线程是干活的
所以线程一定是Thread,或者该线程实现Runnable接口
多线程是竞争关系,所以多个线程竞争同一个资源,也就是同一个对象
所以这个竞争对象放到Thread中
即:
// resources是竞争资源
Resources resources = new Resources();
Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1(resources);
Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2(resources);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
----------------------------------------------------------------------
class Thread1 implements Runnable {
Resources resources = null;
Thread1(Resources resources) {
this.resources = resources;
}
public void run() {
//这个methodA方法时Resources里面的竞争资源方法
resources.methodA();
}
}
class Thread2 implements Runnable {
Resources resources = null;
Thread2(Resources resources) {
this.resources = resources;
}
public void run() {
//这个methodA方法时Resources里面的竞争资源方法
resources.methodA();
}
}
class Resources {
private int count = 100;
//多线程去干活了,它们争着抢着去执行竞争资源里面的方法,所以这个方法区域需要加锁
public synchronized void methodA() {
if(count > 0) {
count--;
}
}
}
例子:
package Thread; public class MultiThread { public static void main(String[] args) { //resources就是竞争资源对象 Resources resources = new Resources(); Runnable1 runnable1 = new Runnable1(resources); for(int i = 0; i <100; i++) { // 这里是创建多线程去执行任务 //多线程是竞争关系,所以多个线程竞争同一个资源,也就是同一个对象 //所以这个竞争对象放到Thread中 new Thread(runnable1,"Thread"+i).start(); } } } class Resources { private int count = 100; //多线程去干活了,它们争着抢着去执行竞争资源里面的方法,所以这个方法区域需要加锁 public synchronized void methodA() { if(count > 0) { count--; } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " +"count:"+count); } } class Runnable1 implements Runnable { Resources resources = null; Runnable1(Resources resources) { this.resources = resources; } public void run() { //这个methodA方法时Resources里面的竞争资源方法 resources.methodA(); } }
.....
多线程可以同时访问同个对象的不同方法吗?
例子:
public class Test66 { public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new A(); Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1(a); Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2(a); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } class A{ public synchronized void method1() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("进入method1方法睡5秒"); Thread.sleep(5000); } public synchronized void method2() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("进入method1方法睡2秒"); Thread.sleep(2000); } } class Thread1 extends Thread { A a; public Thread1(A a) { this.a = a; } @Override public void run() { try { a.method1(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class Thread2 extends Thread { A a; public Thread2(A a) { this.a = a; } @Override public void run() { try { a.method2(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }

修改一下 :讲method2的 synchronized 去掉
class A{ public synchronized void method1() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("进入method1方法睡5秒"); Thread.sleep(5000); System.out.println("进入method1结束"); } public void method2() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("进入method2方法睡2秒"); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("进入method2结束"); } }
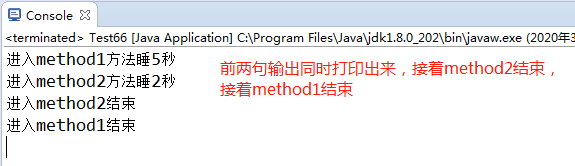
因此得出结论:同个对象的两个同步方法不能并发执行,也就是一个线程获取了一个对象的锁之后,对应这个对象的其他同步方法也被锁住,其他线程只能等待。若方法没有被synchronized 修饰,则可以多线程并发执行