一、事务的概念可以描述为具有以下四个关键属性,也就是 ACID
-
原子性(Atomicity):事务应该当作一个单独单元的操作,这意味着整个序列操作要么是成功,要么是失败;
-
一致性(Consistency):这表示数据库的引用完整性的一致性,表中唯一的主键等;
-
隔离性(Isolation):可能同时处理很多有相同的数据集的事务,每个事务应该与其他事务隔离,以防止数据损坏;
- 持久性(Durability):一个事务一旦完成全部操作,这个事务的结果必须是永久性的,不能因系统故障而从数据库中删除。
二、Spring 事务管理的核心接口有三个
1. PlatformTransactionManager:平台事务管理器,主要具有以下三个方法
- TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition); 用于获取事务状态信息
- void commit(TransactionStatus status); 用于提交事务
- void rollback(TransactionStatus status); 用于回滚事务
PlatformTransactionManager接口只是代表事务管理的接口,常见的几个实现类如下:
- org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager 用于配置JDBC数据源的事务管理器
- org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager 用于配置Hibernate的事务管理器
- org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager 用于配置全局事务管理器
2. TransactionDefinition:事务定义
TransactionDefinition接口是事务定义(描述)的对象,该对象中定义了事务规则,并提供了获取事务相关信息的方法,具体如下表所示:
| 方法 | 说明 |
| String getName( ); | 获取事务对象名称 |
| int getIsolationLevel( ); | 获取事务的隔离级别 |
| int getPropagationBehavior( ); | 获取事务的传播行为 |
| int getTimeout( ); | 获取事务的超时时间 |
| boolean isReadOnly( ); | 获取事务是否只读 |
上述方法中,事务的传播行为是指在同一个方法中,不同操作前后所使用的事务传播行为有很多种,具体如下图所示:
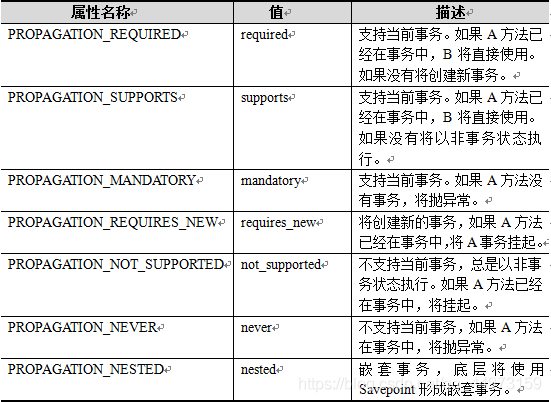
在事务管理过程中,传播行为可以控制是否需要创建事务以及如何创建事务,通常情况下,数据的查询不会影响原数据的改变,所以不需要进行事务管理,而对于数据的插入、更新和删除操作,必须进行事务管理。如果没有指定事务的传播行为,Spring默认传播行为是REQUIRED。
3. TransactionStatus:事务状态
它描述某一时间点上事务在状态信息,具体如下图所示:

三、Spring 支持两种类型的事务管理
- 编程式事务管理 :这意味着你在编程中管理事务,它给你极大的灵活性,但却很难维护。本篇不对此种方式的实现展开讨论。
- 声明式事务管理 :这意味着你可以从业务代码中分离事务管理,它可以使用XML方式或注解方式来管理事务。本篇仅对XML方式和注解方式实现事务展开讨论。
四、基于XML方式的声明式事务
1. 创建表(MySQL数据库)
create table account(id int primary key auto_increment,username varchar(50),balance double);
2. 创建实体类
package com.itheima.jdbc; public class Account { private Integer id; // 账户id private String username; // 用户名 private Double balance; // 账户余额 public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public Double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(Double balance) { this.balance = balance; } public String toString() { return "Account [id=" + id + ", " + "username=" + username + ", balance=" + balance + "]"; } }
3. 创建接口
package com.itheima.jdbc; import java.util.List; public interface AccountDao { // 添加 public int addAccount(Account account); // 更新 public int updateAccount(Account account); // 删除 public int deleteAccount(int id); // 通过id查询 public Account findAccountById(int id); // 查询所有账户 public List<Account> findAllAccount(); // 转账 public void transfer(String outUser,String inUser,Double money); }
4. 创建实现类
package com.itheima.jdbc; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { // 声明JdbcTemplate属性及其setter方法 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } // 添加账户 public int addAccount(Account account) { // 定义SQL String sql = "insert into account(username,balance) value(?,?)"; // 定义数组来存放SQL语句中的参数 Object[] obj = new Object[] { account.getUsername(), account.getBalance() }; // 执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, obj); return num; } // 更新账户 public int updateAccount(Account account) { // 定义SQL String sql = "update account set username=?,balance=? where id = ?"; // 定义数组来存放SQL语句中的参数 Object[] params = new Object[] { account.getUsername(), account.getBalance(), account.getId() }; // 执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, params); return num; } // 删除账户 public int deleteAccount(int id) { // 定义SQL String sql = "delete from account where id = ? "; // 执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, id); return num; } // 通过id查询账户数据信息 public Account findAccountById(int id) { // 定义SQL语句 String sql = "select * from account where id = ?"; // 创建一个新的BeanPropertyRowMapper对象 RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class); // 将id绑定到SQL语句中,并通过RowMapper返回一个Object类型的单行记录 return this.jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, id); } // 查询所有账户信息 public List<Account> findAllAccount() { // 定义SQL语句 String sql = "select * from account"; // 创建一个新的BeanPropertyRowMapper对象 RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class); // 执行静态的SQL查询,并通过RowMapper返回结果 return this.jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rowMapper); } /** * 转账 * inUser:收款人 * outUser:汇款人 * money:收款金额 */ public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) { // 收款时,收款用户的余额=现有余额+所汇金额 this.jdbcTemplate.update("update account set balance = balance +? " + "where username = ?",money, inUser); // 模拟系统运行时的突发性问题 int i = 1/0; // 汇款时,汇款用户的余额=现有余额-所汇金额 this.jdbcTemplate.update("update account set balance = balance-? " + "where username = ?",money, outUser); } }
5. 创建配置文件(applicationContext.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 1.配置数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <!--数据库驱动 --> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <!--连接数据库的url --> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xuejia" /> <!--连接数据库的用户名 --> <property name="username" value="root" /> <!--连接数据库的密码 --> <property name="password" value="admin" /> </bean> <!-- 2.配置JDBC模板 --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <!-- 默认必须使用数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!--3.定义id为accountDao的Bean --> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.jdbc.AccountDaoImpl"> <!-- 将jdbcTemplate注入到AccountDao实例中 --> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate" /> </bean> <!-- 4.事务管理器,依赖于数据源 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class= "org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!-- 5.编写通知:对事务进行增强(通知),需要编写对切入点和具体执行事务细节 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!-- name:*表示任意方法名称 --> <tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT" read-only="false" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 6.编写aop,让spring自动对目标生成代理,需要使用AspectJ的表达式 --> <aop:config> <!-- 切入点 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.itheima.jdbc.*.*(..))" id="txPointCut" /> <!-- 切面:将切入点与通知整合 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointCut" /> </aop:config> </beans>
6. 创建测试程序
package com.itheima.jdbc; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; //测试类 public class TransactionTest { @Test public void xmlTest() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // 获取AccountDao实例 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDao"); // 增加两个用户 Account account1 = new Account(); account1.setUsername("Jack"); account1.setBalance(1000.00); int num1 = accountDao.addAccount(account1); Account account2 = new Account(); account2.setUsername("Rose"); account2.setBalance(500.00); int num2 = accountDao.addAccount(account2); // 调用实例中的转账方法 accountDao.transfer("Jack", "Rose", 100.0); // 输出提示信息 System.out.println("转账成功!"); } }
7. 运行
系统扔出异常:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
如果查询数据库,会发现两条记录已经添加。因为添加记录与转账不在一个事务里面。
8. 修改程序,删除实现类中的如下代码
// 模拟系统运行时的突发性问题 int i = 1/0;
9. 再次运行,结果如下
转账成功!
10. 查询数据库表中的数据
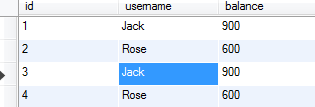
注意,表中出现两个Jack,两个Rose,并且他们的余额都发生改变。因为addAccount执行了两次,每次增加两个人。
五、基于注解声明式的事务
对上面的程序做如下修改:
1. 修改接口实现类
package com.itheima.jdbc; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { // 声明JdbcTemplate属性及其setter方法 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } // 添加账户 public int addAccount(Account account) { // 定义SQL String sql = "insert into account(username,balance) value(?,?)"; // 定义数组来存放SQL语句中的参数 Object[] obj = new Object[] { account.getUsername(), account.getBalance() }; // 执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, obj); return num; } // 更新账户 public int updateAccount(Account account) { // 定义SQL String sql = "update account set username=?,balance=? where id = ?"; // 定义数组来存放SQL语句中的参数 Object[] params = new Object[] { account.getUsername(), account.getBalance(), account.getId() }; // 执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, params); return num; } // 删除账户 public int deleteAccount(int id) { // 定义SQL String sql = "delete from account where id = ? "; // 执行添加操作,返回的是受SQL语句影响的记录条数 int num = this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql, id); return num; } // 通过id查询账户数据信息 public Account findAccountById(int id) { // 定义SQL语句 String sql = "select * from account where id = ?"; // 创建一个新的BeanPropertyRowMapper对象 RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class); // 将id绑定到SQL语句中,并通过RowMapper返回一个Object类型的单行记录 return this.jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, id); } // 查询所有账户信息 public List<Account> findAllAccount() { // 定义SQL语句 String sql = "select * from account"; // 创建一个新的BeanPropertyRowMapper对象 RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class); // 执行静态的SQL查询,并通过RowMapper返回结果 return this.jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rowMapper); } @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT, readOnly = false) public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) { // 收款时,收款用户的余额=现有余额+所汇金额 this.jdbcTemplate.update("update account set balance = balance +? " + "where username = ?",money, inUser); // 模拟系统运行时的突发性问题 int i = 1/0; // 汇款时,汇款用户的余额=现有余额-所汇金额 this.jdbcTemplate.update("update account set balance = balance-? " + "where username = ?",money, outUser); } }
2. 新建配置文件(applicationContext-annotation.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 1.配置数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <!--数据库驱动 --> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <!--连接数据库的url --> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xuejia" /> <!--连接数据库的用户名 --> <property name="username" value="root" /> <!--连接数据库的密码 --> <property name="password" value="admin" /> </bean> <!-- 2.配置JDBC模板 --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <!-- 默认必须使用数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!--3.定义id为accountDao的Bean --> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.jdbc.AccountDaoImpl"> <!-- 将jdbcTemplate注入到AccountDao实例中 --> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate" /> </bean> <!-- 4.事务管理器,依赖于数据源 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class= "org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!-- 5.注册事务管理器驱动 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> </beans>
3. 修改测试程序
package com.itheima.jdbc; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; //测试类 public class TransactionTest { @Test public void annotationTest() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext-annotation.xml"); // 获取AccountDao实例 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDao"); // 调用实例中的转账方法 accountDao.transfer("Jack", "Rose", 100.0); // 输出提示信息 System.out.println("转账成功!"); } }
4. 运行
系统扔出异常:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
5. 修改程序,删除实现类中的如下代码
// 模拟系统运行时的突发性问题 int i = 1/0;
6. 再次运行,结果如下
转账成功!
7. 查询数据库表中的数据
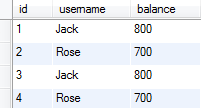
注意,表中出现两个Jack,两个Rose,并且他们的余额再次发生改变。
本文参考:《Java EE企业级应用开发教程》