资料整理的迅为Linux视频教程
本节整理的是GPIO的初始化和调用。
验证:对宏EXYNOS4_GPL2(0)的操作就是对4412芯片管脚AC21寄存器的操作。
1. GPIO初始化的源码
1.1 在源码中查看编译:
1 $ ls drivers/gpio/*.o 2 drivers/gpio/built-in.o drivers/gpio/gpio-exynos4.o drivers/gpio/gpiolib.o drivers/gpio/gpio-plat-samsung.o
通过.o文件判断gpio-exynos4被编译进了内核
1.2 查看drivers/gpio/gpio-exynos4.c文件:
1 $ cat drivers/gpio/gpio-exynos4.c 2 .... 3 core_initcall(exynos4_gpiolib_init); //代表在Linux初始化过程中会调用
1.2.1 初始化函数在源码目录的“include/linux/init.h”文件中定义,该头文件中定义了一系列的初始化函数,在Linux启动的过程中会按等级优先启动
# include/linux/init.h 196 #define core_initcall(fn) __define_initcall("1",fn,1) //level:0最高 167 /* initcalls are now grouped by functionality into separate 168 * subsections. Ordering inside the subsections is determined 169 * by link order. 170 * For backwards compatibility, initcall() puts the call in 171 * the device init subsection. 172 * 173 * The `id' arg to __define_initcall() is needed so that multiple initcalls 174 * can point at the same handler without causing duplicate-symbol build errors. 175 */ 176 177 #define __define_initcall(level,fn,id) 178 static initcall_t __initcall_##fn##id __used 179 __attribute__((__section__(".initcall" level ".init"))) = fn 180
1.3 下面继续回到drivers/gpio/gpio-exynos4.c的初始化位置:
$ cat drivers/gpio/gpio-exynos4.c .... core_initcall(exynos4_gpiolib_init); //代表在Linux初始化过程中会调用 518 static __init int exynos4_gpiolib_init(void) 519 { 520 struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip; 521 int i; 522 int nr_chips; 523 524 /* GPIO common part */ 525 526 chip = exynos4_gpio_common_4bit; //引用了exynos4_gpio_common_4bit结构体,在本文件中定义。 527 nr_chips = ARRAY_SIZE(exynos4_gpio_common_4bit); 528 529 for (i = 0; i < nr_chips; i++, chip++) { 530 if (chip->config == NULL) 531 chip->config = &gpio_cfg; 532 if (chip->base == NULL) 533 pr_err("No allocation of base address for [common gpio]"); 534 } 535 536 samsung_gpiolib_add_4bit_chips(exynos4_gpio_common_4bit, nr_chips); 537 538 /* Only 4210 GPIO part */ 539 if (soc_is_exynos4210()) { 540 chip = exynos4210_gpio_4bit; 541 nr_chips = ARRAY_SIZE(exynos4210_gpio_4bit); 542 543 for (i = 0; i < nr_chips; i++, chip++) { 544 if (chip->config == NULL) 545 chip->config = &gpio_cfg; 546 if (chip->base == NULL) 547 pr_err("No allocation of base address [4210 gpio]"); 548 } 549 550 samsung_gpiolib_add_4bit_chips(exynos4210_gpio_4bit, nr_chips); 551 } else { 552 /* Only 4212/4412 GPIO part */ 553 chip = exynos4212_gpio_4bit; 554 nr_chips = ARRAY_SIZE(exynos4212_gpio_4bit); 555 556 for (i = 0; i < nr_chips; i++, chip++) { 557 if (chip->config == NULL) 558 chip->config = &gpio_cfg; 559 if (chip->base == NULL) 560 pr_err("No allocation of base address [4212 gpio]"); 561 } 562 563 samsung_gpiolib_add_4bit_chips(exynos4212_gpio_4bit, nr_chips); 564 } 565 566 s5p_register_gpioint_bank(IRQ_GPIO_XA, 0, IRQ_GPIO1_NR_GROUPS); 567 s5p_register_gpioint_bank(IRQ_GPIO_XB, IRQ_GPIO1_NR_GROUPS, IRQ_GPIO2_NR_GROUPS); 568 569 return 0; 570 }
1.3.1 exynos4_gpio_common_4bit结构体内容截取:
... 75 static struct s3c_gpio_chip exynos4_gpio_common_4bit[] = { 77 { 78 .base = S5P_VA_GPIO1, 79 .eint_offset = 0x0, 80 .group = 0, 81 .chip = { 82 .base = EXYNOS4_GPA0(0), 83 .ngpio = EXYNOS4_GPIO_A0_NR, 84 .label = "GPA0", 85 }, 86 }, { ... 230 }, { 231 .base = (S5P_VA_GPIO2 + 0x100), //里面用到的VA代表虚拟地址,PA代表物理地址。此处偏移地址值来源于datasheet,下图 232 .eint_offset = 0x20, //中断相关的 233 .group = 22, //给GPIO分组 234 .chip = { 235 .base = EXYNOS4_GPL2(0), //宏定义EXYNOS4_GPL2(0)赋值给初始化函数.==>(./arch/arm/mach-exynos/include/mach/gpio-exynos4.h) 236 .ngpio = EXYNOS4_GPIO_L2_NR, //这一个小组里面有几个GPIO,可以通过手册查到:#define EXYNOS4_GPIO_L2_NR (8) 237 .label = "GPL2", //程序员需要关心的标志,也就是之前查看LEDpin脚所对应的那块 238 }, 239 }, { ...
1.3.1.1 .base = (S5P_VA_GPIO2 + 0x100),的理解
offset可以直接在datasheet中搜索GPL2得到:

S5P_VA_GPIO2的内容:
1 S5P_VA_GPIO2的定义在:./arch/arm/plat-s5p/include/plat/map-s5p.h 2 #define S5P_VA_GPIO2 S3C_ADDR(0x02240000) 3 S3C_ADDR的定义在:./arch/arm/plat-samsung/include/plat/map-base.h 4 5 /* Fit all our registers in at 0xF6000000 upwards, trying to use as 6 * little of the VA space as possible so vmalloc and friends have a 7 * better chance of getting memory. 8 * 9 * we try to ensure stuff like the IRQ registers are available for 10 * an single MOVS instruction (ie, only 8 bits of set data) 11 */ 12 13 #define S3C_ADDR_BASE 0xF6000000 //使用的虚拟地址 14 15 #ifndef __ASSEMBLY__ 16 #define S3C_ADDR(x) ((void __iomem __force *)S3C_ADDR_BASE + (x)) 17 #else 18 #define S3C_ADDR(x) (S3C_ADDR_BASE + (x)) 19 #endif
源码检索,S5P_VA_GPIO2在cpu-exynos[/arch/arm/mach-exynos/cpu-exynos4.c]中也使用了,是一个平台文件
至于虚拟地址和物理地址的映射,在/arch/arm/mach-exynos/cpu-exynos4.c的结构体数组中
1 arch/arm/mach-exynos/cpu-exynos4.c: 2 /* Initial IO mappings */ 3 static struct map_desc exynos4_iodesc[] __initdata = { 4 ... 5 }, { 6 .virtual = (unsigned long)S5P_VA_GPIO2, //表示虚拟地址 7 .pfn = __phys_to_pfn(EXYNOS4_PA_GPIO2), //表示物理地址 8 .length = SZ_4K, //表示映射的宽度,如:#define SZ_4K 0x00001000 [sizes.h] 9 .type = MT_DEVICE, 10 }, { 11 ... 12 }; 13 14 EXYNOS4_PA_GPIO2的定义在./arch/arm/mach-exynos/include/mach/map-exynos4.h中 15 #define EXYNOS4_PA_GPIO2 0x11000000 //此处的物理地址就和基地址对应起来的,也就是datasheet的6.2.3.37上面截图中的内容
1.3.1.2 .base = EXYNOS4_GPL2(0)的理解和调用
1 .base = EXYNOS4_GPL2(0): 2 1)EXYNOS4_GPL2的定义在文件:./arch/arm/mach-exynos/include/mach/gpio-exynos4.h 3 #define EXYNOS4_GPL2(_nr) (EXYNOS4_GPIO_L2_START + (_nr)) 4 2)EXYNOS4_GPIO_L2_START在枚举类型中定义 5 enum exynos4_gpio_number { 6 ... 7 EXYNOS4_GPIO_L2_START = EXYNOS4_GPIO_NEXT(EXYNOS4_GPIO_L1),枚举第17个 8 ... 9 }; 10 3)EXYNOS4_GPIO_NEXT的宏定义 11 /* GPIO bank numbers */ 12 #define EXYNOS4_GPIO_NEXT(__gpio) 13 ((__gpio##_START) + (__gpio##_NR) + CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPACE + 1) //此处的+是连接的意思,不是判断 14 4)CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPACE的定义在:./include/generated/autoconf.h: 15 #define CONFIG_S3C_GPIO_SPACE 0
2. GPIO初始化的简单概括:
1)平台文件分别定义好物理地址和虚拟地址
2)物理地址和虚拟地址之间的映射
在初始化中,引入了程序员需要使用的GPIO宏定义,并将宏定义装入chip结构体中
内核中已经写好了LED的使用,如下drivers/char/itop4412_leds.c:
drivers/char/itop4412_leds.c: 27 #if defined(CONFIG_CPU_TYPE_SCP_ELITE) || defined(CONFIG_CPU_TYPE_POP_ELITE) || defined(CONFIG_CPU_TYPE_POP2G_ELITE) 28 static int led_gpios[] = { 29 EXYNOS4_GPL2(0), //此处为什么用(0)呢?? 30 EXYNOS4_GPK1(1), 31 }; 32 33 #elif defined(CONFIG_CPU_TYPE_SCP_SUPPER) || defined(CONFIG_CPU_TYPE_POP_SUPPER) || defined(CONFIG_CPU_TYPE_POP2G_SUPPER) 34 35 36 static int led_gpios[] = { 37 #if defined(CONFIG_MTK_COMBO_COMM) || defined(CONFIG_MTK_COMBO_COMM_MODULE) 38 EXYNOS4_GPC0(2), 39 #else 40 EXYNOS4_GPX2(5), 41 #endif 42 EXYNOS4_GPX0(1), 43 }; 44 45 46 #endif
在datasheet中的6.2.3.37 GPL2CON

且在ITOP4412_MAIN_CLASICS_V3_2.pdf中搜索如下:
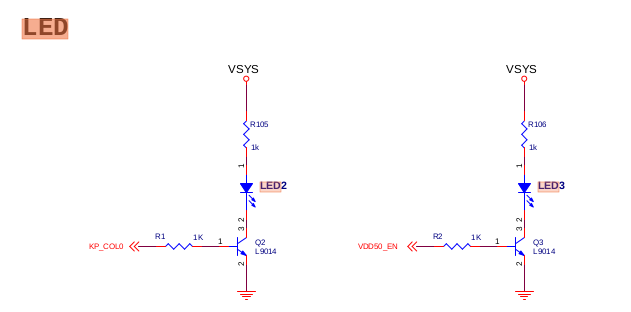
然后搜索KP_CONL0,连接到了连接器上如下图:
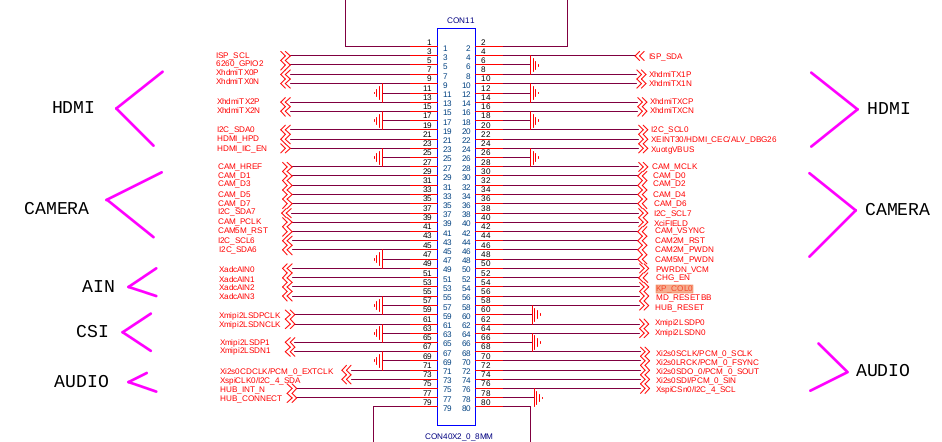
连接器通上核心板,然后在核心板中搜索TOPEET_coreboard4412_scp.pdf:

对应的就是GPL2_0(复用的)。
3. GPIO的调用函数
配置头文件在:arch/arm/plat-samsung/include/plat/gpio-cfg.h
函数:s3c_gpio_cfgpin,参数1:EXYNOS4_GPL2(0),参数2:配置的状态参数
77 /** 78 * s3c_gpio_cfgpin() - Change the GPIO function of a pin. 79 * @pin pin The pin number to configure. 80 * @to to The configuration for the pin's function. 81 * 82 * Configure which function is actually connected to the external 83 * pin, such as an gpio input, output or some form of special function 84 * connected to an internal peripheral block. 85 * 86 * The @to parameter can be one of the generic S3C_GPIO_INPUT, S3C_GPIO_OUTPUT 87 * or S3C_GPIO_SFN() to indicate one of the possible values that the helper 88 * will then generate the correct bit mask and shift for the configuration. 89 * 90 * If a bank of GPIOs all needs to be set to special-function 2, then 91 * the following code will work: 92 * 93 * for (gpio = start; gpio < end; gpio++) 94 * s3c_gpio_cfgpin(gpio, S3C_GPIO_SFN(2)); 95 * 96 * The @to parameter can also be a specific value already shifted to the 97 * correct position in the control register, although these are discouraged 98 * in newer kernels and are only being kept for compatibility. 99 */ 100 extern int s3c_gpio_cfgpin(unsigned int pin, unsigned int to);
这个函数会调用一个结构体,具体的实现在文件./arch/arm/plat-samsung/gpio-config.c中:
./arch/arm/plat-samsung/gpio-config.c 24 int s3c_gpio_cfgpin(unsigned int pin, unsigned int config) 25 { 26 struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip = s3c_gpiolib_getchip(pin); //到结构体中获取chip内容 27 unsigned long flags; 28 int offset; 29 int ret; 30 31 if (!chip) 32 return -EINVAL; 33 34 offset = pin - chip->chip.base; 35 36 s3c_gpio_lock(chip, flags); 37 ret = s3c_gpio_do_setcfg(chip, offset, config); //将值传过去配置 38 s3c_gpio_unlock(chip, flags); 39 40 return ret; 41 } 42 EXPORT_SYMBOL(s3c_gpio_cfgpin);
这个函数中使用的结构体和1.3.1中使用的结构体是相同的。结构体的定义在./arch/arm/plat-samsung/include/plat/gpio-core.h:
./arch/arm/plat-samsung/include/plat/gpio-core.h 42 /** 43 * struct s3c_gpio_chip - wrapper for specific implementation of gpio 44 * @chip: The chip structure to be exported via gpiolib. 45 * @base: The base pointer to the gpio configuration registers. 46 * @group: The group register number for gpio interrupt support. 47 * @irq_base: The base irq number. 48 * @config: special function and pull-resistor control information. 49 * @lock: Lock for exclusive access to this gpio bank. 50 * @pm_save: Save information for suspend/resume support. 51 * 52 * This wrapper provides the necessary information for the Samsung 53 * specific gpios being registered with gpiolib. 54 * 55 * The lock protects each gpio bank from multiple access of the shared 56 * configuration registers, or from reading of data whilst another thread 57 * is writing to the register set. 58 * 59 * Each chip has its own lock to avoid any contention between different 60 * CPU cores trying to get one lock for different GPIO banks, where each 61 * bank of GPIO has its own register space and configuration registers. 62 */ 63 struct s3c_gpio_chip { 64 struct gpio_chip chip; 65 struct s3c_gpio_cfg *config; 66 struct s3c_gpio_pm *pm; 67 void __iomem *base; 68 int irq_base; 69 int group; 70 unsigned int eint_offset; 71 spinlock_t lock; 72 #ifdef CONFIG_PM 73 u32 pm_save[4]; 74 #endif 75 };
所以控制GPIO的时候通过处理函数加上类似EXYNOS4_GPL2(0)的宏定义,就可以操作GPIO。
大部分都是内核或平台已经做成了。
其他:
CPU不直接对register操作,因为CPU是对内存中的一大段一大段的处理,单个寄存器读取是对CPU的浪费。
虚拟地址和物理地址对应的数组,调用是在函数ioremap中,来实现gpio的映射关系。
以上