CyclicBarrier使用:
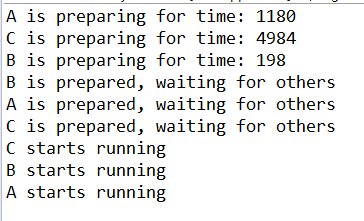
import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException; import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier; /** * 三个运动员各自准备,等到三个人都准备好后,再一起跑</br>@see 1:先创建一个公共 CyclicBarrier 对象,设置 同时等待 的线程数,CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(3);</br> 2:这些线程同时开始自己做准备,自身准备完毕后,需要等待别人准备完毕,这时调用 cyclicBarrier.await(); 即可开始等待别人;</br> 3:当指定的 同时等待 的线程数都调用了 cyclicBarrier.await();时,意味着这些线程都准备完毕好,然后这些线程才 同时继续执行。</br> * */ public class TestCyclicBarrier { public static void main(String[] args) { int runner = 3; final CyclicBarrier cycliBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(runner); final Random random = new Random(); for (char runnerName = 'A'; runnerName <= 'C'; runnerName++) { final String rName = String.valueOf(runnerName); new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { long prepareTime = random.nextInt(10000)+100; System.out.println(rName + " is preparing for time: " + prepareTime); try { Thread.sleep(prepareTime); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(rName + " is prepared, waiting for others"); try { cycliBarrier.await(); // 当前运动员准备完毕,等待别人准备好 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(rName + " starts running"); // 所有运动员都准备好了,一起开始跑 } }).start(); } } }
输出:
CountDownLatch例子
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; /** * 四个线程 A B C D,其中 D 要等到 A B C 全执行完毕后才执行,而且 A B C 是同步运行的@see 1:创建一个计数器,设置初始值,CountdownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);</br> 2:在 等待线程 里调用 countDownLatch.await() 方法,进入等待状态,直到计数值变成 0;</br> 3:在 其他线程 里,调用 countDownLatch.countDown() 方法,该方法会将计数值减小 1;</br> 4:当 其他线程 的 countDown() 方法把计数值变成 0 时,等待线程 里的 countDownLatch.await() 立即退出,继续执行下面的代码。</br> * */ public class TestCountDownLatch { public static void main(String[] args) { int workerNum = 3; final CountDownLatch countDownlatch = new CountDownLatch(workerNum); new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("D is waiting for other three threads"); try { countDownlatch.await(); System.out.println("D is start work"); Thread.sleep(100); System.out.println("D finsh Work"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); for (char threadName = 'A'; threadName <= 'C'; threadName++) { final String tName = String.valueOf(threadName); new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(tName + " is working"); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(tName + " finished"); countDownlatch.countDown(); } }).start(); } } }
输出:

FutureTask、Callable例子
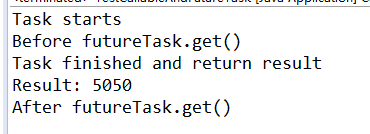
import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; /** * 我们想让子线程去计算从 1 加到 100,并把算出的结果返回到主线程</br> * @see * 如何把子线程的结果回传回来呢?在 Java 里,有一个类是配合 Callable 使用的:FutureTask,不过注意,它获取结果的 get 方法会阻塞主线程。 * */ public class TestCallableAndFutureTask { public static void main(String[] args) { Callable<Integer> callAble = new Callable<Integer>() { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { System.out.println("Task starts"); Thread.sleep(100); int result = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) { result += i; } System.out.println("Task finished and return result"); return result; } }; FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(callAble); new Thread(futureTask).start(); try { System.out.println("Before futureTask.get()"); System.out.println("Result: " + futureTask.get()); System.out.println("After futureTask.get()"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
输出:
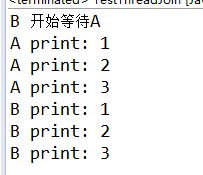
thread.join() 例子
/** * 实现效果:线程B在线程A完成之后再执行 * thread.join() * */ public class TestThreadJoin { public static void main(String[] args) { demo1(); } private static void demo1() { final Thread A = new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { PrintNumber("A"); } }) ; Thread B = new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("B 开始等待A"); try { A.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } PrintNumber("B"); } }) ; A.start(); B.start(); } private static void PrintNumber(String ThreadName) { int i = 0; while (i++ < 3) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch(InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(ThreadName + " print: " + i); } } }
输出:
wait()、notify() 例子:
public class TestWaitAndnotify { public static void main(String[] args) { demo2(); } public static void demo2 () { final Object lock = new Object(); Thread A = new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("INFO: A 等待锁 "); synchronized (lock) { System.out.println("INFO: A 得到了锁 lock"); System.out.println("A1"); try { System.out.println("INFO: A 准备进入等待状态,放弃锁 lock 的控制权 "); lock.wait();//挂起线程A 放弃锁 lock 的控制权 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("INFO: 有人唤醒了 A, A 重新获得锁 lock"); System.out.println("A2"); System.out.println("A3"); } } }); Thread B = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("INFO: B 等待锁 "); synchronized (lock) { System.out.println("INFO: B 得到了锁 lock"); System.out.println("B1"); System.out.println("B2"); System.out.println("B3"); System.out.println("INFO: B 打印完毕,调用 notify 方法 "); lock.notify(); // notify()方法唤醒正在等待lock锁的线程A System.out.println("线程 B do notify method 完毕"); } } }); A.start(); B.start(); } }
输出:

Condition 例子(生产消费):
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class TestCondition { public static void main(String[] args) { final BoundedBuffer b = new BoundedBuffer(); new Thread(new Runnable() { // 写线程 public void run() { int i = 1; while (true) { try { b.put(i++); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }).start(); new Thread(new Runnable() { // 读线程 public void run() { while (true) { try { b.take(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }).start(); } } class BoundedBuffer{ final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // 锁对象 final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition(); // 写线程条件 final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); // 读线程条件 final Integer[] items = new Integer[10]; // 缓存队列 int putptr; // 写索引 int takeptr; // 读索引 int count; // 队列中存在的数据个数 public void put(Integer x) throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try { while(count == items.length) { // 如果队列满了 notFull.await(); // 阻塞写线程 } items[putptr] = x; // 赋值 System.out.println("写入:" + x); if(++putptr == items.length) { // 如果写索引写到队列的最后一个位置了,那么置为0 putptr = 0; } ++count; // 个数++ notEmpty.signal(); // 唤醒读线程 } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public Integer take() throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try { while(count == 0) { // 如果队列为空 notEmpty.await(); // 阻塞读线程 } Integer x = items[takeptr]; // 取值 System.out.println("读取:" + x); if(++takeptr == items.length) { // 如果读索引读到队列的最后一个位置了,那么置为0 takeptr = 0; } --count; // 个数-- notFull.signal(); return x; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
输出:

.......