API 中 Stream 对象随处可见,Stream 用来表示一系列数据。例如,HTM中的按钮点击就是通过 stream 传递的。同样也可以将文件作为数据流来读取。
如果想从 Stream 中获取值,可以有两种选择:
- 使用 async 关键字和一个 异步循环(使用 await for 关键字标识)。
- 使用 Stream API。详情参考库概览。
await for
使用 await for 定义异步循环看起来是这样的:
await for (varOrType identifier in expression) { // 每当 Stream 发出一个值时会执行 }
expression的类型必须是 Stream。执行流程如下:
1. 等待直到 Stream 返回一个数据。
2. 使用 1 中 Stream 返回的数据执行循环体。
3. 重复 1、2 过程直到 Stream close。
使用 break 和 return 语句可以停止接收 Stream 数据,这样就跳出了循环并取消注册监听 Stream。
Stream
https://api.dart.cn/stable/2.10.4/dart-async/Stream-class.html
Stream提供了一种接收事件序列的方法。每个事件要么是一个数据事件,也称为流的一个元素,要么是一个错误事件,它是一个失败的通知。
当Stream已发出其所有事件时,单个“done”事件将通知侦听器已到达结束。
你可以通过Stream.listen()来监听Stream的事件,它会返回一个StreamSubscription对象,你可以在此对象上添加一些监听,暂停恢复事件的监听,或cancel取消监听。
当“done”事件被触发时,订阅者在接收事件之前被取消订阅。事件发送后,Stream就没有订阅者了。允许在此时之后向广播Stream添加新订阅者,但他们将尽快接收到新的“done”事件。
有两种类型的Stream:
- 单订阅Stream,
是只能被listen一次,多次调用是不允许的,即使在取消第一个监听之后在调用也不允许。
并且此Stream是冷流,即只有当有监听者时才会开始产生事件,取消监听后Stream停止发送事件,即使事件源仍然可以提供更多。
单订阅流通常用于流式传输较大的连续数据块,如文件I/O。
- 广播Stream。
可以被多个监听者监听,
并且此Stream是热流,即只要有事件就发送,不管有没有监听者,
单订阅Stream也可以通过asBroadcastStream()来转换成广播Stream。
当注册监听者时,只能接收到注册之后发送的事件,而不能接收到之前已经发送过的。
Stream的Api
属性
- first → Future<T>
监听Stream,只要接收到第一个事件就立马取消监听。
- isBroadcast → bool
Whether this stream is a broadcast stream.
- last → Future<T>
The last element of this stream.
- length → Future<int>
The number of elements in this stream.
方法
- asBroadcastStream({void onListen(StreamSubscription<T> subscription), void onCancel(StreamSubscription<T> subscription)}) → Stream<T>
Returns a multi-subscription stream that produces the same events as this.
- drain<E>([E? futureValue]) → Future<E>
Discards aldata on this stream, but signals when it is done or an error occurred.
- handleError(Function onError, {bootest(dynamic error)}) → Stream<T>
Creates a wrapper Stream that intercepts some errors from this stream.
- listen(void onData(T event), {Function? onError, void onDone(), bool? cancelOnError}) → StreamSubscription<T>
Adds a subscription to this stream.
- skip(int count) → Stream<T>
Skips the first count data events from this stream.
StreamSubscription
- Future<void> cancel();
- void onData(void handleData(T data)?);
- void onError(Function? handleError);
- void onDone(void handleDone()?);
- void pause([Future<void>? resumeSignal]);
- void resume();
- Future<E> asFuture<E>([E? futureValue]);
- booget isPaused;
Generators
当你需要延迟地生成一连串的值时,可以考虑使用 生成器函数。
Dart 内置支持两种形式的生成器方法:
- 同步 生成器:返回一个 Iterable 对象。
- 异步 生成器:返回一个 Stream 对象。
通过在函数上加 sync* 关键字并将返回值类型设置为 Iterable 来实现一个 同步 生成器函数,在函数中使用 yield 语句来传递值:
Iterable<int> naturalsTo(int n) sync* { int k = 0; while (k < n) yield k++; }
实现 异步 生成器函数与同步类似,只不过关键字为 async* 并且返回值为 Stream:
Stream<int> asynchronousNaturalsTo(int n) async* { int k = 0; while (k < n) yield k++; }
如果生成器是递归调用的,可是使用 yield* 语句提升执行性能:
Iterable<int> naturalsDownFrom(int n) sync* { if (n > 0) { yield n; yield* naturalsDownFrom(n - 1); } }
Isolates
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411V7iP/?spm_id_from=333.788.videocard.0
大多数计算机中,甚至在移动平台上,都在使用多核 CPU。为了有效利用多核性能,开发者一般使用共享内存的方式让线程并发地运行。然而,多线程共享数据通常会导致很多潜在的问题,并导致代码运行出错。
为了解决多线程带来的并发问题,Dart 使用 isolates 替代线程。
- 每一个 isolate 有它自己的堆内存以确保其状态不被其它 isolates 访问。公共变量的值都是isolate 独有的,类似于java的ThreadLocal。
- 每一个 isolate都有自己的线程和一个eventloop事件循环系统。
- isolate之间想要沟通是通过ReceivePort, SendPort发送接收事件来解决的。都会发送到对方isolate的eventloop。
可以通过Isolate的spawn来创建一个isloate,
external static Future<Isolate> spawn<T>( void entryPoint(T message), T message, {bool paused = false, bool errorsAreFatal = true, SendPort? onExit, SendPort? onError, @Since("2.3") String? debugName});
- entryPoint:是新的isolate要运行的方法,或者初始化方法,它接收第二个参数类型的值。
- message:用来发送给新isolate的一个消息,通常会把当前isolate创建的SendPort包装在message内传递给新的isolate,那么新isolate就可以用SendPort去通知父isolate。
- debugName:是debug时的名字,一般Isolate.current.debugName来获取到当前Isolate的名字。
static属性
- external static Isolate get current;
Return an Isolate object representing the current isolate.
方法
kill({int priority: beforeNextEvent}) → void
Requests the isolate to shut down.
ReceivePort
- abstract class ReceivePort implements Stream<dynamic>
可以看到它实现了Stream,所以可以调用Stream.listen来监听SendPort发送过来的信息,
此Stream不是广播Stream,所以如果需要的话调用asBroadcastStream()来转换成广播Stream。
- close() → void
Closes this.
- SendPort get sendPort;
Returns a [SendPort] that sends to this receive port.
SendPort
- send(Object? message) → void
Sends an asynchronous message through this send port, to its corresponding ReceivePort.
例子
int age = 18; void main() { age++; print("Isolate:${Isolate.current.debugName},age:$age"); ReceivePort receivePort = ReceivePort(); receivePort.listen((message) { print("receive data:$message"); receivePort.close(); }); Isolate.spawn(initSubIsolate, Data(receivePort.sendPort, "from main", 1), debugName: "sub_isolate"); } void initSubIsolate(Data data) { print("Isolate:${Isolate.current.debugName},age:$age"); print("Isolate:${Isolate.current.debugName}:$data"); Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2), () { data.sendPort.send(Data(null, "fuck you", data.requestCode)); }); } class Data { final SendPort sendPort; final String msg; final int requestCode; Data(this.sendPort, this.msg, this.requestCode); @override String toString() { return 'Data{msg: $msg, requestCode: $requestCode}'; } }
输出:
Isolate:main,age:19 Isolate:sub_isolate,age:18 Isolate:sub_isolate:Data{msg: from main, requestCode: 1} receive data:Data{msg: fuck you, requestCode: 1}