问题:
一台客户现场机器,运行一周左右偶然发生一次应用段错误或者double free问题,cpu可能是arm、mips、x86等架构,有什么好的方法捕捉异常日志?
困难点:
1. 研发环境常使用gdb+coredump技术解决此类问题,客户现场等非研发环境的偶现应用异常问题,不方便使用,操作起来有一定难度
2. 不同架构(arm32、arm64、mips、x86),不同版本C库和gdb,栈回溯效果差异很大。PC ubuntu系统测试,glibc 2.15,发生应用double free,直接打印栈回溯信息,其他架构的CPU上测试没有这个功能。arm64架构的某款CPU上测试,gdb对strip过的应用程序无法栈回溯, PC ubuntu系统测试没有这个问题。
解决方案分析:
当应用程序发生段错误,将执行内核do_page_fault函数,在该函数获取应用段错误当时struct pt_regs,调用get_user从用户空间栈获取栈回溯有关数据,就可以对应用程序栈回溯,实现gdb类似效果。原理没有问题,实际验证也可行。这个栈回溯过程,也可以读取段错误应用的elf文件信息,这样栈回溯时能分析并打印出栈回溯过程每一级函数的名字。这个方法有几个优点。
- 把内核对应用异常栈回溯的代码编译进内核,任何时候应用程序发生段错误、double free,内核都可以对异常应用栈回溯,不需要使用gdb工具
- 内核对异常应用栈回溯,如果支持mips、arm32、arm64、x86等架构,不需要应用程序针对特定架构实现异常栈回溯功能
- 内核对异常应用栈回溯日志,是应用异常时函数调用关系,日志可以保存到存储设备,随时查看,并且一目了然,不需要问题发生后再运行gdb+coredump重现问题
- 如果可执行程序strip过,arm64架构下也能实现内核对异常应用栈回溯,而gdb对这种情况无能为力
栈回溯的原理

如上图所示,是一个传统的arm架构下函数栈数据分布,函数栈由fp和sp寄存器分别指向栈底和栈顶
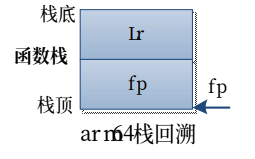
当执行入栈操作时,lr和fp寄存器的值存入栈中,然后令fp寄存器指向函数栈的栈顶,本例是函数栈第二片内存地址(函数无局部变量)。栈回溯时,首先根据fp寄存器指向的地址,取出保存在函数栈中lr和fp寄存器的数据,lr的值是函数返回地址,fp的值是上一级函数栈的栈顶地址
1.堆栈指针r13(SP):每一种异常模式都有其自己独立的r13,它通常指向异常模式所专用的堆栈,也就是说五种异常模式、非异常模式(用户模式和系统模式),
都有各自独立的堆栈,用不同的堆栈指针来索引。这样当ARM进入异常模式的时候,程序就可以把一般通用寄存器压入堆栈,返回时再出栈,保证了各种模式下程序的状态的完整性 2.连接寄存器r14(LR):每种模式下r14都有自身版组,它有两个特殊功能 (1)保存子程序返回地址。使用BL或BLX时,跳转指令自动把返回地址放入r14中;子程序通过把r14复制到PC来实现返回 (2)当异常发生时,异常模式的r14用来保存异常返回地址,将r14如栈可以处理嵌套中断。 3、程序计数器r15(PC):PC是有读写限制的。当
没有超过读取限制的时候,读取的值是指令的地址加上8个字节,由于ARM指令总是以字对齐的,故bit[1:0]总是00。
当用str或stm存储PC的时候,偏移量有可能是8或12等其它值
unwind 形式的栈回溯
1 /* 2 * Unwind a single frame starting with *sp for the symbol at *pc. It 3 * updates the *pc and *sp with the new values. 4 */ 5 int unwind_frame(struct stackframe *frame) 6 { 7 unsigned long low; 8 const struct unwind_idx *idx; 9 struct unwind_ctrl_block ctrl; 10 11 /* store the highest address on the stack to avoid crossing it*/ 12 low = frame->sp; 13 ctrl.sp_high = ALIGN(low, THREAD_SIZE); 14 15 pr_debug("%s(pc = %08lx lr = %08lx sp = %08lx) ", __func__, 16 frame->pc, frame->lr, frame->sp); 17 18 if (!kernel_text_address(frame->pc)) 19 return -URC_FAILURE; 20 21 idx = unwind_find_idx(frame->pc); //根据PC寄存器的值查找段内存地址 22 if (!idx) { 23 pr_warn("unwind: Index not found %08lx ", frame->pc); 24 return -URC_FAILURE; 25 } 26 27 ctrl.vrs[FP] = frame->fp; 28 ctrl.vrs[SP] = frame->sp; 29 ctrl.vrs[LR] = frame->lr; 30 ctrl.vrs[PC] = 0; 31 32 if (idx->insn == 1) 33 /* can't unwind */ 34 return -URC_FAILURE; 35 else if ((idx->insn & 0x80000000) == 0) 36 /* prel31 to the unwind table */ 37 ctrl.insn = (unsigned long *)prel31_to_addr(&idx->insn); 38 else if ((idx->insn & 0xff000000) == 0x80000000) 39 /* only personality routine 0 supported in the index */ 40 ctrl.insn = &idx->insn; 41 else { 42 pr_warn("unwind: Unsupported personality routine %08lx in the index at %p ", 43 idx->insn, idx); 44 return -URC_FAILURE; 45 } 46 47 /* check the personality routine */ 48 if ((*ctrl.insn & 0xff000000) == 0x80000000) { 49 ctrl.byte = 2; 50 ctrl.entries = 1; 51 } else if ((*ctrl.insn & 0xff000000) == 0x81000000) { 52 ctrl.byte = 1; 53 ctrl.entries = 1 + ((*ctrl.insn & 0x00ff0000) >> 16); 54 } else { 55 pr_warn("unwind: Unsupported personality routine %08lx at %p ", 56 *ctrl.insn, ctrl.insn); 57 return -URC_FAILURE; 58 } 59 60 ctrl.check_each_pop = 0; 61 62 while (ctrl.entries > 0) { 63 int urc; 64 if ((ctrl.sp_high - ctrl.vrs[SP]) < sizeof(ctrl.vrs)) 65 ctrl.check_each_pop = 1; 66 /*分析出栈指令相关编码数据,分析函数入栈函数的指令*/ 67 urc = unwind_exec_insn(&ctrl); 68 if (urc < 0) 69 return urc; 70 if (ctrl.vrs[SP] < low || ctrl.vrs[SP] >= ctrl.sp_high) 71 return -URC_FAILURE; 72 } 73 74 if (ctrl.vrs[PC] == 0) 75 ctrl.vrs[PC] = ctrl.vrs[LR]; 76 77 /* check for infinite loop */ 78 if (frame->pc == ctrl.vrs[PC]) 79 return -URC_FAILURE; 80 81 frame->fp = ctrl.vrs[FP]; 82 frame->sp = ctrl.vrs[SP];//上一级函数栈底 83 frame->lr = ctrl.vrs[LR];//函数返回地址 84 frame->pc = ctrl.vrs[PC]; 85 86 return URC_OK; 87 }
问题:
假设应用程序函数执行流程是test_c()->test_b()->test_a(),test_a()函数发生段错误,内核将自动执行do_page_fault(……,struct pt_regs *regs)函数,该结构体中regs->pc是发生段错误test_a()函数的指令地址,假如是0x400538,regs->regs[29]就是fp寄存器。怎么实现内核对段错误应用的栈回溯?
策略:(对应用段错误栈回溯)
模仿unwind_frame函数,增加user_unwind_frame函数,以实现do_page_fault函数中,对段错误应用程序栈回溯,代码如图。经过栈回溯,假设从test_a函数栈中分析出test_a函数返回地址是0x400550(处于test_b函数中),继续栈回溯,找到test_b函数的返回地址是0x400588(处于test_c函数)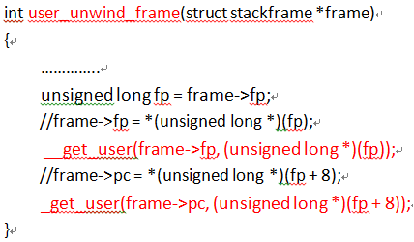
这样可以在内核do_page_fault中,对段错误应用程序栈回溯,执行过程打印如下: user thread backstrace pc1:0x400538 pc2:0x400550 pc3:0x400588
反汇编后可以知道函数调用流程是test_c()->test_b()->test_a()。这个方法还可以继续优化:还是do_page_fault函数中,对应用栈回溯过程,读取可执行程序elf文件信息,分析并打印出该指令地址所在的函数的名字。这需要用到elf可执行程序文件数据分布的原理,尤其是elf文件 section部分的数据
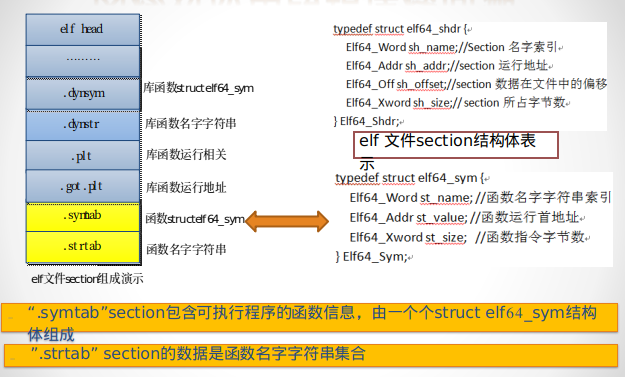
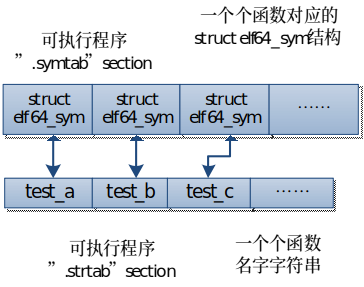
在内核里读取elf可执行程序文件的“.symtab”和”.strtab” section的数据,就可以分析出该文件的test_c()、test_b()、test_a()三个函数名字字符串、函数运行首地址、函数指令字节数。比如数据如下
函数名字 函数指令首地址 函数指令结束地址 test_c 0x400518 0x400518 +0x27 test_b 0x400545 0x400545 +0x35
user thread backstrace [<0x400538>] test_a + 0x20/0x27 [<0x400550>] test_b +0x0b/0x35 [<0x400588>] test_c + 0x08 /0x20
分析实例
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> char buf[5]; int test_a() { printf("%s ", __func__); memcpy(buf, "12345677", 7); return 0; } int test_b() { printf("%s ", __func__); memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); test_a(); return 0; } int test_c() { printf("%s ", __func__); sleep(1); test_b(); return 0; } int main() { printf("%s ", __func__); test_c(); return 0; }
例子是一个可执行程序test演示代码,用到了memcpy等库函数,本例是C库文件libc.so中的函数
可执行程序文件的“.dynstr” section包含了用到的库函数名字,” .dynsym” section的数据是一个个struct elf64_sym结构体,每个对应一个用到的库函数结构体。两个section表述的库函数信息是一一对应的,如下图:
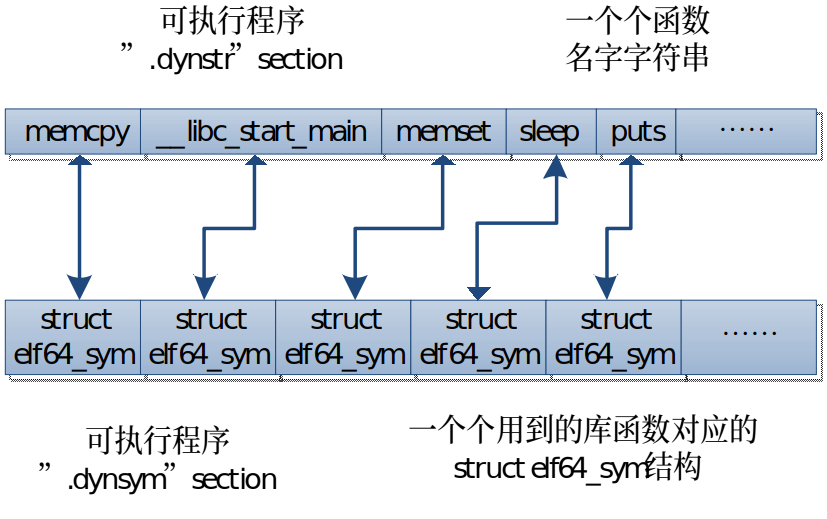
ibc.so库文件的“.dynstr” section包含了C库所有的库函数名字,” .dynsym” section的数据也是一个个struct elf64_sym结构体,每个对应一个C库的库函数结构体
libc.so的”.dynsym” section的库函数结构体struct elf64_sym中, st_value是库函数原始首地址、st_size是库函数指令字节数。为什么是原始首地址?因为可执行程序调用C库函数时,会对C库函数进行一次重定向,然后映射到可执行程序的应用空间,最后才执行C库函数的指令代码
1 “.plt” section汇编代码 2 0000000000400480 <memcpy@plt>: 3 ………….. 4 400484: f944fa11 ldr x17, [x16,#2544] 5 400488: 9127c210 add x16, x16, #0x9f0 6 40048c: d61f0220 br x17
1 test_a函数汇编代码 2 0000000000400650 <test_a>: 3 400650: a9bf7bfd stp x29, x30, [sp,#-16]! 4 400654: 910003fd mov x29, sp 5 …………………. 6 400660: 97ffffa0 bl 4004e0 <puts@plt> 7 ……………… 8 400678: 97ffff82 bl 400480 <memcpy@plt>
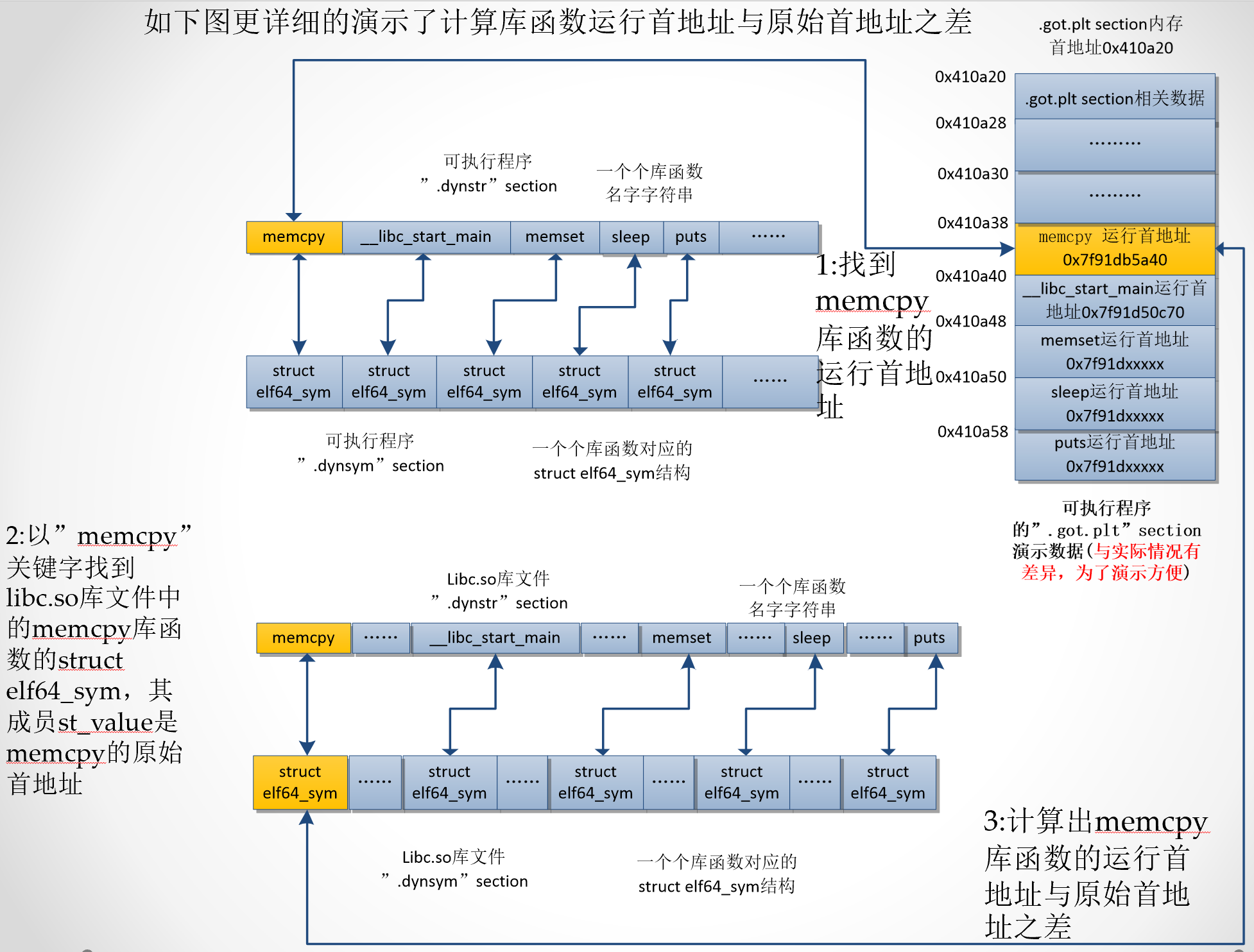
如test_a函数汇编代码,当执行memcpy函数,实际是先执行“.plt” section的memcpy@plt 函数。然后在memcpy@plt函数汇编代码里,ldr x17, [x16,#2544]计算出memcpy库函数实际运行地址在“.got.plt” section的内存地址0x410a38,取出该地址的数据存于x17寄存器。如右图所示,就是把橙色内存单元的数据0x7f91db5a40保存到x17,然后br x17就是跳转到memcpy库函数实际首地址,执行该函数的代码
使用方法:
如果我们能知道libc.so中所有库函数的运行首地址和结束地址,这样当在C库中崩溃,比如此时pc值是0x7f91db5a60,我们就能知道0x7f91db5a60处于哪个库函数,这样就知道怎么在C库中栈回溯了。
具体实现方法:
- 以memcpy中崩溃为例, 从libc.so文件的” .dynsym” section找到memcpy库函数的struct elf64_sym结构,该结构的成员st_value就是memcpy库函数的原始首地址
- 从可执行程序”.got.plt” section找到库函数memcpy的运行首地址,memcpy的运行首地址减去其原始首地址就是库函数的原始首地址与运行首地址之差,命名为dx
- 从libc.so分离出所有库函数的struct elf64_sym结构,知道每个库函数的原始首地址,原始首地址+dx就是每个库函数的运行首地址,再结合st_size就知道库函数的运行结束地址。从libc.so文件的“.dynstr” section又知道了每个库函数的名字。这样知道了每个库函数运行首地址、结束地址、函数名字,就具备了栈回溯的条件
double free应用:
double free是C库检测到异常,然后向当前进程发送SIGABRT信号,然后进入内核空间,会执行到do_send_specific函数发送信号。在该函数中,检测到是SIGABRT信号,通过task_pt_regs(current)获取异常进程进入内核空间前pc、lr、fp等寄存器,然后运用前文的栈回溯原理,对double free应用流程栈回溯,如下是演示效果。
演示效果
应用在test_a函数调用free库函数两次后,内核打印:
[< 0x7f91dxxxx>] raise() 0x38/0x78 [< 0x7f91dxxxx>] abort() 0x1b0/0x308 [<0x000400538>] test_a() 0x6c/0xa4 [<0x000400550>] test_b() 0x20/0x458 [<0x000400588>] test_c() 0x20/0x64
源码:
https://github.com/dongzhiyan-stack/user_stack_backstrace-in-kernel.git

1 /* 2 * 内核对异常应用栈回溯 3 * 4 * author : hujunpeng 5 * email : dongzhiyan_linux@163.com 6 */ 7 8 #include <linux/tick.h> 9 #include <linux/stddef.h> 10 #include <linux/unistd.h> 11 #include <linux/export.h> 12 #include <linux/ptrace.h> 13 #include <linux/sys.h> 14 #include <linux/user.h> 15 #include <linux/init.h> 16 #include <linux/completion.h> 17 #include <linux/kallsyms.h> 18 #include <linux/random.h> 19 #include <linux/module.h> 20 #include <linux/kernel.h> 21 #include <linux/fs.h> 22 #include <linux/mm.h> 23 #include <linux/mman.h> 24 #include <linux/signal.h> 25 #include <linux/binfmts.h> 26 #include <linux/string.h> 27 #include <linux/file.h> 28 #include <linux/slab.h> 29 #include <linux/elfcore.h> 30 #include <linux/init.h> 31 #include <linux/highuid.h> 32 #include <linux/compiler.h> 33 #include <linux/highmem.h> 34 #include <linux/pagemap.h> 35 #include <linux/vmalloc.h> 36 #include <linux/security.h> 37 #include <linux/random.h> 38 #include <linux/elf.h> 39 #include <linux/utsname.h> 40 #include <linux/coredump.h> 41 #include <linux/sched.h> 42 #include <asm/uaccess.h> 43 #include <asm/param.h> 44 #include <asm/page.h> 45 #include <asm/stacktrace.h> 46 47 #ifdef CONFIG_MIPS 48 #include <asm/asm.h> 49 #include <asm/mipsregs.h> 50 #include <asm/processor.h> 51 #include <asm/uaccess.h> 52 #include <asm/io.h> 53 #include <asm/inst.h> 54 #endif 55 56 #define FUN_NAME_LEN 50 57 struct sym_fun_info{ 58 char name[FUN_NAME_LEN]; 59 unsigned long fun_first_instruct_addr; 60 unsigned long fun_end_instruct_addr; 61 }; 62 struct user_stack_unwind{ 63 unsigned long elf_text_start; 64 unsigned long elf_text_end; 65 unsigned long thread_stack_start; 66 struct sym_fun_info sym_info; 67 struct task_struct *thread; 68 struct mutex stack_backstrace_lock; 69 }; 70 71 struct mips_frame_info { 72 void *func; 73 unsigned long func_size; 74 int frame_size; 75 int pc_offset; 76 }; 77 struct elf_file_info{ 78 struct elf_shdr section_dynsym;//保存elf文件的 dynsym section结构体 79 struct elf_shdr section_dynstr;//保存elf文件的 dynstr section结构体 80 struct elf_shdr section_symtab;//保存elf文件的 symtab section结构体 81 82 struct elf_sym *first_lib_sym;//指向elf文件dynsym section数据区,该数据区是一个个库函数的struct elf_sym结构体,elf可执行程序和lib库文件都用到 83 unsigned char *elf_lib_fun_str;//指向elf文件dynstr section的数据区,该数据区是一个个库函数名字字符串,elf可执行程序和lib库文件都用到 84 struct elf_sym *first_elf_sym;//保存elf 可执行程序文件中.symtab section区数据,该数据区是一个个可执行程序自己的函数的struct elf_sym结构体 85 unsigned char *elf_fun_str;//保存elf 可执行程序文件中.strtab section区数据,该数据区是一个个可执行程序函数名字字符串 86 87 unsigned long *got_addr;//保存got段的内存首地址 88 unsigned long elf_lib_fun_off;//库函数原始首函数地址与实际运行首地址的之差 89 int elf_strip;//可执行程序strip过置1,否则为0 90 }; 91 92 static struct elf_file_info elf_info,lib_info; 93 static struct user_stack_unwind user_stack_unwind_info; 94 95 static int print_user_ip_sym(unsigned long pc); 96 static char *get_elflib_path_file_name(struct task_struct *task,unsigned long addr); 97 static long get_file_size(struct file *file); 98 static int get_lib_fun_offset(struct elf_file_info *elf_info,struct elf_file_info *lib_info); 99 static int get_lib_fun_info(struct sym_fun_info * sym_lib_info,struct elf_file_info *lib_info,unsigned long addr,unsigned long lib_fun_offset); 100 static int get_elf_fun_info(struct sym_fun_info * elf_sym_info,struct elf_file_info *elf_info,unsigned long addr); 101 102 #define OPEN_PRINT 0 103 #define user_stack_printk(fmt,...) 104 do{if(OPEN_PRINT) 105 printk(fmt,##__VA_ARGS__); 106 }while(0) 107 108 #ifdef CONFIG_MIPS 109 #define elf_sym elf32_sym 110 111 #define J_TARGET(pc,target) 112 (((unsigned long)(pc) & 0xf0000000) | ((target) << 2)) 113 114 static inline int is_ra_save_ins(union mips_instruction *ip) 115 { 116 #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_MICROMIPS 117 union mips_instruction mmi; 118 119 /* 120 * swsp ra,offset 121 * swm16 reglist,offset(sp) 122 * swm32 reglist,offset(sp) 123 * sw32 ra,offset(sp) 124 * jradiussp - NOT SUPPORTED 125 * 126 * microMIPS is way more fun... 127 */ 128 if (mm_insn_16bit(ip->halfword[0])) { 129 mmi.word = (ip->halfword[0] << 16); 130 return ((mmi.mm16_r5_format.opcode == mm_swsp16_op && 131 mmi.mm16_r5_format.rt == 31) || 132 (mmi.mm16_m_format.opcode == mm_pool16c_op && 133 mmi.mm16_m_format.func == mm_swm16_op)); 134 } 135 else { 136 mmi.halfword[0] = ip->halfword[1]; 137 mmi.halfword[1] = ip->halfword[0]; 138 return ((mmi.mm_m_format.opcode == mm_pool32b_op && 139 mmi.mm_m_format.rd > 9 && 140 mmi.mm_m_format.base == 29 && 141 mmi.mm_m_format.func == mm_swm32_func) || 142 (mmi.i_format.opcode == mm_sw32_op && 143 mmi.i_format.rs == 29 && 144 mmi.i_format.rt == 31)); 145 } 146 #else 147 /* sw / sd $ra, offset($sp) */ 148 return (ip->i_format.opcode == sw_op || ip->i_format.opcode == sd_op) && 149 ip->i_format.rs == 29 && 150 ip->i_format.rt == 31; 151 #endif 152 } 153 154 static inline int is_jump_ins(union mips_instruction *ip) 155 { 156 #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_MICROMIPS 157 /* 158 * jr16,jrc,jalr16,jalr16 159 * jal 160 * jalr/jr,jalr.hb/jr.hb,jalrs,jalrs.hb 161 * jraddiusp - NOT SUPPORTED 162 * 163 * microMIPS is kind of more fun... 164 */ 165 union mips_instruction mmi; 166 167 mmi.word = (ip->halfword[0] << 16); 168 169 if ((mmi.mm16_r5_format.opcode == mm_pool16c_op && 170 (mmi.mm16_r5_format.rt & mm_jr16_op) == mm_jr16_op) || 171 ip->j_format.opcode == mm_jal32_op) 172 return 1; 173 if (ip->r_format.opcode != mm_pool32a_op || 174 ip->r_format.func != mm_pool32axf_op) 175 return 0; 176 return (((ip->u_format.uimmediate >> 6) & mm_jalr_op) == mm_jalr_op); 177 #else 178 if (ip->j_format.opcode == j_op) 179 return 1; 180 if (ip->j_format.opcode == jal_op) 181 return 1; 182 if (ip->r_format.opcode != spec_op) 183 return 0; 184 return ip->r_format.func == jalr_op || ip->r_format.func == jr_op; 185 #endif 186 } 187 188 static inline int is_sp_move_ins(union mips_instruction *ip) 189 { 190 #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_MICROMIPS 191 /* 192 * addiusp -imm 193 * addius5 sp,-imm 194 * addiu32 sp,sp,-imm 195 * jradiussp - NOT SUPPORTED 196 * 197 * microMIPS is not more fun... 198 */ 199 if (mm_insn_16bit(ip->halfword[0])) { 200 union mips_instruction mmi; 201 202 mmi.word = (ip->halfword[0] << 16); 203 return ((mmi.mm16_r3_format.opcode == mm_pool16d_op && 204 mmi.mm16_r3_format.simmediate && mm_addiusp_func) || 205 (mmi.mm16_r5_format.opcode == mm_pool16d_op && 206 mmi.mm16_r5_format.rt == 29)); 207 } 208 return (ip->mm_i_format.opcode == mm_addiu32_op && 209 ip->mm_i_format.rt == 29 && ip->mm_i_format.rs == 29); 210 #else 211 /* addiu/daddiu sp,sp,-imm */ 212 if (ip->i_format.rs != 29 || ip->i_format.rt != 29) 213 return 0; 214 if (ip->i_format.opcode == addiu_op || ip->i_format.opcode == daddiu_op) 215 return 1; 216 #endif 217 return 0; 218 } 219 /** 220 * user_process_lookup_size_offset - 根据传入的指令地址计算所处函数的指令字节数和该指令地址的偏移 221 * @addr - 传入的指令地址 222 * @symbolsize - 根据addr计算出的函数指令字节数 223 * @offset - addr相对函数指令首地址的偏移 224 * 225 * returns: 226 * 1:找到addr所处的函数 227 * 0: 没有找到addr所处的函数 228 */ 229 static int user_process_lookup_size_offset(unsigned long addr, unsigned long *symbolsize,unsigned long *offset) 230 { 231 struct sym_fun_info sym_func_info; 232 int ret; 233 234 //如果addr在可执行程序代码段 235 if(addr >= user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_start && addr <= user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_end) 236 { 237 ret = get_elf_fun_info(&sym_func_info,&elf_info,addr); 238 if(ret) 239 { 240 user_stack_printk("%s get_elf_fun_info:%d error ",__func__,ret); 241 return 0; 242 } 243 } 244 else//addr在库中 245 { 246 //根据可执行程序的.dynstr和.dynsym信息分析出库函数的运行地址和库函数原始的偏差值 247 ret = get_lib_fun_offset(&elf_info,&lib_info); 248 if(ret) 249 { 250 user_stack_printk("%s get_lib_fun_offset:%d error ",__func__,ret); 251 return 0; 252 } 253 memset(&sym_func_info,0,sizeof(struct sym_fun_info)); 254 //根据addr获取库函数所处的函数首地址、函数指令字节数等信息 255 ret = get_lib_fun_info(&sym_func_info,&lib_info,addr,elf_info.elf_lib_fun_off); 256 if(ret) 257 { 258 /*mips架构double free栈回溯时,中途会遇到未知C库函数。比如test_a ->C库未知函数1->C库未知函数2->abort->raise。 259 栈回溯时,abort->raise两个函数都能打印出来,但是回溯到未知函数2,就会终止,arm64用gdb栈回溯也是这样,直接终止调。 260 但是我的arm64内核double free栈回溯能完整回溯,这是比gdb优越的另一点。由于mips栈回溯依赖每个函数的指令首地址,现在 261 碰到C库未知函数2,当然不知道该函数名字和指令首地址,那就直接return 0栈回溯结束,这就从原理上证实,mips架构double free 262 栈回溯存在问题,有时间研究一下"C库未知函数2"出现的原因。 263 */ 264 user_stack_printk("%s get_lib_fun_info:%d error ",__func__,ret); 265 return 0; 266 } 267 } 268 269 *offset = addr - sym_func_info.fun_first_instruct_addr; 270 *symbolsize = sym_func_info.fun_end_instruct_addr - sym_func_info.fun_first_instruct_addr; 271 272 return 1; 273 } 274 /** 275 * get_frame_info - 根据传入的函数指令首地址,依次分析汇编指令,根据汇编指令找到函数栈大小和函数返回地址在栈中的保存位置 276 * @info - info->func就是函数指令首地址,info->frame_size保存函数栈大小,info->pc_offset保存函数返回地址在函数栈中的偏移 277 * 278 * returns: 279 * 0:分析汇编指令后,找到函数栈大小和函数返回地址在栈中的保存位置 280 * 1:没有根据汇编指令分析出函数函数返回地址在栈中的保存位置 281 * <0:其他异常 282 */ 283 static int get_frame_info(struct mips_frame_info *info) 284 { 285 #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_MICROMIPS 286 union mips_instruction *ip = (void *) (((char *) info->func) - 1); 287 #else 288 union mips_instruction *ip = info->func; 289 #endif 290 291 union mips_instruction *tmp_ip = ip; 292 union mips_instruction ip_data; 293 unsigned long tmp_data; 294 unsigned long *p_ip; 295 296 unsigned max_insns = info->func_size / sizeof(union mips_instruction); 297 unsigned i; 298 299 info->pc_offset = -1; 300 info->frame_size = 0; 301 302 if (!ip) 303 goto err; 304 305 if (max_insns == 0) 306 max_insns = 128U; /* unknown function size */ 307 max_insns = min(128U, max_insns); 308 309 for (i = 0; i < max_insns; i++, ip++) { 310 //保留原ip值,下方恢复ip值 311 tmp_ip = ip; 312 //union mips_instruction 结构大小为unsigned long,一条指令占的空间大小 313 p_ip = (unsigned long*)ip; 314 if(get_user(tmp_data,p_ip)) 315 { 316 printk(KERN_ERR"%s get_user error ip:0x%p ",__func__,ip); 317 return -EFAULT; 318 } 319 memcpy(&ip_data,&tmp_data,sizeof(union mips_instruction)); 320 ip = &ip_data; 321 322 if (is_jump_ins(ip)) 323 break; 324 if (!info->frame_size) { 325 if (is_sp_move_ins(ip)) 326 { 327 #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_MICROMIPS 328 if (mm_insn_16bit(ip->halfword[0])) 329 { 330 unsigned short tmp; 331 332 if (ip->halfword[0] & mm_addiusp_func) 333 { 334 tmp = (((ip->halfword[0] >> 1) & 0x1ff) << 2); 335 info->frame_size = -(signed short)(tmp | ((tmp & 0x100) ? 0xfe00 : 0)); 336 } else { 337 info->frame_size = -(signed short)(tmp & 0xf); 338 } 339 ip = (void *) &ip->halfword[1]; 340 ip--; 341 } else 342 #endif 343 info->frame_size = - ip->i_format.simmediate; 344 } 345 ip = tmp_ip; 346 continue; 347 } 348 if (info->pc_offset == -1 && is_ra_save_ins(ip)) { 349 info->pc_offset = 350 ip->i_format.simmediate / sizeof(long); 351 break; 352 } 353 //恢复原ip值,目的是不破坏函数原有框架 354 ip = tmp_ip; 355 } 356 if (info->frame_size && info->pc_offset >= 0) /* nested */ 357 return 0; 358 if (info->pc_offset < 0) /* leaf */ 359 return 1; 360 /* prologue seems boggus... */ 361 printk(KERN_ERR"%s error end ",__func__); 362 err: 363 return -1; 364 } 365 /** user_unwind_stack_by_address - 根据当前函数的pc值,计算出上一级函数的栈顶地址和当前函数的返回地址 366 * @stack_page - 线程内核栈栈顶 367 * @*sp - 保存上一级函数栈顶 368 * @pc - 当前函数的pc值,就是栈回溯过程打印的函数地址 369 * @*ra - 崩溃函数中没有调用其他函数时,是应用段错误当时的ra寄存数据,这种情况第一次栈回溯时使用 370 * 371 * returns: 372 * >0:找到当前函数返回地址,就是上一级函数中的指令地址 373 * 0: 没有找到当前函数返回地址 374 */ 375 static unsigned long user_unwind_stack_by_address(unsigned long stack_page, 376 unsigned long *sp, 377 unsigned long pc, 378 unsigned long *ra) 379 { 380 struct mips_frame_info info; 381 unsigned long size, ofs; 382 int leaf; 383 extern void ret_from_irq(void); 384 extern void ret_from_exception(void); 385 if (!stack_page) 386 return 0; 387 388 if (!user_process_lookup_size_offset(pc, &size, &ofs)) 389 { 390 user_stack_printk("%s can not find vaild user function at pc:0x%lx ",__func__,pc); 391 return 0; 392 } 393 /* 394 * Return ra if an exception occurred at the first instruction 395 */ 396 if (unlikely(ofs == 0)) { 397 pc = *ra; 398 *ra = 0; 399 return pc; 400 } 401 402 info.func = (void *)(pc - ofs); 403 info.func_size = ofs; /* analyze from start to ofs */ 404 leaf = get_frame_info(&info); 405 if (leaf < 0) 406 return 0; 407 408 //判断sp是否超出当前进程的用户空间栈底 409 if(*sp + info.frame_size > user_stack_unwind_info.thread_stack_start) 410 { 411 user_stack_printk("%s expand user thread stack ",__func__); 412 return 0; 413 } 414 415 if (leaf) 416 { 417 /* 418 * For some extreme cases, get_frame_info() can 419 * consider wrongly a nested function as a leaf 420 * one. In that cases avoid to return always the 421 * same value. 422 */ 423 pc = pc != *ra ? *ra : 0; 424 } 425 else 426 { 427 //pc = ((unsigned long *)(*sp))[info.pc_offset]; 428 unsigned long *tmp; 429 tmp = (unsigned long *)(*sp) + info.pc_offset; 430 if(get_user(pc,tmp)) 431 { 432 printk(KERN_ERR"%s get_user sp info.pc_offset error ",__func__); 433 return 0; 434 } 435 } 436 437 *sp += info.frame_size; 438 *ra = 0; 439 440 return pc; 441 } 442 /** user_unwind_stack - 根据当前函数的pc值,计算出上一级函数的栈顶地址和当前函数的返回地址 443 * @task - 当前进程task结构 444 * @*sp - 保存上一级函数栈顶 445 * @pc - 当前函数的pc值,就是栈回溯过程打印的函数地址 446 * @*ra - 崩溃函数中没有调用其他函数时,是应用段错误当时的ra寄存数据,这种情况第一次栈回溯时使用 447 * 448 * returns: 449 * >0:找到当前函数返回地址,就是上一级函数中的指令地址 450 * 0: 没有找到当前函数返回地址 451 */ 452 static unsigned long user_unwind_stack(struct task_struct *task, unsigned long *sp,unsigned long pc, unsigned long *ra) 453 { 454 unsigned long stack_page = (unsigned long)task_stack_page(task); 455 456 return user_unwind_stack_by_address(stack_page, sp, pc, ra); 457 } 458 /** show_user_backtrace - mips架构栈回溯的核心,在该函数计算和打印栈回溯的各级函数信息 459 * @task - 当前进程task结构 460 * @regs - 异常进程的struct pt_regs结构,包含栈回溯过程需要的pc、ra、sp等寄存器 461 * 462 * returns:void 463 */ 464 static void show_user_backtrace(struct task_struct *task, const struct pt_regs *regs) 465 { 466 unsigned long sp = regs->regs[29]; 467 unsigned long ra = regs->regs[31]; 468 unsigned long pc = regs->cp0_epc; 469 unsigned long where; 470 int cycle_count = 0; 471 if (!task) 472 task = user_stack_unwind_info.thread; 473 474 printk("Call Trace: "); 475 do { 476 where = pc; 477 /*如果可执行程序stirp过,并且崩溃发生在可执行程序代码段,这样第一次栈回溯时用pc寄存器值,第二次栈回溯用的ra寄存器的值。 478 如果崩溃发生在C库,C库栈回溯不受影响,但是从C库回到可执行程序代码段时,比如此时pc = user_unwind_stack(),从最后一级C库 479 函数栈中分析出函数返回地址并返回给pc,这是在可执行程序代码段,然后下次循环,user_unwind_stack()就会因为找不到pc所在的函数 480 而返回0,print_user_ip_sym()打印上一个pc值,退出while循环。*/ 481 if((0 == cycle_count) && (elf_info.elf_strip)&& (pc >= user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_start && pc <= user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_end)) 482 pc = ra; 483 else 484 pc = user_unwind_stack(task, &sp, pc, &ra); 485 486 print_user_ip_sym(where); 487 cycle_count++; 488 }while (pc); 489 printk(" "); 490 } 491 492 #elif defined CONFIG_ARM64 493 494 #define elf_sym elf64_sym 495 /** instructions_belong_to_one_fun - 判断pc1和pc2两个指令地址是否处于同一个函数 496 * @pc1 - 函数指令地址1 497 * @pc2 - 函数指令地址2 498 * 499 * returns: 500 * 1:pc1和pc2两个指令地址处于同一个函数 501 * 0:pc1和pc2两个指令地址不处于同一个函数 502 */ 503 static int instructions_belong_to_one_fun(struct elf_file_info *elf_info,unsigned long pc1,unsigned long pc2) 504 { 505 struct elf_sym *elf_fun_sym; 506 int i; 507 508 elf_fun_sym = (struct elf_sym*)elf_info->first_elf_sym; 509 510 //这里只判断pc1和pc2是否处于同一个可执行程序函数的情况,不判断是否处于同一个动态库函数的情况 511 for(i = 0;i < elf_info->section_symtab.sh_size/sizeof(struct elf_sym);i++) 512 { 513 //elf_fun_sym->st_value 是可执行程序文件中每个函数的首地址 514 if((pc1 >= elf_fun_sym->st_value) && (pc1 < elf_fun_sym->st_value + elf_fun_sym->st_size)) 515 { 516 if((pc2 >= elf_fun_sym->st_value) && (pc2 < elf_fun_sym->st_value + elf_fun_sym->st_size)) 517 return 1; 518 } 519 elf_fun_sym ++; 520 } 521 return 0; 522 } 523 /** user_unwind_frame - arm64架构从当前函数栈中分析出当前函数返回地址和和上一级函数栈的地址 524 * @frame->sp 保存上一级函数栈顶 525 * @frame->fp 保存上一级函数的栈的第二片内存地址 526 * @frame->pc 保存当前函数的返回地址 527 * 528 * returns: 529 * 0:获取frame结构成员成功 530 * <0:获取frame结构成员失败 531 */ 532 static int user_unwind_frame(struct stackframe *frame) 533 { 534 unsigned long high, low; 535 unsigned long fp = frame->fp; 536 537 low = frame->sp; 538 high = ALIGN(low, THREAD_SIZE); 539 540 //判断sp是否超出当前进程的用户空间栈底 541 if(frame->sp >= user_stack_unwind_info.thread_stack_start) 542 { 543 user_stack_printk("%s expand user thread stack ",__func__); 544 return -EFAULT; 545 } 546 547 frame->sp = fp + 0x10; 548 549 //frame->fp = *(unsigned long *)(fp); 550 //从用户空间获取上一级函数的栈的第二片内存地址 551 if(get_user(frame->fp, (unsigned long *)(fp))) 552 { 553 printk(KERN_ERR"%s get_user1 error fp:0x%lx ",__func__,fp); 554 return -EFAULT; 555 } 556 //frame->pc = *(unsigned long *)(fp + 8); 557 //从用户空间获取崩溃函数的返回地址 558 if(get_user(frame->pc, (unsigned long *)(fp + 8))) 559 { 560 printk(KERN_ERR"%s get_user2 error fp:0x%lx ",__func__,fp); 561 return -EFAULT; 562 } 563 return 0; 564 } 565 /** show_user_backtrace - arm64栈回溯的核心,在该函数计算和打印栈回溯的各级函数信息 566 * @task - 当前进程task结构 567 * @regs - 异常进程的struct pt_regs结构,包含栈回溯过程需要的pc、sp、fp等寄存器 568 * 569 * returns:void 570 */ 571 static void show_user_backtrace(struct task_struct *task, const struct pt_regs *regs) 572 { 573 struct stackframe frame; 574 int ret,cycle_count; 575 unsigned long where; 576 unsigned long second_fun; 577 struct sym_fun_info sym_func_info; 578 579 frame.fp = regs->regs[29]; 580 frame.sp = regs->sp; 581 frame.pc = regs->pc; 582 583 if(get_user(second_fun, (unsigned long *)(regs->regs[29] + 8))) 584 { 585 printk(KERN_ERR"%s get_user error fp:0x%llx sp:0x%llx ",__func__,regs->regs[29]+8,regs->sp); 586 return; 587 } 588 589 cycle_count = 0; 590 while (1) 591 { 592 /*这里的if判断用于崩溃函数test_a_没有调用其他函数的情况,正常函数lr寄存器数据和函数栈第二片内存中的数据是一致的,崩溃函数没有调用其他函数时,开始开头指令没有把lr和fp寄存器入栈,此时的fp寄存器regs->regs[29]保存的数据还是上一级函数栈的第二片内存地址,则第一片内存地址中的数据一定是再上一级的函数地址,此时与lr寄存器regs->regs[30]肯定不想等,就是下边的second_fun != regs->regs[30]。lr寄存器只要有函数调用,就保存函数返回地址。有个特例,如果崩溃函数有调用其他函数,但是崩溃位置在函数调用后,比如test_a_函数调用了printf后崩溃了,此时lr寄存器数据是printf("22")的下一条指令地址,就是lr还保持执行printf函数时的状态,看来lr寄存器的数据只在函数调用时被修改,在函数返回后不会恢复。这种情况second_fun != regs->regs[30]也成立,就是靠second_fun != regs->regs[30]函数,判断出regs->pc 和 regs->regs[30]指向的指令地址不属于同一个函数的,就可以过滤这种情况了。 593 void test_a_() 594 { 595 int *p =NULL; 596 printf("22"); 597 *p = 0; 598 } 599 */ 600 where = frame.pc; 601 if((0 == cycle_count)&& (task == current) && (second_fun != regs->regs[30]) && (0 == instructions_belong_to_one_fun(&elf_info,regs->regs[30],regs->pc))) 602 { 603 frame.pc = regs->regs[30]; 604 } 605 else 606 { 607 //获取函数的返回地址存于frame.pc和上一级函数的栈的第二片内存地址存于frame.fp 608 ret = user_unwind_frame(&frame); 609 if (ret < 0) 610 break; 611 } 612 613 //在可执行程序代码段 614 if(where >= user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_start && where < user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_end) 615 { 616 //可执行程序没有strip过 617 if(0 == elf_info.elf_strip) 618 { 619 //根据addr获取可执行程序的函数的首地址、函数指令字节数等信息,保存到user_stack_unwind.sym_info结构 620 ret = get_elf_fun_info(&sym_func_info,&elf_info,where); 621 if(ret) 622 { 623 user_stack_printk("%s get_elf_fun_info:%d error ",__func__,ret); 624 return; 625 } 626 } 627 } 628 else//在库函数代码段 629 { 630 //根据可执行程序文件和lib库文件的.dynstr和.dynsym信息分析出库函数的运行首地址和库函数首原始的偏差值 631 ret = get_lib_fun_offset(&elf_info,&lib_info); 632 if(ret) 633 { 634 user_stack_printk("%s get_lib_fun_offset:%d error ",__func__,ret); 635 return; 636 } 637 memset(&sym_func_info,0,sizeof(struct sym_fun_info)); 638 //根据addr获取库函数所处的函数首地址、函数指令字节数等信息,保存到user_stack_unwind.sym_info结构 639 ret = get_lib_fun_info(&sym_func_info,&lib_info,where,elf_info.elf_lib_fun_off); 640 if(ret) 641 { 642 /* 643 arm64 double free过程,test_a ->C库未知函数1->C库未知函数2->abort->raise,在回溯到C库未知函数2时, 644 就找不到C库函数,此时get_lib_fun_info返回-1,但是不出错返回,继续栈回溯,最后能完整回溯到可执行程序代码段,gdb做不到。 645 arm64栈回溯使用fp寄存器定位函数栈,不依赖函数函数指令首地址,所以遇到未知C库函数,照样能栈回溯。 646 */ 647 user_stack_printk("%s get_lib_fun_info:%d error ",__func__,ret); 648 //return 0; 649 } 650 } 651 cycle_count ++; 652 653 print_user_ip_sym(where); 654 } 655 } 656 #else 657 #error "unsupport architecture!!!!!!" 658 #endif 659 660 661 /** print_user_ip_sym - 打印pc所处函数的名字及相对函数指令首地址的偏移等信息 662 * @pc - 栈回溯过程每一级函数的指令地址 663 * 664 * returns: 665 * 1:找到pc所处的函数 666 * 0:没有找到pc所处的函数 667 */ 668 static int print_user_ip_sym(unsigned long pc) 669 { 670 unsigned int fun_size,pc_off; 671 struct sym_fun_info *sym_info; 672 673 //user_stack_unwind_info.sym_info 保存库函数的指令信息,新的改造,也保存可执行程序的自身函数信息 674 sym_info = &user_stack_unwind_info.sym_info; 675 if(pc >= sym_info->fun_first_instruct_addr && pc <= sym_info->fun_end_instruct_addr) 676 { 677 fun_size = sym_info->fun_end_instruct_addr - sym_info->fun_first_instruct_addr; 678 pc_off = pc - sym_info->fun_first_instruct_addr; 679 680 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 681 printk(KERN_ALERT"<0x%010lx> %s() 0x%x/0x%x ",pc,sym_info->name,pc_off,fun_size); 682 #else 683 printk(KERN_ALERT"<0x%08lx> %s() 0x%x/0x%x ",pc,sym_info->name,pc_off,fun_size); 684 #endif 685 memset(sym_info,0x00,sizeof(struct sym_fun_info)); 686 return 1; 687 } 688 else if(elf_info.elf_strip)//可执行程序没有strip过 689 { 690 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 691 printk(KERN_ALERT"<0x%010lx> xxxxxx ",pc); 692 #else 693 printk(KERN_ALERT"<0x%08lx> xxxxxx ",pc); 694 #endif 695 return 1; 696 } 697 else 698 user_stack_printk("cat not find valid user function "); 699 700 return 0; 701 } 702 /** read_elf_section_info - 读取elf可执行程序和库文件的 .dynsym .dynstr .plt .got.plt section的数据保存到struct elf_file_info *elf_info结构, 703 * @elf_file - elf可执行程序和库文件的struct file结构 704 * @elf_info - 该结构体成员保存elf文件的.dynsym .dynstr .plt .got.plt section的数据 705 * @is_elf_file - 1:elf可执行程序 0:elf库文件 706 * 707 * returns: 708 * 0:读取elf文件的.dynsym .dynstr .plt .got.plt section的数据成功 709 * <0:读取失败 710 */ 711 static int read_elf_section_info(struct file *elf_file,struct elf_file_info *elf_info,int is_elf_file) 712 { 713 // struct elf_shdr *section_head; 714 struct elf_shdr *p_section = NULL; 715 char *section_name; 716 int i; 717 long retval; 718 struct elfhdr elf_head; 719 unsigned char *section_data = NULL; 720 721 //读取elf文件头 722 retval = kernel_read(elf_file,0,(unsigned char *)&elf_head,sizeof(struct elfhdr)); 723 if (retval <= 0) { 724 retval = -EIO; 725 goto err; 726 } 727 section_data = kmalloc(sizeof(struct elf_shdr)*elf_head.e_shnum,GFP_KERNEL); 728 if(!section_data) 729 { 730 retval = -ENOMEM; 731 printk(KERN_ERR"%s kmalloc fail 1 ",__func__); 732 goto err; 733 } 734 //读取所有section结构体信息到section_data数组 735 retval = kernel_read(elf_file,elf_head.e_shoff,section_data,sizeof(struct elf_shdr)*elf_head.e_shnum); 736 if (retval <= 0) { 737 retval = -EIO; 738 goto err; 739 } 740 //p_section 指向第一个section首地址 741 p_section = (struct elf_shdr *)section_data; 742 //section指向编号是elf_head->e_shstrndx的section,这个section对应的数据是每个section的名字字符串集合 743 p_section += elf_head.e_shstrndx; 744 section_name = kmalloc(p_section->sh_size,GFP_KERNEL); 745 if(!section_name) 746 { 747 retval = -ENOMEM; 748 printk(KERN_ERR"%s kmalloc fail 2 ",__func__); 749 goto err; 750 } 751 752 //section_name 指向编号是elf_head->e_shstrndx的section的数据区首地址,这个section的数据各个section的名字字符串。p_section->sh_offset是该section对应的数据的偏移 753 retval = kernel_read(elf_file,p_section->sh_offset,section_name,p_section->sh_size); 754 if (retval <= 0) { 755 user_stack_printk("%s line:%d kernel_read fail ",__func__,__LINE__); 756 retval = -EIO; 757 goto err; 758 } 759 //指向第一个section结构 760 p_section = (struct elf_shdr *)section_data; 761 for(i = 0;i < elf_head.e_shnum;i++) 762 { 763 //.dynsym 段 每个section 的 sh_name 是该section名字字符串的索引 764 if(/*SHT_SYMTAB == p_section->sh_type && */strcmp(".dynsym",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name]) == 0) 765 { 766 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 767 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_offset:0x%llx sh_size:0x%llx ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 768 #else 769 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_offset:0x%x sh_size:0x%x ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 770 #endif 771 memcpy(&elf_info->section_dynsym,p_section,sizeof(struct elf_shdr));//保存.dynstr 段的信息 772 elf_info->first_lib_sym = kmalloc(p_section->sh_size,GFP_KERNEL);// 773 if(!elf_info->first_lib_sym) 774 goto err; 775 //从dynsym段指定的文件偏移地址复制dynsym段的数据到 elf_info.first_lib_sym,这些数据就是struct elf_sym结构的集合,每一个struct elf32_sym结构代表一个函数信息,包括该函数名字符串索引、函数默认运行地址、函数指令字节数 776 retval = kernel_read(elf_file,p_section->sh_offset,(unsigned char *)elf_info->first_lib_sym,p_section->sh_size); 777 if (retval <= 0) { 778 user_stack_printk("%s line:%d kernel_read fail d ",__func__,__LINE__); 779 retval = -EIO; 780 goto err; 781 } 782 } 783 //.dynstr 段 784 else if(/*SHT_STRTAB == p_section->sh_type && */strcmp(".dynstr",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name]) == 0) 785 { 786 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 787 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_offset:0x%llx sh_size:0x%llx ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 788 #else 789 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_offset:0x%x sh_size:0x%x ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 790 #endif 791 memcpy(&elf_info->section_dynstr,p_section,sizeof(struct elf_shdr));//保存.dynstr 段section结构 792 elf_info->elf_lib_fun_str = kmalloc(p_section->sh_size,GFP_KERNEL);// 793 if(!elf_info->elf_lib_fun_str) 794 goto err; 795 //从dynstr段指定的文件偏移地址复制函数字符串数据到 elf_info->elf_lib_fun_str 796 retval = kernel_read(elf_file,p_section->sh_offset,elf_info->elf_lib_fun_str,p_section->sh_size); 797 if (retval <= 0) { 798 user_stack_printk("%s line:%d kernel_read fail d ",__func__,__LINE__); 799 retval = -EIO; 800 goto err; 801 } 802 } 803 //.plt段,plt段是库函数跳转表,我们执行的printf库函数,是先跳转到这个段的printf@GLIBC_2.0 函数,然后跳转到got段函数表,这里是每个库函数的重定向后的函数首地址,在这里运行到c库真实的printf函数 804 else if(/*SHT_STRTAB == p_section->sh_type && */strcmp(".plt",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name]) == 0) 805 { 806 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 807 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_addr:0x%llx sh_offset:0x%llx sh_size:0x%llx ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_addr,p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 808 #else 809 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_addr:0x%x sh_offset:0x%x sh_size:0x%x ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_addr,p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 810 #endif 811 } 812 //.got段,该段的sh_addr成员是程序运行后.got.plt段的用户空间内存地址,这片内存的数据是plt段库函数的重定向后库函数首地址 813 else if(/*SHT_STRTAB == p_section->sh_type && */strcmp(".got.plt",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name]) == 0) 814 { 815 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 816 user_stack_printk("%s find sh_addr:0x%llx ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_addr); 817 #else 818 user_stack_printk("%s find sh_addr:0x%x ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_addr); 819 #endif 820 elf_info->got_addr = (unsigned long *)p_section->sh_addr; 821 } 822 823 //是elf可执行程序 824 if(is_elf_file) 825 { 826 //.symtab 段,可执行程序自己的函数的一个个 elf_sym 结构 827 if(/*SHT_SYMTAB == p_section->sh_type && */strcmp(".symtab",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name]) == 0) 828 { 829 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 830 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_offset:0x%llx sh_size:0x%llx ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 831 #else 832 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_offset:0x%x sh_size:0x%x ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 833 #endif 834 memcpy(&elf_info->section_symtab,p_section,sizeof(struct elf_shdr));//保存.symtab 段section结构 835 elf_info->first_elf_sym = kmalloc(p_section->sh_size,GFP_KERNEL);// 836 if(!elf_info->first_elf_sym) 837 goto err; 838 //从.symtab段指定的文件偏移地址读取.symtab段的数据到 elf_info->first_elf_sym,,这些数据就是struct elf_sym结构的集合,每一个struct elf_sym结构代表一个函数信息,包括该函数名字符串索引、函数默认运行地址、函数指令字节数 839 retval = kernel_read(elf_file,p_section->sh_offset,(unsigned char *)elf_info->first_elf_sym,p_section->sh_size); 840 if (retval <= 0) { 841 user_stack_printk("%s line:%d kernel_read fail d ",__func__,__LINE__); 842 retval = -EIO; 843 goto err; 844 } 845 } 846 //.strtab 段,可执行程序自己的函数名字字符串存储在这里 847 else if(/*SHT_STRTAB == p_section->sh_type && */strcmp(".strtab",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name]) == 0) 848 { 849 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 850 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_offset:0x%llx sh_size:0x%llx ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 851 #else 852 user_stack_printk("%s find ,section sh_offset:0x%x sh_size:0x%x ",§ion_name[p_section->sh_name],p_section->sh_offset,p_section->sh_size); 853 #endif 854 elf_info->elf_fun_str = kmalloc(p_section->sh_size,GFP_KERNEL);// 855 if(!elf_info->elf_fun_str) 856 goto err; 857 //从.strtab段指定的文件偏移地址读取函数字符串数据到 elf_info->elf_fun_str 858 retval = kernel_read(elf_file,p_section->sh_offset,elf_info->elf_fun_str,p_section->sh_size); 859 if (retval <= 0) { 860 user_stack_printk("%s line:%d kernel_read fail d ",__func__,__LINE__); 861 retval = -EIO; 862 goto err; 863 } 864 865 elf_info->elf_strip = 0; 866 } 867 868 } 869 p_section++; 870 } 871 872 retval = 0; 873 err: 874 if(section_data) 875 kfree(section_data); 876 return retval; 877 } 878 /** get_lib_fun_offset - 计算库函数的实际运行首地址和原始首地址之差保存到 elf_info->elf_lib_fun_off 879 * @elf_info - 可执行程序的struct elf_file_info 结构 880 * @lib_info - 库文件的struct elf_file_info 结构 881 * 882 * returns: 883 * 0:计算出库函数的实际运行首地址和原始首地址之差 884 * <0:没有计算库函数的实际运行首地址和原始首地址之差 885 * 886 *note:这个函数的功能详细描述:根据可执行程序的got段内存中存储的库函数strcmp运行地址got_lib_fun_val(假设got段第四片内存保存的数据是strcmp库函数的运行地址,got_lib_fun_val保存这个运行地址),然后在lib库文件中,.dynstr段搜索函数名字字符串是"strcmp"的函数,而.dynsym段保存的数据————函数struct elf_sym结构与 .dynstr段的函数名字字符串也是一一对应的。 887 比如, 假如.dynstr 段的第一个函数名字字符串是 "strcmp", .dynsym段的第一个struct elf_sym结构就是strcmp库函数的,该结构的st_value是strcmp库函数的俄原始地址,st_size是库函数的指令字节数。 888 知道了strcmp库函数的运行地址got_lib_fun_val,又在lib库文件中.dynstr段找到了strcmp的字符串,同样的偏移找到了 .dynsym段strcmp库函数的struct elf_sym结构,就知道了它的原始函数地址st_value。got_lib_fun_val-st_value就是库函数的运行地址和原始地址的差值off,应该适用于所有库函数。之后我知道一个库函数的st_value,就知道了它的运行地址首地址st_value+off,函数指令结束地址end,那知道任何一个库函数中的崩溃地址pc, pc > st_value+off并且 pc < end时,就知道崩溃库函数指令pc处于哪个库函数了,当然也知道它的名字字符串。 889 有一点需要注意,库函数的运行地址和原始地址的低12位数据是一样的,测试证实了这一点,我觉得这与PAGE_SIZE是2的12次方有关。 890 */ 891 static int get_lib_fun_offset(struct elf_file_info *elf_info,struct elf_file_info *lib_info) 892 { 893 struct elf_sym *elf_lib_sym,*lib_sym; 894 //section_dynstr first_lib_sym; 895 unsigned char *lib_fun_name,*elf_lib_fun_name; 896 unsigned long *p_got_lib_fun; 897 unsigned long got_lib_fun_val = 0; 898 int i; 899 int ret = -1; 900 901 if(elf_info->elf_lib_fun_off) 902 { 903 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"%s elf_lib_fun_off already ok ",__func__); 904 return 0; 905 } 906 907 //可执行程序的 908 elf_lib_sym = (struct elf_sym*)elf_info->first_lib_sym; 909 elf_lib_fun_name = (char *)elf_info->elf_lib_fun_str; 910 p_got_lib_fun = (unsigned long *)elf_info->got_addr;//这个是用户态的地址,要用get_user复制数据 911 #ifdef CONFIG_MIPS 912 p_got_lib_fun += 2;//函数指针偏移到第3片内存,前几片内存存储的是got段相关信息,第3片内存开始存储的数据才是库函数的首地址数据 913 #else 914 p_got_lib_fun += 3; 915 #endif 916 917 //库文件的 918 lib_sym = (struct elf_sym *)lib_info->first_lib_sym; 919 lib_fun_name = (char *)lib_info->elf_lib_fun_str; 920 921 //调试可执行程序用到的库函数信息 922 #if OPEN_PRINT 923 //elf_info->section_dynsym.sh_size 是elf库文件.dynsym段总大小,除以struct elf_sym大小,就是库函数总数,一个函数信息用一个struct elf_sym结构表示 924 for(i = 0;i < elf_info->section_dynsym.sh_size/sizeof(struct elf_sym);i++) 925 { 926 //从用户空间的got段内存复制库函数的首地址到got_lib_fun_val,这个地址是重定向后的地址,真实的库函数指令首地址 927 if(get_user(got_lib_fun_val,p_got_lib_fun)) 928 { 929 printk(KERN_ERR"%s get_user error 0x%p ",__func__,p_got_lib_fun); 930 return -EFAULT; 931 } 932 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG" %s got_lib_fun_val:0x%lx p_got_lib_fun:0x%p %s ",__func__,got_lib_fun_val,p_got_lib_fun,&elf_lib_fun_name[elf_lib_sym->st_name]); 933 934 #ifdef CONFIG_MIPS 935 if((got_lib_fun_val > 0x70000000) && (STT_FUNC == ELF_ST_TYPE(elf_lib_sym->st_info))) 936 #elif defined CONFIG_ARM64 937 //加上STT_FUNC限制,必须是func类型,测试发现_ITM_deregisterTMCIoneTab函数干扰,但是他的属性是NOTYPE,他也是.dynsym段的成员 938 if((got_lib_fun_val > 0x7000000000) && (STT_FUNC == ELF_ST_TYPE(elf_lib_sym->st_info))) 939 #else 940 #error "not support !!!!!" 941 #endif 942 { 943 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"!!!%s elf_info find %s got_lib_fun_val:0x%lx p_got_lib_fun:0x%p ",__func__,&elf_lib_fun_name[elf_lib_sym->st_name],got_lib_fun_val,p_got_lib_fun); 944 //指向.plt.got区下一片内存地址,.plt.got区的内存地址,amr64从第四片内存开始,都是库函数的运行地址,假设所有库函数都运行过了。而可执行程序文件的.dynsym区除了库函数,还有NOTIFY属性的干扰。所以elf_lib_sym++每次都执行,p_got_lib_fun++只有是有效库函数时才执行。 945 //p_got_lib_fun++;//指向下一个库函数首指令地址所在内存 946 } 947 if(STT_FUNC == ELF_ST_TYPE(elf_lib_sym->st_info)) 948 p_got_lib_fun++;//指向下一个库函数首指令地址所在内存 949 950 elf_lib_sym ++;//指向像一个库函数 struct elf_sym 结构 951 } 952 953 elf_lib_sym = (struct elf_sym*)elf_info->first_lib_sym; 954 elf_lib_fun_name = (char *)elf_info->elf_lib_fun_str; 955 p_got_lib_fun = (unsigned long *)elf_info->got_addr;//这个是用户态的地址,要用get_user复制数据 956 #ifdef CONFIG_MIPS 957 p_got_lib_fun += 2; 958 #else 959 p_got_lib_fun += 3; 960 #endif 961 #endif 962 963 //elf_info->section_dynsym.sh_size 是elf库文件.dynsym段总大小,除以struct elf_sym大小,就是库函数总数,一个函数信息用一个struct elf_sym结构表示 964 for(i = 0;i < elf_info->section_dynsym.sh_size/sizeof(struct elf_sym);i++) 965 { 966 //从用户空间的got段内存复制库函数的首地址到got_lib_fun_val,这个地址是重定向后的地址,真实的库函数指令首地址 967 if(get_user(got_lib_fun_val,p_got_lib_fun)) 968 { 969 printk(KERN_ERR"%s get_user error 0x%p ",__func__,p_got_lib_fun); 970 return -EFAULT; 971 } 972 973 #ifdef CONFIG_MIPS 974 if((got_lib_fun_val > 0x70000000) && (STT_FUNC == ELF_ST_TYPE(elf_lib_sym->st_info))) 975 #elif defined CONFIG_ARM64 976 //加上STT_FUNC限制,必须是func类型,测试发现_ITM_deregisterTMCIoneTab函数干扰,但是他的属性是NOTYPE,他也是.dynsym段的成员 977 if((got_lib_fun_val > 0x7000000000) && (STT_FUNC == ELF_ST_TYPE(elf_lib_sym->st_info))) 978 #else 979 #error "not support !!!!!" 980 #endif 981 { 982 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"%s elf_info find %s got_lib_fun_val:0x%lx ",__func__,&elf_lib_fun_name[elf_lib_sym->st_name],got_lib_fun_val); 983 //p_got_lib_fun++;//指向下一个库函数首指令地址所在内存 984 break; 985 } 986 987 if(STT_FUNC == ELF_ST_TYPE(elf_lib_sym->st_info)) 988 p_got_lib_fun++;//指向下一个库函数首指令地址所在内存 989 990 elf_lib_sym ++;//指向像一个库函数struct elf_sym结构 991 } 992 993 //此时elf_lib_sym指向的可执行程序中的.dynsym段用到的库函数的struct elf_sym结构,got_lib_fun_val是该库函数的 994 //运行指令首地址,&elf_lib_fun_name[elf_lib_sym->st_name]就是该库函名字符串 995 996 /*在库文件中的.dynstr段和.dynsym段分析与 &elf_lib_fun_name[elf_lib_sym->st_name] 库函数名字字符串一致的 997 库函数,找到它的struct elf_sym *lib_sym结构,取出它的st_value就是库函数的原始首地址,与got_lib_fun_val的 998 差值就是库函数的运行首地址与原始首地址的偏差*/ 999 1000 for(i = 0;i < lib_info->section_dynsym.sh_size/sizeof(struct elf_sym);i++) 1001 { 1002 if(0 == strcmp(&elf_lib_fun_name[elf_lib_sym->st_name],&lib_fun_name[lib_sym->st_name])) 1003 { 1004 elf_info->elf_lib_fun_off = got_lib_fun_val - lib_sym->st_value; 1005 1006 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 1007 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"%s lib_info find %s st_value:0x%llx elf_lib_fun_off:0x%lx ",__func__,&lib_fun_name[lib_sym->st_name],lib_sym->st_value,elf_info->elf_lib_fun_off); 1008 #else 1009 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"%s lib_info find %s st_value:0x%x elf_lib_fun_off:0x%lx ",__func__,&lib_fun_name[lib_sym->st_name],lib_sym->st_value,elf_info->elf_lib_fun_off); 1010 #endif 1011 1012 ret =0; 1013 break; 1014 } 1015 1016 lib_sym++; 1017 } 1018 1019 if(0 != ret) 1020 user_stack_printk("%s cat not find match lib fun name from elf_lib_sym ",__func__); 1021 return ret; 1022 } 1023 /** get_lib_fun_info - 根据addr计算出它所处于的库函数的名字、函数运行首地址、函数运行结束地址 1024 * @sym_lib_info - 保存库函数的名字、函数运行首地址、函数运行结束地址 1025 * @lib_info - 该结构体成员主要包含elf库文件的 dynsym、dynstr section数据的首地址 1026 * @addr - 栈回溯过程的函数地址 1027 * @lib_fun_offset - 库函数的运行首地址和结束地址之差 1028 * 1029 * returns: 1030 * 0: 根据addr计算出它所处于的库函数 1031 * <0: 没有找到addr所处的库函数 1032 */ 1033 static int get_lib_fun_info(struct sym_fun_info * sym_lib_info,struct elf_file_info *lib_info,unsigned long addr,unsigned long lib_fun_offset) 1034 { 1035 struct elf_sym *lib_sym; 1036 unsigned char *lib_fun_name; 1037 int i; 1038 int ret = -1; 1039 1040 lib_sym = (struct elf_sym*)lib_info->first_lib_sym; 1041 lib_fun_name = (char *)lib_info->elf_lib_fun_str; 1042 1043 //elf_info->section_dynsym.sh_size 是elf库文件.dynsym段总大小,除以struct elf_sym大小,就是库函数总数,一个函数信息用一个struct elf_sym结构表示 1044 for(i = 0;i < lib_info->section_dynsym.sh_size/sizeof(struct elf_sym);i++) 1045 { 1046 //lib_sym->st_value 是lib库文件中每个库函数的默认函数首地址,lib_sym->st_value + lib_fun_offset 是库函数重定向后的函数首地址 1047 if((addr >= lib_sym->st_value + lib_fun_offset) && (addr < lib_sym->st_value + lib_fun_offset + lib_sym->st_size)) 1048 { 1049 //lib_fun_name 是库函数名字字符串集合首地址,elf_lib_sym->st_name是当前函数名字字符串在lib_fun_name数组的索引 1050 strncpy(sym_lib_info->name,&lib_fun_name[lib_sym->st_name],FUN_NAME_LEN); 1051 sym_lib_info->fun_first_instruct_addr = lib_sym->st_value + lib_fun_offset;//库函数指令首地址 1052 sym_lib_info->fun_end_instruct_addr = lib_sym->st_value + lib_fun_offset + lib_sym->st_size;//库函数指令结束地址 1053 memcpy(&user_stack_unwind_info.sym_info,sym_lib_info,sizeof(struct sym_fun_info)); 1054 1055 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 1056 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"%s find %s first_fun_addr:0x%lx size:0x%llx st_value:0x%llx ",__func__,sym_lib_info->name,sym_lib_info->fun_first_instruct_addr,lib_sym->st_size,lib_sym->st_value); 1057 #else 1058 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"%s find %s first_fun_addr:0x%lx size:0x%x st_value:0x%x ",__func__,sym_lib_info->name,sym_lib_info->fun_first_instruct_addr,lib_sym->st_size,lib_sym->st_value); 1059 #endif 1060 /*测试证实,double free栈回溯时,第一级函数是gsignal或者raise,这两个函数的st_value和st_size完全一样,就是两个不同的函数 1061 名字,但是对应同一个函数。但是gsignal会先搜索到,gdb此时栈回溯时打印的是raise函数,所以这里就不直接return 0,而是一直搜索, 1062 使用最后找到的库函数*/ 1063 ret = 0; 1064 return 0; 1065 } 1066 1067 lib_sym ++;//指向下一个库函数struct elf_sym结构 1068 } 1069 return ret; 1070 } 1071 /** get_elf_fun_info - 根据addr计算出它所处于的可执行程序中的函数名字、函数运行首地址、函数运行结束地址 1072 * @sym_lib_info - 保存函数的名字、函数运行首地址、函数运行结束地址 1073 * @lib_info - 该结构体成员主要包含elf可执行程序文件的 dynsym、dynstr section数据的首地址 1074 * @addr - 栈回溯过程的函数地址 1075 * 1076 * returns: 1077 * 0: 根据addr计算出它所处于的函数 1078 * <0: 没有找到addr所处的函数 1079 */ 1080 static int get_elf_fun_info(struct sym_fun_info * elf_sym_info,struct elf_file_info *elf_info,unsigned long addr) 1081 { 1082 struct elf_sym *elf_fun_sym; 1083 unsigned char *elf_fun_name; 1084 int i; 1085 int ret = -1; 1086 1087 elf_fun_sym = (struct elf_sym*)elf_info->first_elf_sym; 1088 elf_fun_name = (char *)elf_info->elf_fun_str; 1089 1090 //elf_info->section_dynsym.sh_size 是elf文件.dynsym段总大小,除以struct elf_sym大小,就是函数总数,一个函数信息用一个struct elf_sym结构表示 1091 for(i = 0;i < elf_info->section_symtab.sh_size/sizeof(struct elf_sym);i++) 1092 { 1093 //elf_fun_sym->st_value 是可执行程序文件中每个函数的函数首地址 1094 if((addr >= elf_fun_sym->st_value) && (addr < elf_fun_sym->st_value + elf_fun_sym->st_size)) 1095 { 1096 //elf_fun_name 是函数名字字符串集合首地址,elf_lib_sym->st_name是当前函数名字字符串在lib_fun_name数组的索引 1097 strncpy(elf_sym_info->name,&elf_fun_name[elf_fun_sym->st_name],FUN_NAME_LEN); 1098 elf_sym_info->fun_first_instruct_addr = elf_fun_sym->st_value;//函数指令首地址 1099 elf_sym_info->fun_end_instruct_addr = elf_fun_sym->st_value + elf_fun_sym->st_size;//函数指令结束地址 1100 memcpy(&user_stack_unwind_info.sym_info,elf_sym_info,sizeof(struct sym_fun_info)); 1101 1102 #ifdef CONFIG_ARM64 1103 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"%s find %s first_fun_addr:0x%lx size:0x%llx st_value:0x%llx ",__func__,elf_sym_info->name,elf_sym_info->fun_first_instruct_addr,elf_fun_sym->st_size,elf_fun_sym->st_value); 1104 #else 1105 user_stack_printk(KERN_DEBUG"%s find %s first_fun_addr:0x%lx size:0x%x st_value:0x%x ",__func__,elf_sym_info->name,elf_sym_info->fun_first_instruct_addr,elf_fun_sym->st_size,elf_fun_sym->st_value); 1106 #endif 1107 ret = 0; 1108 return 0; 1109 } 1110 1111 elf_fun_sym ++;//指向下一个函数struct elf_sym结构 1112 } 1113 return ret; 1114 } 1115 /** get_elflib_path_file_name - 根据传入的addr这个某个库函数指令地址计算出属于哪个库文件 1116 * @task - 当前栈回溯进程 1117 * @addr - 与栈回溯有关的某个库函数指令地址 1118 * 1119 * returns: 1120 * NULL:没有找到与addr构成文件映射的库文件 1121 * 其他:与addr所在内存构成文件映射的库文件名字字符串 1122 */ 1123 static char *get_elflib_path_file_name(struct task_struct *task,unsigned long addr) 1124 { 1125 struct vm_area_struct *vma; 1126 char buf[50]; 1127 char *filename; 1128 //基本原理是,根据传入的addr在进程vma链表里搜索,找到地址符合的vma 1129 vma = find_vma(task->mm,addr); 1130 if(NULL == vma) 1131 { 1132 printk(KERN_ERR"cat not find valid elf_lib file at addr:0x%lx ",addr); 1133 return NULL; 1134 } 1135 if(vma && vma->vm_file) 1136 { 1137 filename = d_path(&vma->vm_file->f_path,buf, sizeof(buf)); 1138 printk("elflib file path: %s ",filename); 1139 return filename; 1140 } 1141 return NULL; 1142 } 1143 /** get_elf_path_file - 得到异常可执行程序的文件名字 1144 * @task - 栈回溯进程的task结构 1145 * @text_start - 可执行程序代码段首地址 1146 * @text_end - 可执行程序代码段结束地址 1147 * 1148 * returns: 1149 * NULL:没有找到可执行程序文件 1150 * 其他:可执行程序的文件名称 1151 */ 1152 static char *get_elf_path_file(struct task_struct *task,unsigned long *text_start,unsigned long *text_end) 1153 { 1154 struct vm_area_struct *vma; 1155 struct mm_struct *mm; 1156 char buf[50]; 1157 char *filename; 1158 1159 mm = get_task_mm(task); 1160 if(!mm) 1161 return NULL; 1162 1163 //进程的用户空间vma链表挂在mm->mmap起始的vma里,第一个vma应该是进程elf文件路径 1164 vma = mm->mmap; 1165 if(vma && vma->vm_file) 1166 { 1167 filename = d_path(&vma->vm_file->f_path,buf, sizeof(buf)); 1168 printk("elf file path: %s ",filename); 1169 //可执行程序的代码段起始地址和结束地址,这个vma是可执行程序应用空间的第一个vma,第一个vma就是text段 1170 *text_start = vma->vm_start; 1171 *text_end = vma->vm_end; 1172 return filename; 1173 } 1174 return NULL; 1175 } 1176 /** get_file_size - 内核态得到文件大小 1177 * @file - 文件的struct file结构 1178 * 1179 * returns: 1180 * -1:获取文件大小失败 1181 * 其他:文件大小 1182 */ 1183 static long get_file_size(struct file *file) 1184 { 1185 struct kstat st; 1186 if (vfs_getattr(&file->f_path, &st)) 1187 return -1; 1188 if (!S_ISREG(st.mode)) 1189 return -1; 1190 if (st.size != (long)st.size) 1191 return -1; 1192 return st.size; 1193 } 1194 /** user_stack_backstrace - 内核对异常应用栈回溯的入口函数 1195 * @regs - 栈回溯进程当时的struct pt_regs结构 1196 * @task - 栈回溯进程的结构 1197 * 1198 * returns: 1199 * 0:栈回溯过程没有报错 1200 * <0:栈回溯过程发生报错 1201 */ 1202 int user_stack_backstrace(struct pt_regs *regs,struct task_struct *task) 1203 { 1204 char elf_path_name[100],lib_path_name[100]; 1205 int retval = 0; 1206 unsigned long text_start,text_end; 1207 unsigned long addr; 1208 mm_segment_t oldfs; 1209 struct file *elf_file = NULL; 1210 struct file *lib_file = NULL; 1211 1212 printk(KERN_ALERT"user thread:%s pid:%d stack strace ",current->comm,current->pid); 1213 1214 //mutex_init(&user_stack_unwind_info.stack_backstrace_lock); 1215 1216 strncpy(elf_path_name,get_elf_path_file(current,&text_start,&text_end),sizeof(elf_path_name)); 1217 if(elf_path_name[0] == '�') 1218 { 1219 printk(KERN_ERR"cat not find elf path file "); 1220 retval = -ENOEXEC; 1221 goto err; 1222 } 1223 1224 memset(&user_stack_unwind_info,0,sizeof(struct user_stack_unwind)); 1225 memset(&elf_info,0,sizeof(struct elf_file_info)); 1226 memset(&lib_info,0,sizeof(struct elf_file_info)); 1227 elf_info.elf_strip = 1;//初值先默认strip过,如果read_elf_section_info发现有strtab段再清0 1228 1229 user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_start = text_start; 1230 user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_end = text_end; 1231 user_stack_unwind_info.thread_stack_start = task->mm->start_stack; 1232 user_stack_unwind_info.thread = task; 1233 1234 oldfs = get_fs(); 1235 set_fs(KERNEL_DS); 1236 1237 elf_file = open_exec(elf_path_name); 1238 retval = PTR_ERR(elf_file); 1239 if (IS_ERR(elf_file)) 1240 { 1241 printk(KERN_ERR"open elf file:%s fail ",elf_path_name); 1242 retval = -ENOEXEC; 1243 goto err; 1244 } 1245 printk("%s size:%ld ",elf_path_name,get_file_size(elf_file)); 1246 1247 #ifdef CONFIG_MIPS 1248 addr = regs->cp0_epc; 1249 #else 1250 addr = regs->pc; 1251 #endif 1252 1253 //崩溃地址在库中 1254 if(addr > user_stack_unwind_info.elf_text_end) 1255 { 1256 strncpy(lib_path_name,get_elflib_path_file_name(user_stack_unwind_info.thread,addr),sizeof(lib_path_name)); 1257 lib_file = open_exec(lib_path_name); 1258 retval = PTR_ERR(lib_file); 1259 if (IS_ERR(lib_file)) 1260 { 1261 printk(KERN_ERR"open lib file:%s fail ",lib_path_name); 1262 retval = -ENOEXEC; 1263 goto err; 1264 } 1265 //获取动态库的symtab、dynsym、dynstr、symstr、plt、got.plt等section的数据 1266 retval = read_elf_section_info(lib_file,&lib_info,0); 1267 if(retval) 1268 { 1269 goto err; 1270 } 1271 } 1272 1273 //获取可执行程序的symtab、dynsym、dynstr、symstr、plt、got.plt等section的数据 1274 retval = read_elf_section_info(elf_file,&elf_info,1); 1275 if(retval) 1276 { 1277 goto err; 1278 } 1279 1280 set_fs(oldfs); 1281 1282 show_user_backtrace(current,regs); 1283 1284 retval = 0; 1285 1286 err: 1287 1288 if(elf_info.first_lib_sym) 1289 kfree(elf_info.first_lib_sym); 1290 if(elf_info.elf_lib_fun_str) 1291 kfree(elf_info.elf_lib_fun_str); 1292 if(elf_info.first_elf_sym) 1293 kfree(elf_info.first_elf_sym); 1294 if(elf_info.elf_fun_str) 1295 kfree(elf_info.elf_fun_str); 1296 1297 if(lib_info.first_lib_sym) 1298 kfree(lib_info.first_lib_sym); 1299 if(lib_info.elf_lib_fun_str) 1300 kfree(lib_info.elf_lib_fun_str); 1301 1302 if (elf_file) 1303 fput(elf_file); 1304 if (lib_file) 1305 fput(lib_file); 1306 return retval; 1307 } 1308 EXPORT_SYMBOL(user_stack_backstrace);
使用方法:
#内核对异常应用栈回溯基本方法
1 将 user_stack_unwind.c 编译进内核
2 内核对应用段错误栈回溯实现方法:arm64架构,在 do_page_fault->__do_user_fault 函数中,添加 user_stack_backstrace(regs,current)。mips架构,do_page_fault 函数,if (user_mode(regs))分支里添加,user_stack_backstrace(regs,current)。
3 内核对应用double free 问题栈回溯实现方法: do_send_specific() 函数最后添加,if(SIGABRT == sig) user_stack_backstrace(task_pt_regs(current),current)。arm64架构对double free问题能完整栈回溯,mips架构由于栈回溯原理问题,栈回溯过程会出错返回。
4 其他应用,内核对应用程序所有进程/线程栈回溯,对调试偶然出现的应用程序锁死,实时观察应用程序应用层函数调用流程,有比较大的用处。这个功能目前在开发中。
