说树状数组其实是一个索引表,但是是一个特殊的,树状的索引表,它利用了二进制的一些特性。
就区间求和的要求来说:
首先我们用a[]数组来存储原始数据。然后在a[]之上构造c[]数组来作为树状数组。
如图
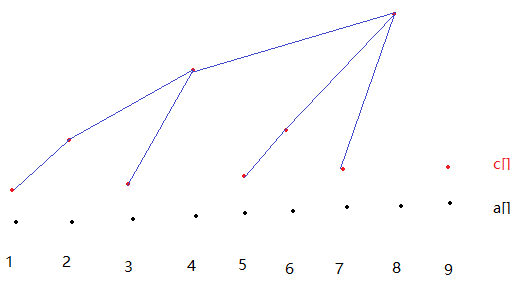
这个图表示,当i为奇数时,c[i]中保存的都是a[i]本身。然后,c[2]中保存了a[1], a[2],共2个,c[4]中保存的是a[1], a[2], a[3], a[4],c[6]又是保存两个,c[5]和c[6]。c[8]保存8个,c[1], c[2], c[3], c[4], c[5], c[6], c[7], c[8]。
看出什么规律没有?
如果将这些下标差成2进制序列就容易看出来规律了——
如果从右向左看,第一个是1的数位是第1位,那么c[i]中只有1个数,如果第一个是1的数位式第2位,那么c[i]中有2个数,如果是3,那么c[i]中有4个数,以此类推。
但是怎么代码怎么实现呢?
我们可以这样做——
首先取这个数的下标i,然后取这个数按位数最右边的1加在i上,所得就是下一个需要加当前数的下标,以此类推,直到取到下标大于等于最大下标n。
代码——
void Add(int x, int y) { a[x] += y; while(x <= n) { c[x] += y; x += lowbit(x); } }
当然,给某个数加上减上多少也可以用这个做。
区间求和的方法:
取从i到j之间的区间和
一种方法是取从1到j的和,然后减去从1到i的和。
取的方法——
从j开始,然后j减去j按位数最右端的1,得到的就是下一个需要的下标,减到0时结束。
int Sum(int x) { int rt = 0; while(x > 0) { rt += c[x]; x -= lowbit(x); } return rt; } printf("%d ", Sum(b)-Sum(a-1));
另一种方法是从j开始,如果j减去从右往左第一个1的差小于i,则结果加a[j],然后j -= 1;否则结果加c[j], j减去从右向左第一个1。
int Summ(int l, int r) { int rt = 0; while(r >= l) { if(r-lowbit(r) < l) { rt += a[r]; r -= 1; } else { rt += c[r]; r -= lowbit(r); } } return rt; }
不过这个貌似较慢……
完整代码——

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int N = 50005; 8 9 int t, n; 10 int a[N]; 11 int c[N]; 12 char s[10]; 13 int x, y; 14 15 int lowbit(int x) 16 { 17 return x&(-x); 18 } 19 20 void Add(int x, int y) 21 { 22 a[x] += y; 23 while(x <= n) 24 { 25 c[x] += y; 26 x += lowbit(x); 27 } 28 } 29 30 int Sum(int x) 31 { 32 int rt = 0; 33 while(x > 0) 34 { 35 rt += c[x]; 36 x -= lowbit(x); 37 } 38 return rt; 39 } 40 41 int Summ(int l, int r) 42 { 43 int rt = 0; 44 while(r >= l) 45 { 46 if(r-lowbit(r) < l) 47 { 48 rt += a[r]; 49 r -= 1; 50 } 51 else 52 { 53 rt += c[r]; 54 r -= lowbit(r); 55 } 56 } 57 return rt; 58 } 59 60 void Query(int a, int b) 61 { 62 printf("%d ", Sum(b)-Sum(a-1)); 63 //printf("%d ", Summ(a, b)); 64 } 65 66 int main() 67 { 68 //freopen("test.in", "r", stdin); 69 scanf("%d", &t); 70 for(int tm = 1; tm <= t; tm++) 71 { 72 scanf("%d", &n); 73 memset(c, 0, sizeof(c)); 74 memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)); 75 int y; 76 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 77 { 78 scanf("%d", &y); 79 Add(i, y); 80 } 81 printf("Case %d: ", tm); 82 83 scanf("%s", s); 84 while(s[0] != 'E') 85 { 86 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y); 87 if(s[0] == 'A') Add(x, y); 88 if(s[0] == 'Q') Query(x, y); 89 if(s[0] == 'S') Add(x, -y); 90 scanf("%s", s); 91 } 92 } 93 }
