一、文件的读写
1、文件的打开,注意事项
1)路径要正确
2)格式要带全(.txt)
filedir = D:softwareHelloWorldsongqinpythonlesson11 文件的读写/test1.txt' # /的好处是避免出现转义字符 filedir1 = 'd:softwareHelloWorldsongqin/lesson11 文件的读写\test2.txt' # 的坏处是会出现转义字符,如 ,可以用\对进行转义 filedir2 = r 'd:softwareHelloWorldsongqin/lesson11 文件的读写\test3.txt' # 使用 r,可以避免出现 的情况 fo = open(filedir) # 执行结果 ---文件操作---
3)读模式的r可以缺省
fileDir = 'D:softwareHelloWorldsongqinpythonlesson11 文件的读写/test1.txt' fo = open(fileDir, 'r') # r可缺省 print(fo) # 运行结果 ---文件操作--- <_io.TextIOWrapper name='D:\software\HelloWorld\songqin\python\lesson11 文件的读写/test1.txt' mode='r' encoding='cp936'>
2、绝对路径:带盘符---如,C、G
3、相对路径:
1)当前目录: ./
2)上一层目录:.. ../
4、tell()方法:获取文件指针位置
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') print(fo.tell()) # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 0
5、fo.read(数量):读文件
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') print(fo.tell()) # 文件指针初始位置 fo.read(2) # 读取两个字符 print(fo.tell()) # 文件指针当前位置 # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 0 2
1)返回的类型是--str
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') str1 = fo.read(2) print(type(str1)) # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- <class 'str'>
2)fo.read()---读取所有
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') str1 = fo.read() # 读取全部内容 print(fo.tell()) # 获取文件指针位置 print(str1) # 打印读取到的内容 # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 14 123456 abcdef
>>> fo = open('test1.txt') >>> fo.read() '123456 abcdef'
6、文件内部的换行符是2个字符长度(windows)--举例,如上面的
7、fo.close():关闭文件
8、fo.seek(长度):移动文件指针位置
1)移动到文件初始位置:fo.seek(0)---0 模式,从头(0)开始。0为绝对位置,如果当前位置为2,那么要移动到3的位置,则为seek(3),而不是seek(1)。
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') print('移动前', fo.tell()) fo.seek(2) # 移动位置 print('移动后', fo.tell()) # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 移动前 0 移动后 2
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') print('移动前', fo.tell()) fo.seek(2) print('移动后', fo.tell()) fo.seek(0) # seek(0), 又回到初始位置 print('再次移动后', fo.tell()) # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 移动前 0 移动后 2 再次移动后 0
2)1模式---从当前位置开始算---一定要是'br'
fo = open(fileDir, 'br') # 1模式,必须用'br' fo.seek(2, 1) print('移动后', fo.tell()) fo.seek(3, 1) print('再次移动后', fo.tell()) # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 移动后 2 再次移动后 5
3)2模式:从尾部位置开始算---一定要是'br'。如果从尾部往前移,则要用负数。
fo = open(fileDir, 'br') print('移动前', fo.tell()) fo.seek(1, 2) print('移动后', fo.tell()) fo.seek(-3, 2) print('再次移动后', fo.tell()) # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 移动前 0 移动后 15 再次移动后 11
4)seek(长度, 模式)
9、读一行:fo.readline()---str
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') str1 = fo.readline() print(str1) print(fo.readline()) # 读取下一行 # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 123456
abcedf
10、读取所有行:fo.readlines()----返回结果是列表
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') print(fo.readlines()) # 返回结果 ---文件操作--- ['123456 ', 'abcdef']
fo = open(fileDir, 'r') # print(fo.readlines()) print(fo.readlines()[0]) # 获取结果列表的元素 # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 123456
1)举例:提取文档中的编号
# 提取文档中的编号 11:12:11> 001 enter chatroom, level 2 11:12:13> 003 enter chatroom, level 25
fileDir = 'D:workHelloWorldsongqinpythonlesson11 文件的读写\test.txt' fo = open(fileDir, 'r') #print(fo.readlines()) # 这一句没注掉,结果一直显示为列表。因为先执行这一句的话,文件指针已经在最后一行的末尾。下面的语句读取不到数据 for str1 in fo.readlines(): print(str1.split(' ')[1]) # 执行结果 001 003
11、fo.read().splitlines()---获取所有行的同时----去掉所有
fileDir = 'D:workHelloWorldsongqinpythonlesson11 文件的读写\test.txt' # fo.read().splitlines()----获取所有行的同时---去掉所有 fo = open(fileDir, 'r') print(fo.read().splitlines()) # 执行结果 ['11:12:11> 001 enter chatroom, level 2', '11:12:13> 003 enter chatroom, level 25']
12、写模式:w
1)如果该文件存在,则所有内容被清空。

fileDir1 = 'D:workHelloWorldsongqinpythonlesson11 文件的读写\test1.txt' fo = open(fileDir1, 'w')
2)如果该文件不存在,则创建该文件。
fileDir1 = 'D:workHelloWorldsongqinpythonlesson11 文件的读写\pytest.txt' fo = open(fileDir1, 'w')
3)fo.write('123456')---只是保存在内存中
4)fo.flush() / fo.close()---从内存写到磁盘
fo = open(fileDir, 'w') fo.write('Hello Python') # pycharm 里面这一步自动把内容保存在硬盘上,如果是idle则会先保存在内存中 fo.close() # 或者fo.flush(),执行这一句,idle才会把数据存在硬盘上 # 执行结果 ---文件操作---
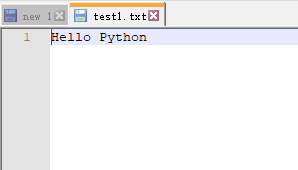
5)写入的内容换行用---
fo = open(fileDir, 'w') fo.write('123456 abcdef') # 执行结果 ---文件操作---
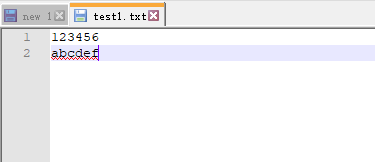
6)print(fo.write('Hello Python')) ----结果有返回值
fo = open(fileDir, 'w') print(fo.write('Hello Python')) # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 12
13、a--追加模式--接着已有的内容写
fo = open(fileDir, 'a') # 目前test1里面已有的内容--Hello Python print(fo.write('123456 abcdef')) fo.close() # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 13
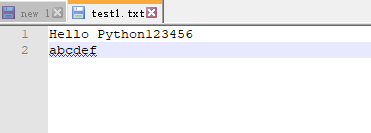
14、读写打开方式
1)r+:为了读取并且写文件而打开文件。如果文件不存在会报错,文件指针在文件的开始位置。
2)w+:为了读取并写文件而打开文件。如果文件不存在,会创建一个文件。文件指针在文件的开始位置。如果文件已经存在,其内容将被清空。
3)a+:为了读取并写文件而打开文件。如果文件不存在则创建一个文件。文件指针在文件的结尾,很多OS上写操作永远在文件结尾进行,不管是否用了seek()。所以为了保证内容不被清空,建议最好用a+。
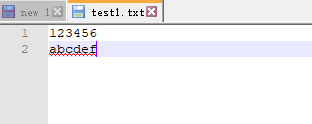
fo = open(fileDir, 'a+') print(fo.write(' Hello Python')) fo.close() # 执行结果 ---文件操作--- 12
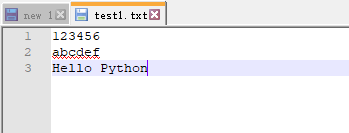
15、with open(fileDir) as fo ===== fo = open(fileDir, 'r'),with open()的优势
1)可以操作多个文件
2)会自动执行fo.close()
with open(fileDir, 'r') as rFile, open(fileDir1, 'w') as wFile: #句尾加英文冒号 print()