学习笔记,整理自《Hadoop权威指南 第3版》
一、序列化
序列化:序列化是将 内存 中的结构化数据 转化为 能在网络上传输 或 磁盘中进行永久保存的二进制流的过程;反序列化:序列化的逆过程;
应用:进程间通信、网络传输、持久化;
Hadoop中是使用的自己的序列化格式Writable,以及结合用Avro弥补一些Writable的不足;
二:Writable接口 相关:
主要是3个接口:
Writable接口
WritableComparable接口
RawComparator接口
Writable接口中主要是两个方法:write 和 readFields
//Writable接口原形 public interface Writabel{ void write(DataOutput out)throws IOException; void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException; }
WritableComparable接口:继承自Writable接口 和 Comparable<T>接口;即有序列功能,也有比较排序功能;
public interface WritableComparable<T> extends Writable,Comparable<T>{ }
Hadoop自定义比较排序接口:RawComparator接口,该接口允许实现比较数据流中的记录,而不用把数据流反序列化为对象,从而避免了新建对象的额外开销;
可参考:Hadoop-2.4.1学习之RawComparator及其实现
public interface RawComparator<T> extends Comparator<T>{ public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2); }
工具类WritableComparator:a. 充当RawComparator的实例工厂;b. 提供了对原始compare()方法的一个默认实现;
RawComparator<IntWritable> comparator = WritableComparator.get(IntWritable.class); //获取的comparator 即可比较两个IntWritable对象,也可直接比较两个序列化数据: //比较两上IntWritable对象 IntWritable w1 = new IntWritable(163); IntWritable w2 = new IntWritable(67): comparator.compare(w1, w2); //比较其序列化 byte[] b1 = serialize(w1); byte[] b2 = serialize(w2); comparator.compare(b1, 0, b1.length, b2, 0, b2.length);
三、Writable继承图
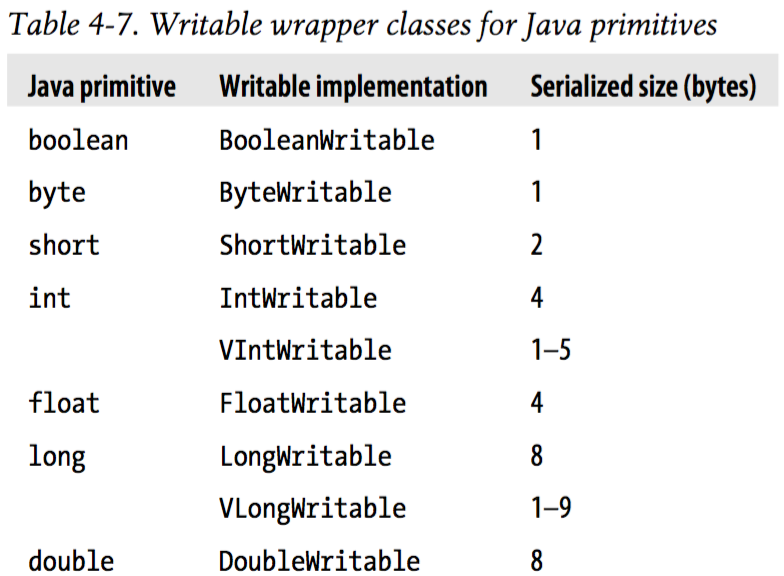
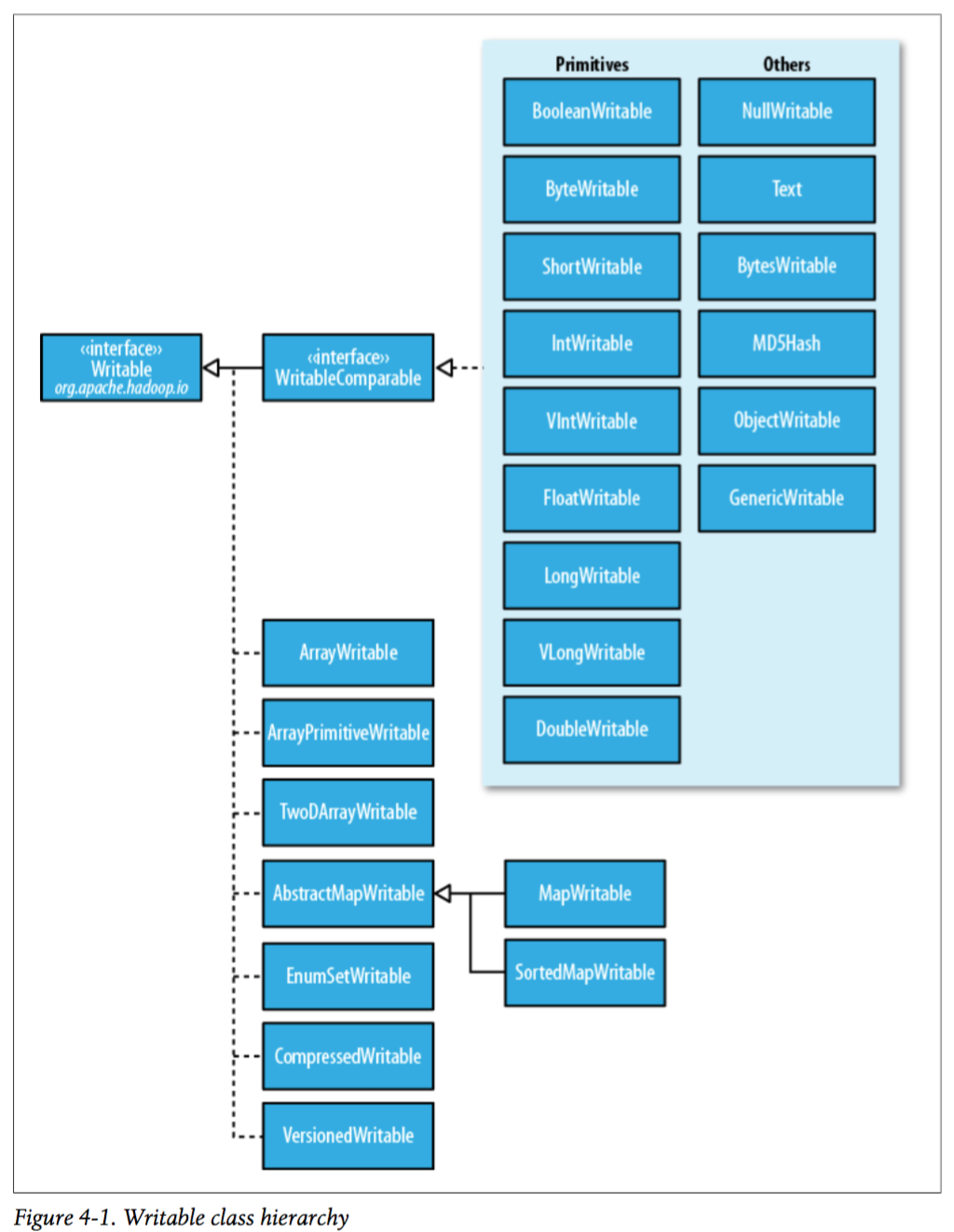
以上可以看出,包含了除了char类型外 Java基本类型的封装;其中Text对应Java中的String;
四、自定义一个Writable

import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; public class TextPair implements WritableComparable<TextPair> { private Text first; private Text second; public TextPair() { set(new Text(), new Text()); } public void set(Text first, Text second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public Text getFirst() { return this.first; } public Text getSecond() { return this.second; } @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { first.write(out); second.write(out); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { first.readFields(in); second.readFields(in); } @Override public int hashCode() { return first.hashCode() * 163 + second.hashCode(); } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o instanceof TextPair) { TextPair tp = (TextPair) o; return first.equals(tp.first) && second.equals(tp.second); } return false; } @Override public int compareTo(TextPair tp) { int cmp = first.compareTo(tp.first); if (cmp != 0) { return cmp; } return second.compareTo(tp.second); } @Override public String toString() { return first + " " + second; } }
以上可以看出,主要是要实现5个方法,都是重写方法,其中序列化的write()、readFields()2个方法,排序的compareTo(),以及hashCode()和equals()2两个基本方法。
五、序列化框架Avro
可参考:Avro总结(RPC/序列化)
http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1369363962228.html
六、SequenceFile MapFile
SequenceFile
SequenceFile是一个由二进制序列化过的key/value的字节流组成的文本存储文件;在map/reduce过程中,map处理文件的临时输出就是使用SequenceFile处理过的。
用途:
1、纯文本不合适记录二进制类型的数据,这种情况下,Hadoop的SequenceFile类非常合适,为二进制键/值对提供一个持久数据结构。并可对key value压缩处理。
2、SequenceFile可作为小文件的容器,HDFS和MR更适合处理大文件。
定位文件位置的两种方法:
1、seek(long poisitiuion):poisition必须是记录的边界,否则调用next()方法时会报错
2、sync(long poisition):Poisition可以不是记录的边界,如果不是边界,会定位到下一个同步点,如果Poisition之后没有同步点了,会跳转到文件的结尾位置
三种压缩态:
Uncompressed – 未进行压缩的状
Record compressed - 对每一条记录的value值进行了压缩(文件头中包含上使用哪种压缩算法的信息)
Block compressed – 当数据量达到一定大小后,将停止写入一个block压缩;整体压缩的方法是把所有的keylength,key,vlength,value 分别合在一起进行整体压缩,块的压缩效率要比记录的压缩效率高;
写入SequenceFile:

package com.lcy.hadoop.io; import java.net.URI; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; public class SequenceFileWriteDemo { private static final String [] DATA={ "One,two,buckle my shoe", "Three,four,shut the door", "Five,six,pick up sticks", "Seven,eight,lay them straight", "Nine,ten,a big fat hen" }; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // TODO Auto-generated method stub String uri=args[0]; Configuration conf=new Configuration(); FileSystem fs=FileSystem.get(URI.create(uri),conf); Path path=new Path(uri); IntWritable key=new IntWritable(); Text value=new Text(); SequenceFile.Writer writer=null; try{ writer=SequenceFile.createWriter(fs,conf,path,key.getClass(),value.getClass()); for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ key.set(100-i); value.set(DATA[i%DATA.length]); System.out.printf("[%s] %s %s ",writer.getLength(),key,value); writer.append(key, value); } }finally{ IOUtils.closeStream(writer); } } }
读取SequenceFile:

//从头到尾读取顺序文件就是创建SequenceFile.Reader实例后反复调用next()方法迭代读取记录 //如果next()方法返回的是非null对象,则可以从该数据流中读取键值对 package com.lcy.hadoop.io; import java.net.URI; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable; import org.apache.hadoop.util.ReflectionUtils; public class SequenceFileReadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // TODO Auto-generated method stub String uri=args[0]; Configuration conf=new Configuration(); FileSystem fs=FileSystem.get(URI.create(uri),conf); Path path=new Path(uri); SequenceFile.Reader reader=null; try{ reader=new SequenceFile.Reader(fs, path, conf); Writable key=(Writable)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(reader.getKeyClass(), conf); Writable value=(Writable)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(reader.getValueClass(), conf); long position=reader.getPosition(); while(reader.next(key,value)){ String syncSeen=reader.syncSeen()?"*":" "; System.out.printf("[%s%s] %s %s ",position,syncSeen,key,value); position=reader.getPosition(); } }finally{ IOUtils.closeStream(reader); } } }
在命令行下,可有-text 参数来查看gzip压缩文件 和 序列文件,否则直接查看可能是乱码;
SequenceFile内部格式:
组成:
SequenceFile由一个header 和 随后的 多条记录组成;
header包含:前三字节是SequenceFile文件代码SEQ;版本号;key value类型;压缩细节;
同步标识sync:用于读取文件时能够从任意位置开始识别记录边界。同步标识位于记录和记录之间,因为额外存储开销(1%),没必要在每个记录后都有标识
1、 record压缩:
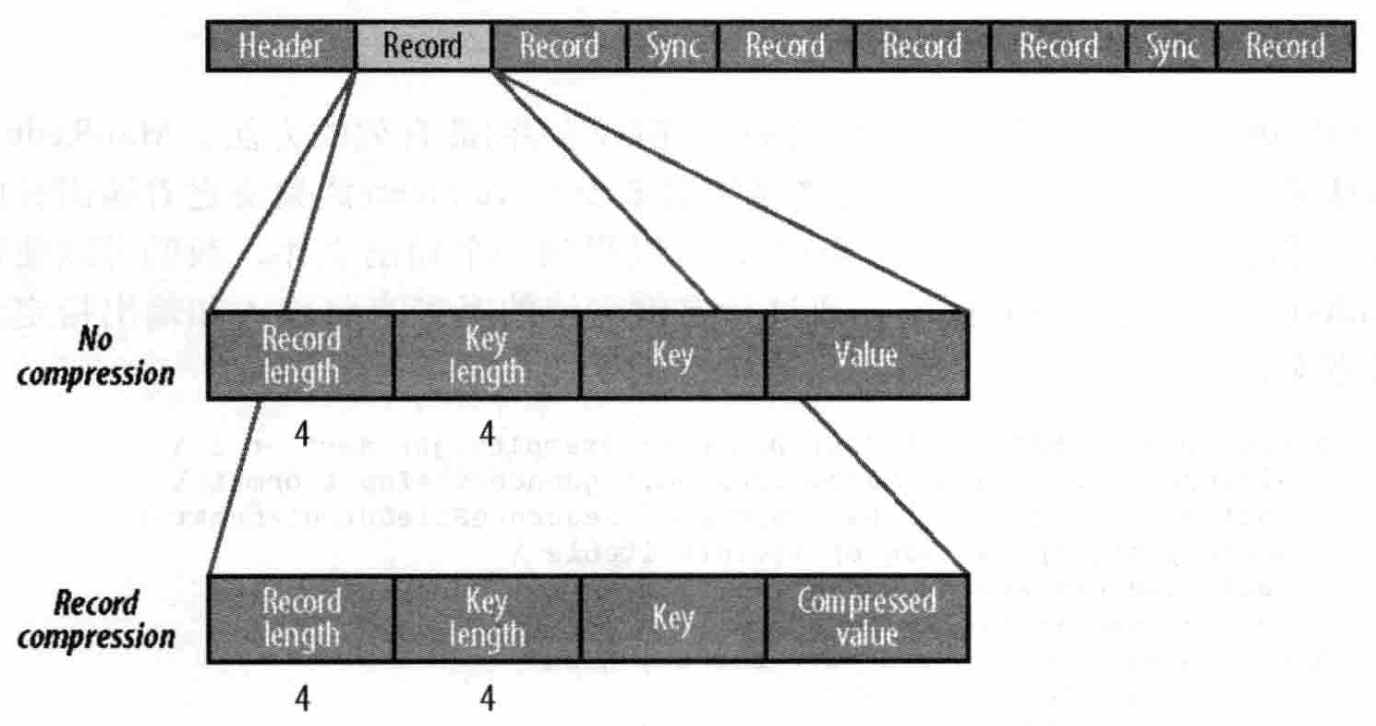
record压缩 和 无压缩基本相同,只不过是值value用文件头中定义的codec压缩过,而其它key、length都不变;
2、block压缩:

block压缩是指一次性压缩多条记录,压缩率较高;
压缩时是向一个压缩块中添加记录,直到压缩后的block大于定义的值(默认为1MB)每个新块的开始都会有一个同步标识;
压缩后的格式:首先是一个指示数据块中字节数的字段;紧接着是4个字段(键长,键;值长,值 )
MapFile
MapFile是已排序过的SequenceFile,它含有索引,可快速随机读取(二分查找);
创建一个map类型的文件,实际会合成一个文件夹,文件夹中包含两部分:


MapFile的读类型SequenceFile,别外包含两个随机读取key的方法:
public Writable get(WritableComparable key, Writable val) throws IOException
public Writable getClosest(WritableComparable key, Writable val) throws IOException//返回最近的key,不会因为找不到返回null;
