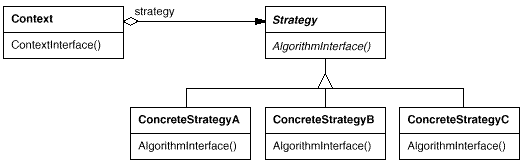
意图:
定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来, 并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法可独立于使用它的客户而变化。
适用性:
许多相关的类仅仅是行为有异。“策略”提供了一种用多个行为中的一个行为来配置一个类的方法。
需要使用一个算法的不同变体。例如,你可能会定义一些反映不同的空间/时间权衡的算法。当这些变体实现为一个算法的类层次时[H087] ,可以使用策略模式。
算法使用客户不应该知道的数据。可使用策略模式以避免暴露复杂的、与算法相关的数据结构。
一个类定义了多种行为, 并且这些行为在这个类的操作中以多个条件语句的形式出现。将相关的条件分支移入它们各自的Strategy类中以代替这些条件语句。
#!/usr/bin/python #coding:utf8 """ Strategy In most of other languages Strategy pattern is implemented via creating some base strategy interface/abstract class and subclassing it with a number of concrete strategies (as we can see at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strategy_pattern), however Python supports higher-order functions and allows us to have only one class and inject functions into it's instances, as shown in this example. """ import types class StrategyExample: def __init__(self, func=None): self.name = 'Strategy Example 0' if func is not None: self.execute = types.MethodType(func, self) def execute(self): print(self.name) def execute_replacement1(self): print(self.name + ' from execute 1') def execute_replacement2(self): print(self.name + ' from execute 2') if __name__ == '__main__': strat0 = StrategyExample() strat1 = StrategyExample(execute_replacement1) strat1.name = 'Strategy Example 1' strat2 = StrategyExample(execute_replacement2) strat2.name = 'Strategy Example 2' strat0.execute() strat1.execute() strat2.execute()