一、加载Spring配置文件
我们首先指定我们需要加载的Spring配置文件,在tomcat容器启动后,会寻找项目中的web.xml文件,加载其中的信息,
并创建一个ServletContext上下文对象,以后再web应用中可以获得其中的值。
1.1 最先加载的就是<context-param>节点
该节点加载我们的Spring配置文件,配置文件中是我们需要往Spring容器中注册的Bean对象配置。
有两种加载方式,如果在web.xml中不指定<context-param>,会默认去加载/WEB-INF/下的ApplicationContext.xml。
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/config/application-context.xml
/WEB-INF/config/zxw/zxw-context.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
web.xml的配置中<context-param>配置作用:
1. 启动一个WEB项目的时候,容器(如:Tomcat)会去读它的配置文件web.xml.读两个节点: <listener></listener> 和 <context-param></context-param>2.紧接着,容器创建一个ServletContext(上下文),这个WEB项目所有部分都将共享这个上下文.3.容器将<context-param></context-param>转化为键值对,并交给ServletContext.4.容器创建<listener></listener>中的类实例,即创建监听.5.在监听中会有contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent args)初始化方法,在这个方法中获得ServletContext = ServletContextEvent.getServletContext();
context-param的值 = ServletContext.getInitParameter("context-param的键");6.得到这个context-param的值之后,你就可以做一些操作了.注意,这个时候你的WEB项目还没有完全启动完成.这个动作会比所有的Servlet都要早.
换句话说,这个时候,你对<context-param>中的键值做的操作,将在你的WEB项目完全启动之前被执行.7.举例.你可能想在项目启动之前就打开数据库.
那么这里就可以在<context-param>中设置数据库的连接方式,在监听类中初始化数据库的连接.
1.2 加载完配置文件后,需要配置监听器,触发监听事件。
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.util.IntrospectorCleanupListener</listener-class>
</listener>
监听器的作用是监听ServletContext的对象是否创建,web容器一旦启动,就会创建一个ServletContext对象,所以监听器一定会触发,从而执行监听器的contextInitialized方法。方法看Spring源码如下
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
//执行的监听器方法
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
web.xml
1 <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC 2 "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" 3 "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > 4 5 <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 6 xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" 7 xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd 8 http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"> 9 10 <!-- 项目名称 --> 11 <display-name>spring nacos demo</display-name> 12 13 <!-- 加载spring的xml配置文件到 spring的上下文容器中,配置文件位置和名称:默认为/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml 15 在param-value里指定相应的xml文件名,如果有多个xml文件,可以使用“,”号分隔。applicationContext-*.xml采用通配符, 18 比如这那个目录下有applicationContext-mybatis.xml,applicationContext-hessian.xml,applicationContext-logic.xml等文件,都会一同被载入--> 21 <context-param> 22 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 23 <param-value>classpath*:/spring/spring-context-customer.xml</param-value> 24 </context-param> 25 26 27 <!-- 上下文Spring监听器 在启动web容器时,自动装配Spring的applicationContext.xml的配置信息。 28 ContextLoaderListener继承ContextLoader类,所以加载applicationContext.xml的配置文件过程中由ContextLoader类来完成 30 在配置applicationContext.xml的过程中,如果在web.xml中不写任何参数配置信息 31 默认的路径是/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml,在WEB-INF目录下创建的xml文件的名称必须是applicationContext.xml 33 如果是要自定义文件名可以在web.xml里加入contextConfigLocation这个context参数 即context-param标签配置--> 34 <listener> 35 <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> 36 </listener> 39 40 <!-- 字符集过滤器:解决项目中出现的中文乱码问题,在Spring框架中是如何解决从页面传来的字符串的编码问题的呢? 42 下面我们来看看Spring框架给我们提供过滤器CharacterEncodingFilter,这个过滤器就是针对于每次浏览器请求进行过滤的,然后再其之上添加了父类没有的功能即处理字符编码。 44 其中encoding用来设置编码格式,forceEncoding用来设置是否理会 request.getCharacterEncoding()方法,设置为true则强制覆盖之前的编码格式。--> 46 <filter> 47 <filter-name>EncodingFilter</filter-name> 48 <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> 49 <init-param> 50 <param-name>encoding</param-name> 51 <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> 52 </init-param> 53 <init-param> 54 <param-name>forceEncoding</param-name> 55 <param-value>true</param-value> 56 </init-param> 57 </filter> 58 <filter-mapping> 59 <filter-name>EncodingFilter</filter-name> 60 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> 61 </filter-mapping> 62 63 <!--使用Spring MVC,配置DispatcherServlet是第一步。DispatcherServlet是一个Servlet,所以可以配置多个DispatcherServlet--> 64 <!--DispatcherServlet是前置控制器,配置在web.xml文件中的。拦截匹配的请求, 65 Servlet拦截匹配规则要自已定义,把拦截下来的请求,依据某某规则分发到目标Controller(我们写的Action)来处理。--> 66 <servlet> 67 <!--在DispatcherServlet的初始化过程中,框架会在web应用的WEB-INF文件夹下寻找名为[servlet-name]-servlet.xml 的配置文件,生成文件中定义的bean。--> 69 <servlet-name>springServlet</servlet-name> 70 <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> 71 <!--指明了配置文件的文件名,不使用默认配置文件名,而不使用使用dispatcher-servlet.xml配置文件。--> 72 <init-param> 73 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 74 <param-value>classpath*:/spring/spring-mvc.xml</param-value> 75 </init-param> 76 <!--是启动顺序,让这个Servlet随Servletp容器一起启动。--> 77 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 78 </servlet> 80 <servlet-mapping> 81 <!--这个Servlet的名字是dispatcher,可以有多个DispatcherServlet,是通过名字来区分的。 82 每一个DispatcherServlet有自己的WebApplicationContext上下文对象。同时保存的ServletContext中和Request对象中.--> 83 <!--ApplicationContext是Spring的核心,Context我们通常解释为上下文环境, 84 我想用“容器”来表述它更容易理解一些,ApplicationContext则是“应用的容器”了:P, 85 Spring把Bean放在这个容器中,在需要的时候,用getBean方法取出--> 86 <servlet-name>springServlet</servlet-name> 87 <!--Servlet拦截匹配规则可以自已定义,当映射为@RequestMapping("/user/add")时,为例,拦截哪种URL合适?--> 88 <!--1、拦截*.do、*.htm, 例如:/user/add.do,这是最传统的方式,最简单也最实用。不会导致静态文件(jpg,js,css)被拦截。--> 89 <!--2、拦截/,例如:/user/add,可以实现现在很流行的REST风格。很多互联网类型的应用很喜欢这种风格的URL。 90 弊端:会导致静态文件(jpg,js,css)被拦截后不能正常显示。 --> 91 <!--会拦截URL中带“/”的请求。--> 92 <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> 93 </servlet-mapping> 94 95 </web-app>
二、DispatcherServlet 处理流程
在整个 Spring MVC 框架中,DispatcherServlet 处于核心位置,它负责协调和组织不同组件完成请求处理并返回响应工作。在看 DispatcherServlet 类之前,我们先来看一下请求处理的大致流程:
- Tomcat 启动,对 DispatcherServlet 进行实例化,然后调用它的 init() 方法进行初始化,在这个初始化过程中完成了: 对 web.xml 中初始化参数的加载;建立 WebApplicationContext (SpringMVC的IOC容器);进行组件的初始化;
- 客户端发出请求,由 Tomcat 接收到这个请求,如果匹配 DispatcherServlet 在 web.xml 中配置的映射路径,Tomcat 就将请求转交给 DispatcherServlet 处理;
- DispatcherServlet 从容器中取出所有 HandlerMapping 实例(每个实例对应一个 HandlerMapping 接口的实现类)并遍历,每个 HandlerMapping 会根据请求信息,通过自己实现类中的方式去找到处理该请求的 Handler (执行程序,如Controller中的方法),并且将这个 Handler 与一堆 HandlerInterceptor (拦截器) 封装成一个 HandlerExecutionChain 对象,一旦有一个 HandlerMapping 可以找到 Handler 则退出循环;(详情可以看 [Java]SpringMVC工作原理之二:HandlerMapping和HandlerAdpater 这篇文章)
- DispatcherServlet 取出 HandlerAdapter 组件,根据已经找到的 Handler,再从所有 HandlerAdapter 中找到可以处理该 Handler 的 HandlerAdapter 对象;
- 执行 HandlerExecutionChain 中所有拦截器的 preHandler() 方法,然后再利用 HandlerAdapter 执行 Handler ,执行完成得到 ModelAndView,再依次调用拦截器的 postHandler() 方法;
- 利用 ViewResolver 将 ModelAndView 或是 Exception(可解析成 ModelAndView)解析成 View,然后 View 会调用 render() 方法再根据 ModelAndView 中的数据渲染出页面;
- 最后再依次调用拦截器的 afterCompletion() 方法,这一次请求就结束了。
Servlet的执行过程如下:

三、DispatcherServlet 源码分析
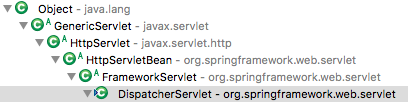
DispatcherServlet 继承自 HttpServlet,它遵循 Servlet 里的“init-service-destroy”三个阶段,首先我们先来看一下它的 init() 阶段。
1 初始化
1.1 HttpServletBean 的 init() 方法
DispatcherServlet 的 init() 方法在其父类 HttpServletBean 中实现的,它覆盖了 GenericServlet 的 init() 方法,主要作用是加载 web.xml 中 DispatcherServlet 的 <init-param> 配置,并调用子类的初始化。下面是 init() 方法的具体代码:
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
try {
// ServletConfigPropertyValues 是静态内部类,使用 ServletConfig 获取 web.xml 中配置的参数
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
// 使用 BeanWrapper 来构造 DispatcherServlet
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
} catch (BeansException ex) {}
// 让子类实现的方法,这种在父类定义在子类实现的方式叫做模版方法模式
initServletBean();
}
1.2 FrameworkServlet 的 initServletBean() 方法
在 HttpServletBean 的 init() 方法中调用了 initServletBean() 这个方法,它是在 FrameworkServlet 类中实现的,主要作用是建立 WebApplicationContext 容器(有时也称上下文),并加载 SpringMVC 配置文件中定义的 Bean 到改容器中,最后将该容器添加到 ServletContext 中。下面是 initServletBean() 方法的具体代码:
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
try {
// 初始化 WebApplicationContext (即SpringMVC的IOC容器)
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
} catch (ServletException ex) {
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
}
}
WebApplicationContext 继承于 ApplicationContext 接口,从容器中可以获取当前应用程序环境信息,它也是 SpringMVC 的 IOC 容器。下面是 initWebApplicationContext() 方法的具体代码:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 获取 ContextLoaderListener 初始化并注册在 ServletContext 中的根容器,即 Spring 的容器
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// 因为 WebApplicationContext 不为空,说明该类在构造时已经将其注入
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// 将 Spring 的容器设为 SpringMVC 容器的父容器
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// 如果 WebApplicationContext 为空,则进行查找,能找到说明上下文已经在别处初始化。
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 如果 WebApplicationContext 仍为空,则以 Spring 的容器为父上下文建立一个新的。
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// 模版方法,由 DispatcherServlet 实现
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// 发布这个 WebApplicationContext 容器到 ServletContext 中
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
下面是查找 WebApplicationContext 的 findWebApplicationContext() 方法代码:
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
// 从 ServletContext 中查找已经发布的 WebApplicationContext 容器
WebApplicationContext wac =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: initializer not registered?");
}
return wac;
}
1.3 DispatcherServlet 的 onRefresh() 方法
建立好 WebApplicationContext(上下文) 后,通过 onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) 方法回调,进入 DispatcherServlet 类中。onRefresh() 方法,提供 SpringMVC 的初始化,具体代码如下:
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
在 initStrategies() 方法中进行了各个组件的初始化,先来看一下这些组件的初始化方法,稍后再来详细分析这些组件。
1.3.1 initHandlerMappings 方法
initHandlerMappings() 方法从 SpringMVC 的容器及 Spring 的容器中查找所有的 HandlerMapping 实例,并把它们放入到 handlerMappings 这个 list 中。这个方法并不是对 HandlerMapping 实例的创建,HandlerMapping 实例是在上面 WebApplicationContext 容器初始化,即 SpringMVC 容器初始化的时候创建的。
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// 从 SpringMVC 的 IOC 容器及 Spring 的 IOC 容器中查找 HandlerMapping 实例
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
// 按一定顺序放置 HandlerMapping 对象
OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
} else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// 如果没有 HandlerMapping,则加载默认的
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
}
}
1.3.2 initHandlerAdapters 方法
private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerAdapters = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) {
// Find all HandlerAdapters in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<HandlerAdapter>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerAdapters in sorted order.
OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);
}
} else {
try {
HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean(HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerAdapter.class);
this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerAdapter later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least some HandlerAdapters, by registering
// default HandlerAdapters if no other adapters are found.
if (this.handlerAdapters == null) {
this.handlerAdapters = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class);
}
}
2 处理请求
HttpServlet 提供了 doGet()、doPost() 等方法,DispatcherServlet 中这些方法是在其父类 FrameworkServlet 中实现的,代码如下:
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
这些方法又都调用了 processRequest() 方法,我们来看一下代码:
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
// 返回与当前线程相关联的 LocaleContext
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
// 根据请求构建 LocaleContext,公开请求的语言环境为当前语言环境
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
// 返回当前绑定到线程的 RequestAttributes
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
// 根据请求构建ServletRequestAttributes
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
// 获取当前请求的 WebAsyncManager,如果没有找到则创建
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
// 使 LocaleContext 和 requestAttributes 关联
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
// 由 DispatcherServlet 实现
doService(request, response);
} catch (ServletException ex) {
} catch (IOException ex) {
} catch (Throwable ex) {
} finally {
// 重置 LocaleContext 和 requestAttributes,解除关联
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}// 发布 ServletRequestHandlerEvent 事件
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
DispatcherServlet 的 doService() 方法主要是设置一些 request 属性,并调用 doDispatch() 方法进行请求分发处理,doDispatch() 方法的主要过程是通过 HandlerMapping 获取 Handler,再找到用于执行它的 HandlerAdapter,执行 Handler 后得到 ModelAndView ,ModelAndView 是连接“业务逻辑层”与“视图展示层”的桥梁,接下来就要通过 ModelAndView 获得 View,再通过它的 Model 对 View 进行渲染。doDispatch() 方法如下:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
// 获取当前请求的WebAsyncManager,如果没找到则创建并与请求关联
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 检查是否有 Multipart,有则将请求转换为 Multipart 请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 遍历所有的 HandlerMapping 找到与请求对应的 Handler,并将其与一堆拦截器封装到 HandlerExecution 对象中。
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 遍历所有的 HandlerAdapter,找到可以处理该 Handler 的 HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 处理 last-modified 请求头
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 遍历拦截器,执行它们的 preHandle() 方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
try {
// 执行实际的处理程序
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
}
applyDefaultViewName(request, mv);
// 遍历拦截器,执行它们的 postHandle() 方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
// 处理执行结果,是一个 ModelAndView 或 Exception,然后进行渲染
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
} catch (Exception ex) {
} catch (Error err) {
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// 遍历拦截器,执行它们的 afterCompletion() 方法
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
