一.AOP(Aspect Oriented Programing)面向切面编程
AOP的终极目标:让我们可以专心做事
下面通过一个例子来介绍AOP的具体使用
案例的要求:使用AOP实现日志记录系统 , 核心模块 和 增强 单独 开发 ,运行时再组装
首先定义接口和方法
接口和实现类中的代码,我放在一起了,应该比较简单
package demo04.dao; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/5. */ public interface IHelloDao { public void doSome(); }
package demo04.dao;
/**
* Created by mycom on 2018/3/5.
*/
public class HelloDaoImpl implements IHelloDao {
public void doSome() {
System.out.println("已经成功加入到DB中了");
}
}
package demo04.service;
/**
* Created by mycom on 2018/3/5.
*/
public interface IHelloService {
public void doSome();
}
package demo04.service;
import demo04.dao.IHelloDao;
/**
* Created by mycom on 2018/3/5.
*/
public class HelloServiceImpl implements IHelloService {
//创建一个Dao的对象
IHelloDao dao;
public IHelloDao getDao() {
return dao;
}
public void setDao(IHelloDao dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
public void doSome() {
dao.doSome();
}
}
同样在resources下面也要有一个xml文件----applicationContext.xml
<!--返回的类型只能是实现类--> 这里需要注意一下 class的值只能是实现类的包
<bean id="dao" class="demo04.dao.HelloDaoImpl">
</bean>
<bean id="service" class="demo04.service.HelloServiceImpl">
<property name="dao" ref="dao"></property>
</bean>
然后编写测试类进行测试
@Test public void t1(){ ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextAop.xml"); //这里的返回值只能是接口 IHelloService service =(IHelloService) context.getBean("service"); service.doSome(); }
运行的结果
现在我们要在这句话出现之前,先记录一下日志,出现之后,再出现一句话
首先要创建一个新的包AOP包,并且在包下面写两个类
LoggerAfter是后置增强
LoggerBefore是前置增强
这两个类中的代码如下
package demo04.aop; import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice; import java.lang.reflect.Method; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/5. */ public class LoggerAfter implements AfterReturningAdvice { public void afterReturning(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, Object o1) throws Throwable { System.out.println("=======after"); } }
package demo04.aop; import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice; import java.lang.reflect.Method; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/5. */ public class LoggerBefore implements MethodBeforeAdvice { public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable { System.out.println("日志记录"); } }
在xml中配置,在配置xml是要给AOP添加一个约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="service" class="demo04.service.HelloServiceImpl"> <property name="dao" ref="dao"></property> </bean> <!--前置--> <bean id="beforeAdvice" class="demo04.aop.LoggerBefore"> </bean> <!--后置--> <bean id="afterAdvice" class="demo04.aop.LoggerAfter"> </bean> <!--配置aop--> <aop:config> <!--切点--> <aop:pointcut id="mypoint" expression="execution(public void demo04.service.HelloServiceImpl.doSome())"></aop:pointcut> <!--<aop:pointcut id="mypoint" expression="execution(* *..service.*.*(..))"></aop:pointcut>--> <!--advice-ref:做什么样的配置,是前置还是后置 pointcut-ref:锁定什么样的方法规则,那个方法需要被锁定 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:advisor> <aop:advisor advice-ref="afterAdvice" pointcut-ref="mypoint"></aop:advisor> </aop:config>
测试类
import demo04.service.HelloServiceImpl; import demo04.service.IHelloService; import demo05.MyCollection; import demo05.Student; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/3. */ public class Test20180305 { @Test public void t1(){ ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextAop.xml"); //这里的返回值只能是接口 IHelloService service =(IHelloService) context.getBean("service"); service.doSome(); } }
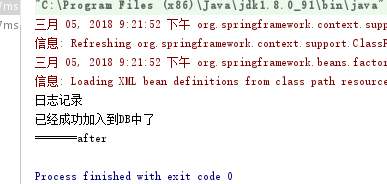
在这里和要介绍两个单词的意思
advice :通知
advisor:顾问
顾问可以包装通知
execution(【modifiers-pattern?】 访问修饰符
ret-type-pattern 返回值类型
【declaring-type-pattern?】 全限定性类名
name-pattern(param-pattern) 方法名(参数名) 包名.类型名.方法名
【throws-pattern?】) 抛出异常类型
public void doLog(String log){
}
方法签名
切入点表达式要匹配的对象就是目标方法的方法名。所以,execution表达式中明显就是方法的签名。
注意:表达式中加[]的部分表示可省略部分,各部分间用空格分开。在其中可以使用以下符号:
符号 意义
* 0至多个任意字符
.. 用在方法参数中,表示任意多个参数
用在包名后,表示当前包及其子包路径
+ 用在类名后,表示当前类及其子类
用在接口后,表示当前接口及其实现类
案例:
execution(public * *(..)) 指定切入点为:任意公共方法
execution(* set*(..)) 指定切入点为:任何一个以"set"开始的方法
二.给属性注入值(四种)
1.setter方法注入(就是在bean节点下有property节点给里面的属性值赋值
<bean id="service" class="demo04.service.HelloServiceImpl"> <property name="dao" ref="dao"></property> </bean>
2.构造注入
3.p命名空间注入(使用前要先要在Spring配置文件中引入p命名空间xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p")
这里的两种我写在一起了
首先写一个学生类,车类,MyCollection
package demo05; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/5. */ public class Student { private String name; private Integer age; private Car car; public Student() { } public Student(String name, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } }
package demo05; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/5. */ public class Car { private String color; private String brand; public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } }
在xml中的配置
<!--构造注入-->
<!--<bean id="stu" class="demo05.Student">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="小明"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="12"></constructor-arg>
</bean>-->
<!--p命名空间注入-->
<bean id="stu" class="demo05.Student" p:name="小明" p:age="12" p:car-ref="car"></bean>
最后编写测试类
以p命名空间注入为例进行测试
import demo04.service.HelloServiceImpl; import demo04.service.IHelloService; import demo05.MyCollection; import demo05.Student; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/3. */ public class Test20180305 { @Test public void t1(){ ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextCon.xml");
Student service2 =(Student) context.getBean("stu");
System.out.println(service2.getName());
} }
4.集合注入
再写一个MyCollection类
package demo05; import java.util.*; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/5. */ public class MyCollection { private String[] array; private List<String> list; private Set<String> set; private Map<String,String> map; private Properties properties; public MyCollection() { System.out.println("创建对象==========="); } public MyCollection(String[] array, List<String> list, Set<String> set, Map<String, String> map, Properties properties) { this.array = array; this.list = list; this.set = set; this.map = map; this.properties = properties; } @Override public String toString() { return "MyCollection{" + "array=" + Arrays.toString(array) + ", list=" + list + ", set=" + set + ", map=" + map + ", properties=" + properties + '}'; } public String[] getArray() { return array; } public void setArray(String[] array) { this.array = array; } public List<String> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public Set<String> getSet() { return set; } public void setSet(Set<String> set) { this.set = set; } public Map<String, String> getMap() { return map; } public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) { this.map = map; } public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } }
<!--集合注入-->
<bean id="collection" class="demo05.MyCollection" scope="prototype">
<!--Array-->
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>小明</value>
<value>小兰</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--list-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--set-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>set1</value>
<value>set2</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--map-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="1">
<value>01</value>
</entry>
<entry key="2">
<value>02</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--propreties-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="001">001</prop>
<prop key="002">002</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
import demo04.service.HelloServiceImpl; import demo04.service.IHelloService; import demo05.MyCollection; import demo05.Student; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/3. */ public class Test20180305 { @Test public void t1(){ ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextCon.xml"); //返回的类型只能是接口 MyCollection service =(MyCollection) context.getBean("collection"); System.out.println(service); } }
三.Spring中bean是单例的问题
单例:一个类在内存中只能有一个对象。
单利满足的三个条件:
1.构造私有
2.是有的静态变量,变量的类型就是当前类的类型
3.提供一个静态方法
在xml中配置实现单例还是多例的属性是scope
他的值有两个singleton 单例
prototype 多例
在上面的集合注入的例子中进行改动,并且如果MyCollection中有toString方法,也要注释掉,可以更直观的看到,如下
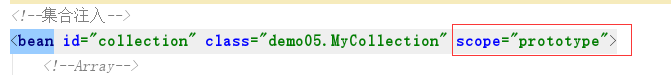
然后我们来编写测试方法进行测试
import demo04.service.HelloServiceImpl; import demo04.service.IHelloService; import demo05.MyCollection; import demo05.Student; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * Created by mycom on 2018/3/3. */ public class Test20180305 { @Test public void t1(){ ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextCon.xml"); MyCollection service =(MyCollection) context.getBean("collection"); System.out.println(service); MyCollection service2 =(MyCollection) context.getBean("collection"); System.out.println(service2); } }
运行结果
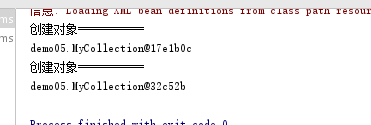
从运行结果来看,两次创建的对象的指针不同,创建的是两个对象,这是多例
线面再来看单例,将scope的属性值改为singleton
此时的运行结果如下
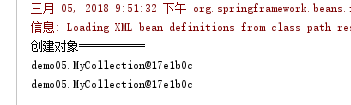
他只创建了依次对象,实现了单利