目录
· 概况
· 原理
· 容错机制
· API
· 概况
· Mapper类
· Reducer类
· 示例:连接
· 示例:二次排序
概况
1. 起源:一篇Google论文。
2. 特点
a) 开发简单:用户可不考虑进程通信、套接字编程,无需高深技巧,只需符合MapReduce编程模型。
b) 伸缩性:当集群资源无法满足计算需求时,可通过增加节点达到线性伸缩集群的目的。
c) 容错性:节点故障导致的作业失败,计算框架自动将作业安排到健康节点重新执行,直到任务完成。
3. MapReduce含义:MapReduce编程模型;MapReduce运行环境(YARN)。
4. 局限性
a) 执行速度慢:普通MapReduce作业一般分钟级别完成,复杂作业或数据量更大时可能花费一小时或更多。MapReduce通常时数据密集型作业,大量中间结果写到磁盘并通过网络传输,消耗大量时间。
b) 过于底层:与SQL相比,过于底层。对于习惯关心数据库的用户,或数据分析师,编写map和reduce函数无疑头疼。
c) 无法实现所有算法。
原理
MapReduce编程模型
1. Map与Reduce起源:LISP和其他函数式编程语言中的古老映射和化简操作。
2. MapReduce操作数据最小单位:键值对。
3. MapReduce模型执行过程
(Key1, Value1) → (Key1, List<Value2>) → (Key3, Value3)
a) 将数据抽象为键值对形式作为map函数输入;
b) 经过map函数处理,生成一系列新键值对作为中间结果输出到本地;
c) 计算框架自动将中间结果按键聚合,并将键相同的数据分发到reduce函数,以键和对应指的集合作为reduce函数输入;
d) 经过reduce函数处理,生成一系列键值对作为最终输出。
4. WordCount举例
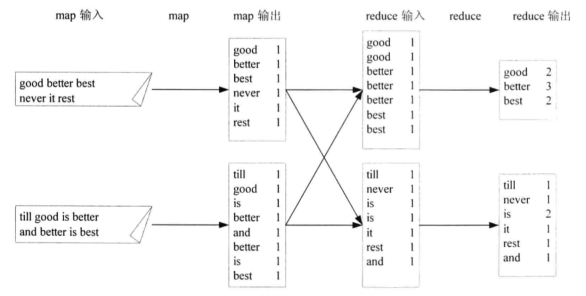
MapReduce过程
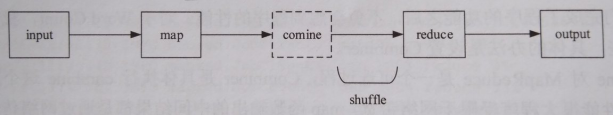
1. 过程描述:input、map、combine、reduce和output五个阶段,其中combine阶段不一定发生,map函数输出的中间结果被被分发到reduce函数的过程称为shuffle,shuffle阶段还会发生copy和sort。
1. Map与Reduce任务:一个作业被分成Map和Reduce计算两个阶段,分别由一个或多个Map任务和Reduce任务组成。
2. input阶段
a) input过程:如果使用HDFS上文件作为MapReduce输入,计算框架以“org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat”抽象类的子类“org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat”作为该文件的InputSplit,每个InputSplit作为一个Map任务的输入,再将InputSplit解析成键值对。
b) InputSplit对数据影响:InputSplit只在逻辑上对数据切分,不影响磁盘上存储的文件。
c) InputSplit包含信息:分片的元数据信息,包括起始位置、长度和所在节点列表等。
1 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input; 2 3 // ... 4 5 public class FileSplit extends InputSplit implements Writable { 6 7 // ... 8 9 /** Constructs a split with host information 10 * 11 * @param file the file name 12 * @param start the position of the first byte in the file to process 13 * @param length the number of bytes in the file to process 14 * @param hosts the list of hosts containing the block, possibly null 15 */ 16 public FileSplit(Path file, long start, long length, String[] hosts) { 17 this.file = file; 18 this.start = start; 19 this.length = length; 20 this.hosts = hosts; 21 } 22 23 // ... 24 }
d) InputSplit大小计算:minSize取自mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize”,默认1;maxSize取自mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize”,默认Long.MAX_VALUE;blockSize取自hdfs-site.xml参数“dfs.block.size”。所以,使用默认配置时,InputSplit大小为块大小。
1 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input; 2 3 // ... 4 5 public abstract class FileInputFormat<K, V> extends InputFormat<K, V> { 6 7 // ... 8 9 protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize, 10 long maxSize) { 11 return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize)); 12 } 13 14 // ... 15 }
e) input数量计算:文件大小÷InputSplit大小。
f) 对齐:任务调度时,优先考虑本节点的数据,如果本节点没有可处理的数据或还需其他节点数据,Map任务所在节点会从其他节点将数据网络传输给自己。当InputSplit大小大于块大小时,Map任务会从其他节点读取一部分数据,就无法实现完全数据本地化,所以InputSplit大小应等于块大小。
g) map函数输入:通过InputFormat.createRecordReader()方法将InputSplit解析为键值对。
1 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input; 2 3 // ... 4 5 public class TextInputFormat extends FileInputFormat<LongWritable, Text> { 6 7 // ... 8 9 @Override 10 public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> 11 createRecordReader(InputSplit split, 12 TaskAttemptContext context) { 13 String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get( 14 "textinputformat.record.delimiter"); 15 byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null; 16 if (null != delimiter) 17 recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8); 18 return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes); 19 } 20 21 // ... 22 }
4. map阶段
a) 写缓冲区:map函数输出时,先写到内存环形缓冲区,并做一次预排序;每个Map任务都有一个环形缓冲区,大小取自mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb”,默认100MB。
b) 缓冲区溢写磁盘:当环形缓冲区达到阀值(mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent”,默认0.80)时,一个后台线程将缓冲区内容溢写(spill)到磁盘mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.cluster.local.dir”指定的目录,默认${hadoop.tmp.dir}/mapred/local。
c) 溢写磁盘前排序:溢写磁盘前,线程根据数据要传送的Reducer对缓冲区数据分区(默认按键),每个分区内再按键排序。
d) Combiner:当已指定Combiner且溢写次数至少3次时,在溢写磁盘前执行Combiner;效果是对map函数输出的中间结果进行一次合并,作用与reduce函数一样;目的是降低中间结果数据量(中间结果要写磁盘且通过网络传至Reducer),提升运行效率。
e) 压缩:对中间结果压缩,目的与Combiner相同;mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.map.output.compress”,默认false,参数“mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec”。
|
压缩格式 |
算法 |
文件扩展名 |
可切分 |
codec类 |
说明 |
|
Deflate |
Deflate |
.deflate |
否 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DeflateCodec |
|
|
gzip |
Deflate |
.gz |
否 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec |
|
|
bzip2 |
bzip2 |
.bz2 |
是 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec |
|
|
LZO |
LZOP |
.lzo |
否 |
com.hadoop.compression.lzo.LzopCodec |
|
|
Snappy |
Snappy |
.snappy |
否 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec |
高压缩、高速,推荐 |
f) 中间结果传输:中间结果通过HTTP方式传至Reducer,传输工作线程数配置mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.tasktracker.http.threads”,默认40。
5. shuffle阶段
a) copy:一个Reduce任务可能需多个Map任务输出,而每个Map任务完成时间很可能不同,当只要有一个Map任务完成,Reduce任务即开始复制其输出;复制线程数配置mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.reduce.shuffle.parallelcopies”,默认5。
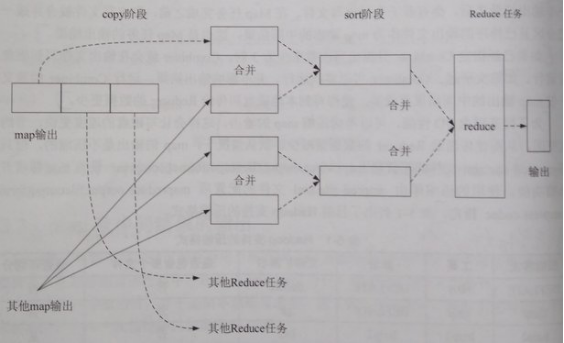
b) copy的缓冲区:如果map输出相当小,数据先被复制到Reducer所在节点的内存缓冲区(大小配置mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.reduce.shuffle.input.buffer.percent”,默认0.70),当内存缓冲区大小达到阀值(mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.reduce.shuffle.merge.percent”,默认0.66)或内存缓冲区文件数达到阀值(mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.reduce.merge.inmem.threshold”,默认1000)时,则合并后溢写磁盘。否则,map输出被复制到磁盘。
c) copy的合并:随复制到磁盘的文件增多,后台线程将其合并为更大、有序的文件,为后续合并节约时间。合并时,压缩的中间结果将在内存中解压缩。
d) sort:复制完成所有map输出后,合并map输出文件并归并排序。
e) sort的合并:将map输出文件合并,直至≤合并因子(mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.task.io.sort.factor”,默认10)。例如,有50个map输出文件,进行5次合并,每次将10个文件合并成一个文件,最后5个文件。
6. reduce阶段
a) reduce函数输入:经过shuffle的文件都是按键分区且有序,相同分区的文件调用一次reduce函数。
b) reduce函数输出:一般为HDFS。
7. 排序
a) MapReduce中的排序算法:快速排序、归并排序。
b) MapReduce发生的3次排序:map阶段的缓冲区排序(快速排序算法);map阶段溢写磁盘前,对溢写文件合并时的排序(归并排序算法);shuffle阶段的文件合并sort(归并排序算法)。
容错机制
1. 任务错误:对错误任务不断重试,直到总尝试次数超过N次认为彻底失败;Map任务、Reduce任务总尝试次数分别为mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.map.maxattempts”和“mapreduce.reduce.maxattempts”,默认均为4。
2. ApplicationMaster错误:通过YARN容错机制完成。
3. NodeManager错误:通过YARN容错机制完成。
4. ResourceManager错误:通过YARN容错机制完成。
API
概况
1. 新旧API
a) 旧API包:org.apache.hadoop.mapred
b) 新API包:org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce
2. Maven依赖
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> 3 <artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId> 4 <version>2.6.5</version> 5 </dependency>
WordCount示例
1. Mapper类
1 package mr.wordcount; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.util.StringTokenizer; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 9 10 public class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> { 11 12 private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); 13 14 private Text word = new Text(); 15 16 @Override 17 protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, 18 Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) 19 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 20 StringTokenizer stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); 21 while (stringTokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) { 22 word.set(stringTokenizer.nextToken()); 23 context.write(word, one); 24 } 25 } 26 27 }
2. Reducer类
1 package mr.wordcount; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 7 8 public class IntSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { 9 10 private IntWritable result = new IntWritable(); 11 12 @Override 13 protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, 14 Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) 15 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 16 int sum = 0; 17 for (IntWritable value : values) { 18 sum += value.get(); 19 } 20 result.set(sum); 21 context.write(key, result); 22 } 23 24 }
3. main方法
1 package mr.wordcount; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 10 11 public class WordCount { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 14 if (args.length != 2) { 15 System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>"); 16 System.exit(2); 17 } 18 19 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 20 Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "WordCount"); 21 job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class); 22 job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class); 23 job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class); 24 job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class); 25 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 26 job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); 27 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0])); 28 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); 29 System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); 30 } 31 32 }
4. 执行命令
hadoop jar wordcount.jar mr.wordcount.WordCount /test/wordcount/in /test/wordcount/out hadoop fs -ls /test/wordcount/out hadoop fs -cat /test/wordcount/out/part-r-00000
Writable接口
1. 职责:Hadoop序列化格式。
2. Hadoop序列化场景:IPC(进程间通信)、数据持久化。
3. 源码(2个重要方法)
1 package org.apache.hadoop.io; 2 3 // ... 4 5 public interface Writable { 6 /** 7 * Serialize the fields of this object to <code>out</code>. 8 * 9 * @param out <code>DataOuput</code> to serialize this object into. 10 * @throws IOException 11 */ 12 void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException; 13 14 /** 15 * Deserialize the fields of this object from <code>in</code>. 16 * 17 * <p>For efficiency, implementations should attempt to re-use storage in the 18 * existing object where possible.</p> 19 * 20 * @param in <code>DataInput</code> to deseriablize this object from. 21 * @throws IOException 22 */ 23 void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException; 24 }
4. 内置实现类
a) 包:org.apache.hadoop.io。
b) 类图
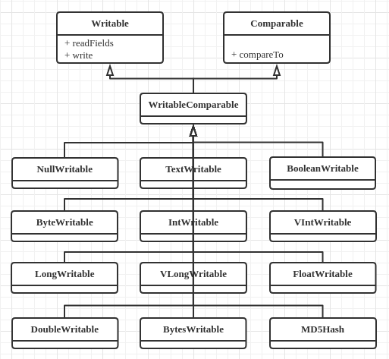
c) 与Java类型对照
|
Java类型 |
Writable实现 |
备注 |
|
null |
NullWritable |
序列化长度为0,充当占位符 |
|
String |
Text |
|
|
boolean |
BooleanWritable |
|
|
byte |
ByteWritable |
|
|
int |
IntWritable、VIntWritable |
V开头表示变长,否则定长 |
|
long |
LongWritable、VLongWritable |
V开头表示变长,否则定长 |
|
float |
FloatWritable |
|
|
double |
DoubleWritable |
5. 自定义实现类
1 import java.io.DataInput; 2 import java.io.DataOutput; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 6 7 public class TextPair implements WritableComparable<TextPair> { 8 9 private Text first; 10 11 private Text second; 12 13 public TextPair() { 14 this(new Text(), new Text()); 15 } 16 17 public TextPair(Text first, Text second) { 18 this.first = first; 19 this.second = second; 20 } 21 22 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 23 first.write(out); 24 second.write(out); 25 } 26 27 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 28 first.readFields(in); 29 second.readFields(in); 30 } 31 32 // 用于MapReduce过程中的排序 33 public int compareTo(TextPair o) { 34 int result = first.compareTo(o.first); 35 if (result == 0) { 36 result = second.compareTo(o.second); 37 } 38 return result; 39 } 40 41 public Text getFirst() { 42 return first; 43 } 44 45 public void setFirst(Text first) { 46 this.first = first; 47 } 48 49 public Text getSecond() { 50 return second; 51 } 52 53 public void setSecond(Text second) { 54 this.second = second; 55 } 56 57 }
Mapper类
1. 源码(4个重要方法)
1 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce; 2 3 // ... 4 5 public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> { 6 7 /** 8 * The <code>Context</code> passed on to the {@link Mapper} implementations. 9 */ 10 public abstract class Context 11 implements MapContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> { 12 } 13 14 /** 15 * Called once at the beginning of the task. 16 */ 17 protected void setup(Context context 18 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 19 // NOTHING 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * Called once for each key/value pair in the input split. Most applications 24 * should override this, but the default is the identity function. 25 */ 26 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 27 protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value, 28 Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 29 context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value); 30 } 31 32 /** 33 * Called once at the end of the task. 34 */ 35 protected void cleanup(Context context 36 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 37 // NOTHING 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * Expert users can override this method for more complete control over the 42 * execution of the Mapper. 43 * @param context 44 * @throws IOException 45 */ 46 public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 47 setup(context); 48 try { 49 while (context.nextKeyValue()) { 50 map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context); 51 } 52 } finally { 53 cleanup(context); 54 } 55 } 56 }
2. run方法:setup→map→cleanup的执行模板。
Reducer类
1. 源码
1 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce; 2 3 // ... 4 5 public class Reducer<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> { 6 7 /** 8 * The <code>Context</code> passed on to the {@link Reducer} implementations. 9 */ 10 public abstract class Context 11 implements ReduceContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> { 12 } 13 14 /** 15 * Called once at the start of the task. 16 */ 17 protected void setup(Context context 18 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 19 // NOTHING 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * This method is called once for each key. Most applications will define 24 * their reduce class by overriding this method. The default implementation 25 * is an identity function. 26 */ 27 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 28 protected void reduce(KEYIN key, Iterable<VALUEIN> values, Context context 29 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 30 for(VALUEIN value: values) { 31 context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value); 32 } 33 } 34 35 /** 36 * Called once at the end of the task. 37 */ 38 protected void cleanup(Context context 39 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 40 // NOTHING 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * Advanced application writers can use the 45 * {@link #run(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer.Context)} method to 46 * control how the reduce task works. 47 */ 48 public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 49 setup(context); 50 try { 51 while (context.nextKey()) { 52 reduce(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getValues(), context); 53 // If a back up store is used, reset it 54 Iterator<VALUEIN> iter = context.getValues().iterator(); 55 if(iter instanceof ReduceContext.ValueIterator) { 56 ((ReduceContext.ValueIterator<VALUEIN>)iter).resetBackupStore(); 57 } 58 } 59 } finally { 60 cleanup(context); 61 } 62 } 63 }
2. run方法:setup→reduce→cleanup的执行模板。
Partitioner抽象类
1. 场景:控制shuffle,即控制中间结果分发的目的Reducer。
2. 源码
1 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce; 2 3 // ... 4 5 public abstract class Partitioner<KEY, VALUE> { 6 7 /** 8 * Get the partition number for a given key (hence record) given the total 9 * number of partitions i.e. number of reduce-tasks for the job. 10 * 11 * <p>Typically a hash function on a all or a subset of the key.</p> 12 * 13 * @param key the key to be partioned. 14 * @param value the entry value. 15 * @param numPartitions the total number of partitions. 16 * @return the partition number for the <code>key</code>. 17 */ 18 public abstract int getPartition(KEY key, VALUE value, int numPartitions); 19 20 }
3. 内置子类
a) org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.HashPartitioner:按键的Hash值分区,默认。
1 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition; 2 3 // ... 4 5 public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> { 6 7 /** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */ 8 public int getPartition(K key, V value, 9 int numReduceTasks) { 10 return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks; 11 } 12 13 }
b) org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.TotalOrderPartitioner:按键分区,使得每个Reduce任务处理一个键连续区间(如1~1000、1000~2000……)的数据,最终输出是全局有序的;如果键对应的数据分布不均匀,则导致部分Reduce任务完成时间变长。
4. 自定义子类
1 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 2 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 3 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; 4 5 public class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, IntWritable> { 6 7 @Override 8 public int getPartition(Text key, IntWritable value, int numReduceTasks) { 9 return ((new Boolean(value.get() > 10000)).hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks; 10 } 11 12 }
1 // main方法设置Partitioner 2 job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
WritableComparator接口
1. 场景:控制MapReduce过程中第2次和第3次排序的排序规则。
2. 内置实现类:org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator。
3. 自定义实现类
1 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 2 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 3 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; 4 5 public class MyWritableComparator extends WritableComparator { 6 7 protected MyWritableComparator() { 8 super(IntWritable.class, true); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") 13 public int compare(WritableComparable key1, WritableComparable key2) { 14 IntWritable x = (IntWritable) key1; 15 IntWritable y = (IntWritable) key2; 16 return (x.get() % 5 - y.get() % 5) > 0 ? 1 : -1; 17 } 18 19 }
1 // main方法设置WritableComparator 2 job.setSortComparatorClass(MyWritableComparator.class); 3 job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyWritableComparator.class);
示例:连接
1. 数据准备(一对多关系)
a) 学生信息
Jenny,00001 Hardy,00002 Bradley,00003
b) 选课信息
00001,Chinese 00001,Math 00002,Music 00002,Math 00003,Physic
2. 代码
a) Mapper类
1 package mr.join; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit; 8 9 public class JoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> { 10 11 public static final String LEFT_PATH = "student_info"; 12 13 public static final String RIGHT_PATH = "student_class_info"; 14 15 public static final String LEFT_TABLE_FLAG = "lu0001"; 16 17 public static final String RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG = "ru0001"; 18 19 private Text outKey = new Text(); 20 21 private Text outValue = new Text(); 22 23 @Override 24 protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, 25 Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>.Context context) 26 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 27 String filePath = ((FileSplit) context.getInputSplit()).getPath().toString(); 28 String tableFlag = null; 29 String joinKey = null; 30 String joinValue = null; 31 32 if (filePath.contains(LEFT_PATH)) { 33 tableFlag = LEFT_TABLE_FLAG; 34 String[] values = value.toString().split(","); 35 joinKey = values[1]; 36 joinValue = values[0]; 37 38 } else if (filePath.contains(RIGHT_PATH)) { 39 tableFlag = RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG; 40 String[] values = value.toString().split(","); 41 joinKey = values[0]; 42 joinValue = values[1]; 43 } else { 44 return; 45 } 46 47 outKey.set(joinKey); 48 outValue.set(tableFlag + joinValue); 49 context.write(outKey, outValue); 50 } 51 52 }
b) Reducer类
1 package mr.join; 2 3 import static mr.join.JoinMapper.LEFT_TABLE_FLAG; 4 import static mr.join.JoinMapper.RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.util.ArrayList; 7 import java.util.Iterator; 8 import java.util.List; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 11 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 12 13 public class JoinReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable> { 14 15 private Text result = new Text(); 16 17 @Override 18 protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, 19 Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) 20 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 21 Iterator<Text> iterator = values.iterator(); 22 List<String> studentClassNames = new ArrayList<>(); 23 String studentName = null; 24 25 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 26 String value = iterator.next().toString(); 27 if (value.startsWith(LEFT_TABLE_FLAG)) { 28 studentName = value.substring(LEFT_TABLE_FLAG.length()); 29 } else if (value.startsWith(RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG)) { 30 studentClassNames.add(value.substring(RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG.length())); 31 } 32 } 33 // 笛卡尔积 34 for (String studentClassName : studentClassNames) { 35 result.set(studentName + "," + studentClassName); 36 context.write(result, NullWritable.get()); 37 } 38 } 39 40 }
c) main方法
1 package mr.join; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 9 10 public class Join { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 13 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 14 Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "Join"); 15 job.setJarByClass(Join.class); 16 job.setMapperClass(JoinMapper.class); 17 job.setReducerClass(JoinReducer.class); 18 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 19 job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); 20 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/test/join/student_info")); 21 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/test/join/student_class_info")); 22 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/test/join/result")); 23 System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); 24 } 25 26 }
d) 执行命令
hadoop jar join.jar mr.join.Join
e) 结果
Jenny,Math
Jenny,Chinese
Hardy,Math
Hardy,Music
Bradley,Physic
示例:二次排序
1. 二次排序:key由两个字段组成,先第1个字段排序,在此基础上再按第2个字段排序。本示例实现先按第1个字段正序,再按第2个字段倒序,类似SQL的“order by column1 asc, column2 desc”。
2. 原理
a) map阶段后期:先调用job.setPartitionerClass()的类对map函数输出分区;每个分区内再调用job.setSortComparatorClass()的类对key排序;如果未设置job.setSortComparatorClass(),则调用key的compareTo()方法排序。
b) reduce阶段:先调用job.setSortComparatorClass()的类对key排序,再开始构造key对应的value迭代器,调用job.setGroupingComparatorClass()的类将key相同的value分到相同value迭代器。
3. 数据准备(column1、column2、column3)
4,3,h 4,2,g 4,1,e 3,4,b 2,7,c 2,3,a 3,1,f 3,3,j 3,2,i 3,3,d
4. 代码
a) Map key类
1 package mr.secondarysort; 2 3 import java.io.DataInput; 4 import java.io.DataOutput; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 8 9 public class CompositeKey implements WritableComparable<CompositeKey> { 10 11 private Text column1 = new Text(); 12 13 private Text column2 = new Text(); 14 15 @Override 16 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 17 column1.write(out); 18 column2.write(out); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 23 column1.readFields(in); 24 column2.readFields(in); 25 } 26 27 // 用于环形缓冲区排序 28 @Override 29 public int compareTo(CompositeKey o) { 30 // 仅按第1个字段排序 31 return column1.compareTo(o.column1); 32 } 33 34 public Text getColumn1() { 35 return column1; 36 } 37 38 public Text getColumn2() { 39 return column2; 40 } 41 42 public void set(String column1, String column2) { 43 this.column1.set(column1); 44 this.column2.set(column2); 45 } 46 47 }
b) Mapper类
1 package mr.secondarysort; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 7 8 public class SecondarySortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CompositeKey, Text> { 9 10 private CompositeKey outKey = new CompositeKey(); 11 12 private Text outValue = new Text(); 13 14 @Override 15 protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, 16 Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CompositeKey, Text>.Context context) 17 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 18 String valueString = value.toString(); 19 String[] columns = valueString.split(","); 20 outKey.set(columns[0], columns[1]); 21 outValue.set(valueString); 22 context.write(outKey, outValue); 23 } 24 25 }
c) Partitioner类
1 package mr.secondarysort; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; 5 6 public class SecondarySortPartitioner extends Partitioner<CompositeKey, Text> { 7 8 @Override 9 public int getPartition(CompositeKey key, Text value, int numReduceTasks) { 10 return (key.getColumn1().hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks; 11 } 12 13 }
d) SortComparator类
1 package mr.secondarysort; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; 5 6 // 用于二次排序 7 public class SortComparator extends WritableComparator { 8 9 protected SortComparator() { 10 super(CompositeKey.class, true); 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") 15 public int compare(WritableComparable key1, WritableComparable key2) { 16 // 按两个字段排序 17 CompositeKey compositeKey1 = (CompositeKey) key1; 18 CompositeKey compositeKey2 = (CompositeKey) key2; 19 int result = compositeKey1.getColumn1().compareTo(compositeKey2.getColumn1()); 20 if (result == 0) { 21 // 第2个字段倒序 22 result = -compositeKey1.getColumn2().compareTo(compositeKey2.getColumn2()); 23 } 24 return result; 25 } 26 27 }
e) GroupingComparator类
1 package mr.secondarysort; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; 5 6 // 用于对value分组 7 public class GroupingComparator extends WritableComparator { 8 9 protected GroupingComparator() { 10 super(CompositeKey.class, true); 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") 15 public int compare(WritableComparable key1, WritableComparable key2) { 16 // 按第1个字段分组 17 CompositeKey compositeKey1 = (CompositeKey) key1; 18 CompositeKey compositeKey2 = (CompositeKey) key2; 19 return compositeKey1.getColumn1().compareTo(compositeKey2.getColumn1()); 20 } 21 22 }
f) Reducer类
1 package mr.secondarysort; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 8 9 public class SecondarySortReducer extends Reducer<CompositeKey, Text, Text, NullWritable> { 10 11 private Text result = new Text(); 12 13 @Override 14 protected void reduce(CompositeKey key, Iterable<Text> values, 15 Reducer<CompositeKey, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) 16 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 17 Iterator<Text> iterator = values.iterator(); 18 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 19 result.set(iterator.next()); 20 context.write(result, NullWritable.get()); 21 } 22 } 23 24 }
g) main方法
1 package mr.secondarysort; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 9 10 public class SecondarySort { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 13 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 14 Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "SecondarySort"); 15 job.setJarByClass(SecondarySort.class); 16 job.setMapperClass(SecondarySortMapper.class); 17 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(CompositeKey.class); 18 job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); 19 job.setPartitionerClass(SecondarySortPartitioner.class); 20 job.setSortComparatorClass(SortComparator.class); 21 job.setGroupingComparatorClass(GroupingComparator.class); 22 job.setReducerClass(SecondarySortReducer.class); 23 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 24 job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); 25 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/test/secondarysort/in")); 26 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/test/secondarysort/out")); 27 System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); 28 } 29 30 }
5. 执行命令
hadoop jar secondarysort.jar mr.secondarysort.SecondarySort
6. 结果
2,7,c 2,3,a 3,4,b 3,3,d 3,3,j 3,2,i 3,1,f 4,3,h 4,2,g 4,1,e
作者:netoxi
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/netoxi
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,未经同意须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。欢迎指正与交流。