1.使用 SSL/TLS 创建安全的 Netty 程序
SSL 和 TLS 是众所周知的标准和分层的协议,它们可以确保数据时私有的
Netty提供了SSLHandler对网络数据进行加密
使用Https
public class SslChannelInitialzer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel>{ private final SSLContext context; private final boolean client; private final boolean startTls; public SslChannelInitialzer(SSLContext context, boolean client, boolean startTls) { this.context = context; this.client = client; this.startTls = startTls; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { SSLEngine engine = context.createSSLEngine(); engine.setUseClientMode(client); ch.pipeline().addFirst("ssl", new SslHandler(engine, startTls)); } }
2.使用 Netty 创建 HTTP/HTTPS 程序
public class HttpDecoderEncodeIntializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel>{ private final boolean client; public HttpDecoderEncodeIntializer(boolean client) { this.client = client; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); if (client) { pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpResponseDecoder()); pipeline.addLast("", new HttpRequestEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("decompressor", new HttpContentDecompressor()); //添加解压缩 Handler } else { pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpRequestEncoder()); pipeline.addLast("encoder", new HttpResponseDecoder()); } } }
如果你需要在 ChannelPipeline 中有一个解码器和编码器,还分别有一个在客户端和服务器简单的编解码器:HttpClientCodec 和 HttpServerCodec
pipeline.addLast("aggegator", new HttpObjectAggregator(512 * 1024)); 聚合消息
WebSocket
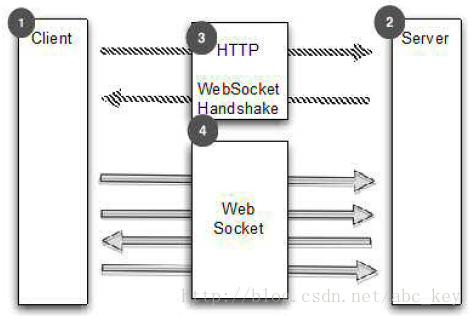
WebSocketServerProtocolHandler
处理空闲连接和超时
- IdleStateHandler,当一个通道没有进行读写或运行了一段时间后出发IdleStateEvent
- ReadTimeoutHandler,在指定时间内没有接收到任何数据将抛出ReadTimeoutException
- WriteTimeoutHandler,在指定时间内有写入数据将抛出WriteTimeoutException、
最常用的是IdleStateHandler,下面代码显示了如何使用IdleStateHandler,如果60秒内没有接收数据或发送数据,操作将失败,连接将关闭
public class IdleStateHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); pipeline.addLast(new HeartbeatHandler()); } public static final class HeartbeatHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private static final ByteBuf HEARTBEAT_SEQUENCE = Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer(Unpooled.copiedBuffer( "HEARTBEAT", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); @Override public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception { if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) { ctx.writeAndFlush(HEARTBEAT_SEQUENCE.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE); } else { super.userEventTriggered(ctx, evt); } } } }
分隔符协议 解决粘包问题
使用LineBasedFrameDecoder提取" "分隔帧
/** * 处理换行分隔符消息 * */ public class LineBasedHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(65 * 1204), new FrameHandler()); } public static final class FrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { // do something with the frame } } }
如果框架的东西除了换行符还有别的分隔符,可以使用DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder,只需要将分隔符传递到构造方法中。如果想实现自己的以分隔符为基础的协议,这些解码器是有用的。
例如,现在有个协议,它只处理命令,这些命令由名称和参数形成,名称和参数由一个空格分隔
public class CmdHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new CmdDecoder(65 * 1024), new CmdHandler()); } public static final class Cmd { private final ByteBuf name; private final ByteBuf args; public Cmd(ByteBuf name, ByteBuf args) { this.name = name; this.args = args; } public ByteBuf getName() { return name; } public ByteBuf getArgs() { return args; } } public static final class CmdDecoder extends LineBasedFrameDecoder { public CmdDecoder(int maxLength) { super(maxLength); } @Override protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buffer) throws Exception { ByteBuf frame = (ByteBuf) super.decode(ctx, buffer); if (frame == null) { return null; } int index = frame.indexOf(frame.readerIndex(), frame.writerIndex(), (byte) ' '); return new Cmd(frame.slice(frame.readerIndex(), index), frame.slice(index + 1, frame.writerIndex())); } } public static final class CmdHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Cmd> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Cmd msg) throws Exception { // do something with the command } } }
- FixedLengthFrameDecoder
- LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(65*1024, 0, 8))
读取大文件
@Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { File file = new File("test.txt"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion(fis.getChannel(), 0, file.length()); Channel channel = ctx.channel(); channel.writeAndFlush(region).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if(!future.isSuccess()){ Throwable cause = future.cause(); // do something } } }); }
public class ChunkedWriteHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final File file; public ChunkedWriteHandlerInitializer(File file) { this.file = file; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler()) .addLast(new WriteStreamHandler()); } public final class WriteStreamHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { super.channelActive(ctx); ctx.writeAndFlush(new ChunkedStream(new FileInputStream(file))); } } }
通过JBoss编组序列化
使用ProtoBuf序列化

/** * 使用protobuf序列化数据,进行编码解码 * 注意:使用protobuf需要protobuf-java-2.5.0.jar * @author Administrator * */ public class ProtoBufInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final MessageLite lite; public ProtoBufInitializer(MessageLite lite) { this.lite = lite; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder()) .addLast(new ProtobufEncoder()) .addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(lite)) .addLast(new ObjectHandler()); } public final class ObjectHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Serializable> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Serializable msg) throws Exception { // do something } } }
Bootstrap 当需要引导客户端或一些无连接协议时
- group(...),设置EventLoopGroup,EventLoopGroup用来处理所有通道的IO事件
- channel(...),设置通道类型
- channelFactory(...),使用ChannelFactory来设置通道类型
- localAddress(...),设置本地地址,也可以通过bind(...)或connect(...)
- option(ChannelOption<T>, T),设置通道选项,若使用null,则删除上一个设置的ChannelOption
- attr(AttributeKey<T>, T),设置属性到Channel,若值为null,则指定键的属性被删除
- handler(ChannelHandler),设置ChannelHandler用于处理请求事件
- clone(),深度复制Bootstrap,Bootstrap的配置相同
- remoteAddress(...),设置连接地址
- connect(...),连接远程通道
- bind(...),创建一个新的Channel并绑
ServerBootstrap 引导服务器
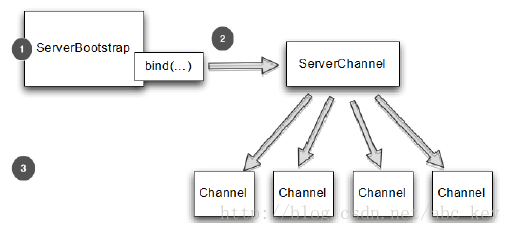
从Channel引导客户端
有时候需要从另一个Channel引导客户端,例如写一个代理或需要从其他系统检索数据。从其他系统获取数据时比较常见的,有很多Netty应用程序必须要和企业现有的系统集成,如Netty程序与内部系统进行身份验证,查询数据库等
可以不用再创建新的引导
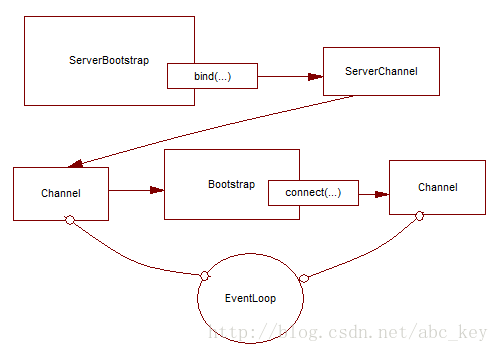

public class BootstrapingFromChannel { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { ChannelFuture connectFuture; @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler( new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("Received data"); msg.clear(); } }); b.group(ctx.channel().eventLoop()); connectFuture = b.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 2048)); } @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { if (connectFuture.isDone()) { // do something with the data } } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind(2048); f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (future.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("Server bound"); } else { System.err.println("bound fail"); future.cause().printStackTrace(); } } }); } }
使用通道选项和属性
使用ChannelOption和属性可以让事情变得很简单,例如Netty WebSocket服务器根据用户自动路由消息,通过使用属性,应用程序能在通道存储用户ID以确定消息应该发送到哪里。应用程序可以通过使用一个通道选项进一步自动化,给定时间内没有收到消息将自动断开连接
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建属性键对象 final AttributeKey<Integer> id = AttributeKey.valueOf("ID"); //客户端引导对象 Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); //设置EventLoop,设置通道类型 b.group(new NioEventLoopGroup()).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) //设置ChannelHandler .handler(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { @Override public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //通道注册后执行,获取属性值 Integer idValue = ctx.channel().attr(id).get(); System.out.println(idValue); //do something with the idValue } @Override protected void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("Reveived data"); msg.clear(); } }); //设置通道选项,在通道注册后或被创建后设置 b.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true).option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000); //设置通道属性 b.attr(id, 123456); ChannelFuture f = b.connect("www.manning.com",80); f.syncUninterruptibly(); }
