本篇文章主要带大家简单分析一下AOP的代理对象,至于AOP是什么,如何配置等基础性知识,不在这里讨论。阅读前请先参考:代理模式,在这之前我们需要了解springframework的三个核心接口与getBean方法
一、FactoryBean&BeanFactory&ObjectFactory
这三个接口都为Springframework的核心接口,虽然这三个名字很像,但是意义却千差万别。面试的时候也常问它们之间的区别。BeanFactory本身就是一个bean的工厂,同时也是我们的IOC容器,而FactoryBean是一个特殊的Bean,我们可以来看看这个接口:

/* * Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.beans.factory; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; /** * Interface to be implemented by objects used within a {@link BeanFactory} which * are themselves factories for individual objects. If a bean implements this * interface, it is used as a factory for an object to expose, not directly as a * bean instance that will be exposed itself. * * <p><b>NB: A bean that implements this interface cannot be used as a normal bean.</b> * A FactoryBean is defined in a bean style, but the object exposed for bean * references ({@link #getObject()}) is always the object that it creates. * * <p>FactoryBeans can support singletons and prototypes, and can either create * objects lazily on demand or eagerly on startup. The {@link SmartFactoryBean} * interface allows for exposing more fine-grained behavioral metadata. * * <p>This interface is heavily used within the framework itself, for example for * the AOP {@link org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean} or the * {@link org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean}. It can be used for * custom components as well; however, this is only common for infrastructure code. * * <p><b>{@code FactoryBean} is a programmatic contract. Implementations are not * supposed to rely on annotation-driven injection or other reflective facilities.</b> * {@link #getObjectType()} {@link #getObject()} invocations may arrive early in * the bootstrap process, even ahead of any post-processor setup. If you need access * other beans, implement {@link BeanFactoryAware} and obtain them programmatically. * * <p>Finally, FactoryBean objects participate in the containing BeanFactory's * synchronization of bean creation. There is usually no need for internal * synchronization other than for purposes of lazy initialization within the * FactoryBean itself (or the like). * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 08.03.2003 * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory * @see org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean * @see org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean */ public interface FactoryBean<T> { /** * Return an instance (possibly shared or independent) of the object * managed by this factory. * <p>As with a {@link BeanFactory}, this allows support for both the * Singleton and Prototype design pattern. * <p>If this FactoryBean is not fully initialized yet at the time of * the call (for example because it is involved in a circular reference), * throw a corresponding {@link FactoryBeanNotInitializedException}. * <p>As of Spring 2.0, FactoryBeans are allowed to return {@code null} * objects. The factory will consider this as normal value to be used; it * will not throw a FactoryBeanNotInitializedException in this case anymore. * FactoryBean implementations are encouraged to throw * FactoryBeanNotInitializedException themselves now, as appropriate. * @return an instance of the bean (can be {@code null}) * @throws Exception in case of creation errors * @see FactoryBeanNotInitializedException */ @Nullable T getObject() throws Exception; /** * Return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates, * or {@code null} if not known in advance. * <p>This allows one to check for specific types of beans without * instantiating objects, for example on autowiring. * <p>In the case of implementations that are creating a singleton object, * this method should try to avoid singleton creation as far as possible; * it should rather estimate the type in advance. * For prototypes, returning a meaningful type here is advisable too. * <p>This method can be called <i>before</i> this FactoryBean has * been fully initialized. It must not rely on state created during * initialization; of course, it can still use such state if available. * <p><b>NOTE:</b> Autowiring will simply ignore FactoryBeans that return * {@code null} here. Therefore it is highly recommended to implement * this method properly, using the current state of the FactoryBean. * @return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates, * or {@code null} if not known at the time of the call * @see ListableBeanFactory#getBeansOfType */ @Nullable Class<?> getObjectType(); /** * Is the object managed by this factory a singleton? That is, * will {@link #getObject()} always return the same object * (a reference that can be cached)? * <p><b>NOTE:</b> If a FactoryBean indicates to hold a singleton object, * the object returned from {@code getObject()} might get cached * by the owning BeanFactory. Hence, do not return {@code true} * unless the FactoryBean always exposes the same reference. * <p>The singleton status of the FactoryBean itself will generally * be provided by the owning BeanFactory; usually, it has to be * defined as singleton there. * <p><b>NOTE:</b> This method returning {@code false} does not * necessarily indicate that returned objects are independent instances. * An implementation of the extended {@link SmartFactoryBean} interface * may explicitly indicate independent instances through its * {@link SmartFactoryBean#isPrototype()} method. Plain {@link FactoryBean} * implementations which do not implement this extended interface are * simply assumed to always return independent instances if the * {@code isSingleton()} implementation returns {@code false}. * <p>The default implementation returns {@code true}, since a * {@code FactoryBean} typically manages a singleton instance. * @return whether the exposed object is a singleton * @see #getObject() * @see SmartFactoryBean#isPrototype() */ default boolean isSingleton() { return true; } }
这里面有三个方法,分别为:getObject,getObjectType,isSingleton。根据文档解释,它只是一个生产对象的工厂,被Spring管理 。这个工厂负责提供我们需要的对象。当需要特殊的方式创建Bean时,则考虑实现该接口。我举个例子来说明:
package org.hzgj.spring.study; import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class WaterFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Water> { @Override public Water getObject() throws Exception { Water water=new Water(); water.setCapacity(20); return water; } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return Water.class; } @Override public boolean isSingleton() { return true; } } //..... package org.hzgj.spring.study; @Deprecated public class Water { private int capacity; public int getCapacity() { return capacity; } public void setCapacity(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; } public void test() { System.out.println("test"); } @Deprecated public void test1() { System.out.println("test1"); } } //..... ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); Water water = applicationContext.getBean(Water.class); water.test1(); // ....能够成功获取到对象
在上面例子里,我们本身是要获得Water对象,那么此时Water对象实际上是通过FactoryBean创建的,因此我们在获取对象时可以添加我们自己的逻辑。
下面我们根据源代码来追溯一下getBean与BeanFactory关联,具体可以参考一下AbstractBeanFactory的doGetBean方法,那么在这里简单的说明一下执行过程:
1) 如果是单例对象的Bean会去缓存中获取
我们先看一下getSinglelone方法:
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */ private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(256); /** Cache of singleton factories: bean name --> ObjectFactory */ private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<String, ObjectFactory<?>>(16); /** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */ private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<String, Object>(16); /** * Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name. * <p>Checks already instantiated singletons and also allows for an early * reference to a currently created singleton (resolving a circular reference). * @param beanName the name of the bean to look for * @param allowEarlyReference whether early references should be created or not * @return the registered singleton object, or {@code null} if none found */ protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) { Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName); if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) { ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName); if (singletonFactory != null) { singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject); this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName); } } } } return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null); }
在这里我们获取单例对象时一定和ObjectFactory有关系
2)从它的parentBeanFactory中获取
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory. BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { // Not found -> check parent. String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); if (args != null) { // Delegation to parent with explicit args. return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); } else { // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); } }
3)处理bean的dependsOn
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on. String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); if (dependsOn != null) { for (String dep : dependsOn) { if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'"); } registerDependentBean(dep, beanName); getBean(dep); } }
4)根据bean的scope类型来获取对应的bean
// Create bean instance. if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // It's a prototype -> create a new instance. Object prototypeInstance = null; try { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else { String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'"); } try { Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " + "defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", ex); } } } catch (BeansException ex) { cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); throw ex; } }
5) 根据需要做类型转换
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance. if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) { try { return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); } catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex); } throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); } }
6)getObjectForBeanInstance
通过源代码我们可以发觉 getObjectForBeanInstance方法调用频率异常之高,那么我们就来看一看,它到底是做什么的:
/** * Get the object for the given bean instance, either the bean * instance itself or its created object in case of a FactoryBean. * @param beanInstance the shared bean instance * @param name name that may include factory dereference prefix * @param beanName the canonical bean name * @param mbd the merged bean definition * @return the object to expose for the bean */ protected Object getObjectForBeanInstance( Object beanInstance, String name, String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { // Don't let calling code try to dereference the factory if the bean isn't a factory. if (BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name) && !(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean)) { throw new BeanIsNotAFactoryException(transformedBeanName(name), beanInstance.getClass()); } // Now we have the bean instance, which may be a normal bean or a FactoryBean. // If it's a FactoryBean, we use it to create a bean instance, unless the // caller actually wants a reference to the factory. if (!(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean) || BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name)) { return beanInstance; } Object object = null; if (mbd == null) { object = getCachedObjectForFactoryBean(beanName); } if (object == null) { // Return bean instance from factory. FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) beanInstance; // Caches object obtained from FactoryBean if it is a singleton. if (mbd == null && containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); } boolean synthetic = (mbd != null && mbd.isSynthetic()); object = getObjectFromFactoryBean(factory, beanName, !synthetic); } return object; }
这段代码最主要是看看是否需要从FactoryBean获取对象的。
最后我们在聊聊ObjectFactory:
public interface ObjectFactory<T> { /** * Return an instance (possibly shared or independent) * of the object managed by this factory. * @return an instance of the bean (should never be {@code null}) * @throws BeansException in case of creation errors */ T getObject() throws BeansException; }
该接口和FactoryBean很像,根据文档说明其getObject方法的返回值不建议为null,另外我们可以发现Bean为singlone时会大量的使用ObjectFactory处理,代码示例:
package org.hzgj.spring.study; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class WaterFactory implements ObjectFactory { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { return new Water(); } } //这样子无法获取water,它只单纯是个工厂
ObjectFactory更像是一个在BeanFactory通过Bean名称关联的对象,只不过它在运行时确定getObject()方法返回的对象内容,再者它不像BeanFactory一样能够制定Bean的类型
二、AOP的核心探究
2.1、核心接口初探
为什么刚开始要说FactoryBean,因为它的文档注释已经提醒我们去参考ProxyFactoryBean了,ProxyFactoryBean是生成目标对象代理的核心,那么我们在此先看一下类图:
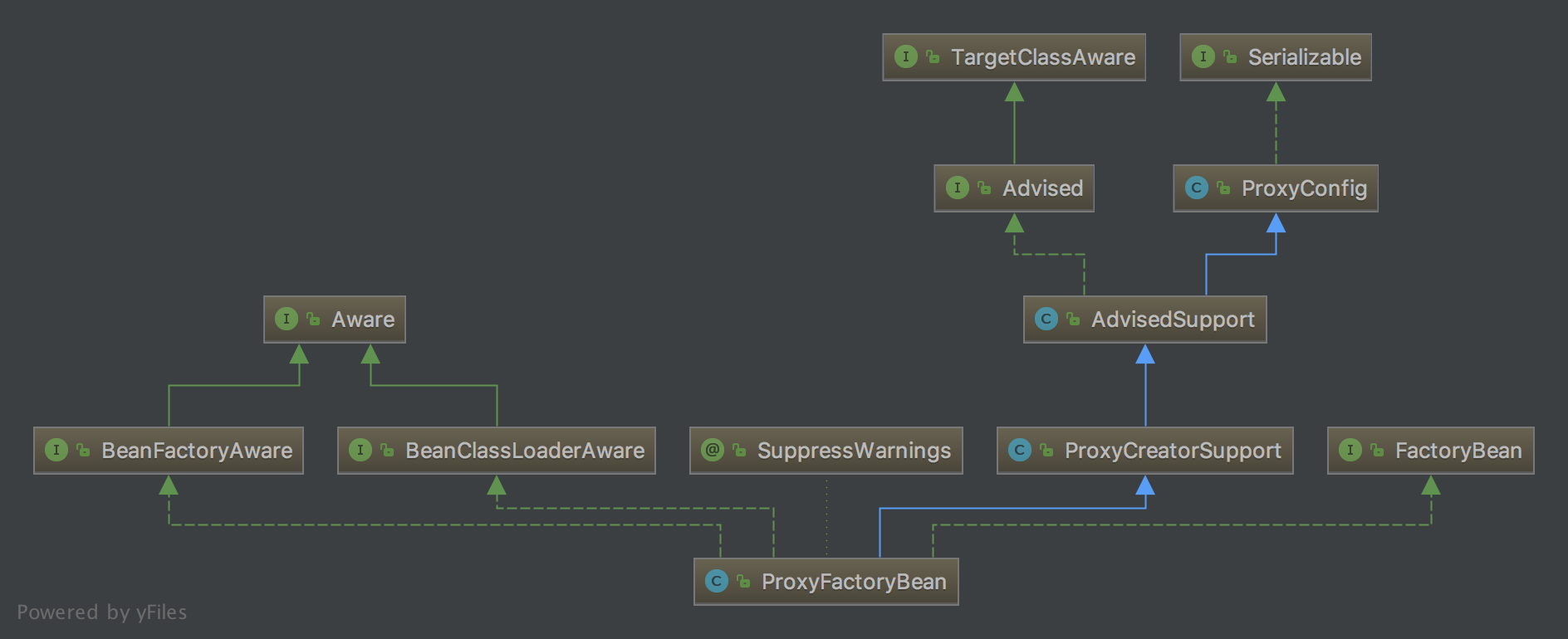
我们可以得知ProxyFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean。
关于AOP的几个重要的核心接口和类如下:
ProxyConfig:

/* * Copyright 2002-2012 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.aop.framework; import java.io.Serializable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; /** * Convenience superclass for configuration used in creating proxies, * to ensure that all proxy creators have consistent properties. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @see AdvisedSupport */ public class ProxyConfig implements Serializable { /** use serialVersionUID from Spring 1.2 for interoperability */ private static final long serialVersionUID = -8409359707199703185L; private boolean proxyTargetClass = false; private boolean optimize = false; boolean opaque = false; boolean exposeProxy = false; private boolean frozen = false; /** * Set whether to proxy the target class directly, instead of just proxying * specific interfaces. Default is "false". * <p>Set this to "true" to force proxying for the TargetSource's exposed * target class. If that target class is an interface, a JDK proxy will be * created for the given interface. If that target class is any other class, * a CGLIB proxy will be created for the given class. * <p>Note: Depending on the configuration of the concrete proxy factory, * the proxy-target-class behavior will also be applied if no interfaces * have been specified (and no interface autodetection is activated). * @see org.springframework.aop.TargetSource#getTargetClass() */ public void setProxyTargetClass(boolean proxyTargetClass) { this.proxyTargetClass = proxyTargetClass; } /** * Return whether to proxy the target class directly as well as any interfaces. */ public boolean isProxyTargetClass() { return this.proxyTargetClass; } /** * Set whether proxies should perform aggressive optimizations. * The exact meaning of "aggressive optimizations" will differ * between proxies, but there is usually some tradeoff. * Default is "false". * <p>For example, optimization will usually mean that advice changes won't * take effect after a proxy has been created. For this reason, optimization * is disabled by default. An optimize value of "true" may be ignored * if other settings preclude optimization: for example, if "exposeProxy" * is set to "true" and that's not compatible with the optimization. */ public void setOptimize(boolean optimize) { this.optimize = optimize; } /** * Return whether proxies should perform aggressive optimizations. */ public boolean isOptimize() { return this.optimize; } /** * Set whether proxies created by this configuration should be prevented * from being cast to {@link Advised} to query proxy status. * <p>Default is "false", meaning that any AOP proxy can be cast to * {@link Advised}. */ public void setOpaque(boolean opaque) { this.opaque = opaque; } /** * Return whether proxies created by this configuration should be * prevented from being cast to {@link Advised}. */ public boolean isOpaque() { return this.opaque; } /** * Set whether the proxy should be exposed by the AOP framework as a * ThreadLocal for retrieval via the AopContext class. This is useful * if an advised object needs to call another advised method on itself. * (If it uses {@code this}, the invocation will not be advised). * <p>Default is "false", in order to avoid unnecessary extra interception. * This means that no guarantees are provided that AopContext access will * work consistently within any method of the advised object. */ public void setExposeProxy(boolean exposeProxy) { this.exposeProxy = exposeProxy; } /** * Return whether the AOP proxy will expose the AOP proxy for * each invocation. */ public boolean isExposeProxy() { return this.exposeProxy; } /** * Set whether this config should be frozen. * <p>When a config is frozen, no advice changes can be made. This is * useful for optimization, and useful when we don't want callers to * be able to manipulate configuration after casting to Advised. */ public void setFrozen(boolean frozen) { this.frozen = frozen; } /** * Return whether the config is frozen, and no advice changes can be made. */ public boolean isFrozen() { return this.frozen; } /** * Copy configuration from the other config object. * @param other object to copy configuration from */ public void copyFrom(ProxyConfig other) { Assert.notNull(other, "Other ProxyConfig object must not be null"); this.proxyTargetClass = other.proxyTargetClass; this.optimize = other.optimize; this.exposeProxy = other.exposeProxy; this.frozen = other.frozen; this.opaque = other.opaque; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append("proxyTargetClass=").append(this.proxyTargetClass).append("; "); sb.append("optimize=").append(this.optimize).append("; "); sb.append("opaque=").append(this.opaque).append("; "); sb.append("exposeProxy=").append(this.exposeProxy).append("; "); sb.append("frozen=").append(this.frozen); return sb.toString(); } }
该类定义代理类最基本的代理配置
Advised:

/* * Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.aop.framework; import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice; import org.springframework.aop.Advisor; import org.springframework.aop.TargetClassAware; import org.springframework.aop.TargetSource; /** * Interface to be implemented by classes that hold the configuration * of a factory of AOP proxies. This configuration includes the * Interceptors and other advice, Advisors, and the proxied interfaces. * * <p>Any AOP proxy obtained from Spring can be cast to this interface to * allow manipulation of its AOP advice. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 13.03.2003 * @see org.springframework.aop.framework.AdvisedSupport */ public interface Advised extends TargetClassAware { /** * Return whether the Advised configuration is frozen, * in which case no advice changes can be made. */ boolean isFrozen(); /** * Are we proxying the full target class instead of specified interfaces? */ boolean isProxyTargetClass(); /** * Return the interfaces proxied by the AOP proxy. * <p>Will not include the target class, which may also be proxied. */ Class<?>[] getProxiedInterfaces(); /** * Determine whether the given interface is proxied. * @param intf the interface to check */ boolean isInterfaceProxied(Class<?> intf); /** * Change the {@code TargetSource} used by this {@code Advised} object. * <p>Only works if the configuration isn't {@linkplain #isFrozen frozen}. * @param targetSource new TargetSource to use */ void setTargetSource(TargetSource targetSource); /** * Return the {@code TargetSource} used by this {@code Advised} object. */ TargetSource getTargetSource(); /** * Set whether the proxy should be exposed by the AOP framework as a * {@link ThreadLocal} for retrieval via the {@link AopContext} class. * <p>It can be necessary to expose the proxy if an advised object needs * to invoke a method on itself with advice applied. Otherwise, if an * advised object invokes a method on {@code this}, no advice will be applied. * <p>Default is {@code false}, for optimal performance. */ void setExposeProxy(boolean exposeProxy); /** * Return whether the factory should expose the proxy as a {@link ThreadLocal}. * <p>It can be necessary to expose the proxy if an advised object needs * to invoke a method on itself with advice applied. Otherwise, if an * advised object invokes a method on {@code this}, no advice will be applied. * <p>Getting the proxy is analogous to an EJB calling {@code getEJBObject()}. * @see AopContext */ boolean isExposeProxy(); /** * Set whether this proxy configuration is pre-filtered so that it only * contains applicable advisors (matching this proxy's target class). * <p>Default is "false". Set this to "true" if the advisors have been * pre-filtered already, meaning that the ClassFilter check can be skipped * when building the actual advisor chain for proxy invocations. * @see org.springframework.aop.ClassFilter */ void setPreFiltered(boolean preFiltered); /** * Return whether this proxy configuration is pre-filtered so that it only * contains applicable advisors (matching this proxy's target class). */ boolean isPreFiltered(); /** * Return the advisors applying to this proxy. * @return a list of Advisors applying to this proxy (never {@code null}) */ Advisor[] getAdvisors(); /** * Add an advisor at the end of the advisor chain. * <p>The Advisor may be an {@link org.springframework.aop.IntroductionAdvisor}, * in which new interfaces will be available when a proxy is next obtained * from the relevant factory. * @param advisor the advisor to add to the end of the chain * @throws AopConfigException in case of invalid advice */ void addAdvisor(Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException; /** * Add an Advisor at the specified position in the chain. * @param advisor the advisor to add at the specified position in the chain * @param pos position in chain (0 is head). Must be valid. * @throws AopConfigException in case of invalid advice */ void addAdvisor(int pos, Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException; /** * Remove the given advisor. * @param advisor the advisor to remove * @return {@code true} if the advisor was removed; {@code false} * if the advisor was not found and hence could not be removed */ boolean removeAdvisor(Advisor advisor); /** * Remove the advisor at the given index. * @param index index of advisor to remove * @throws AopConfigException if the index is invalid */ void removeAdvisor(int index) throws AopConfigException; /** * Return the index (from 0) of the given advisor, * or -1 if no such advisor applies to this proxy. * <p>The return value of this method can be used to index into the advisors array. * @param advisor the advisor to search for * @return index from 0 of this advisor, or -1 if there's no such advisor */ int indexOf(Advisor advisor); /** * Replace the given advisor. * <p><b>Note:</b> If the advisor is an {@link org.springframework.aop.IntroductionAdvisor} * and the replacement is not or implements different interfaces, the proxy will need * to be re-obtained or the old interfaces won't be supported and the new interface * won't be implemented. * @param a the advisor to replace * @param b the advisor to replace it with * @return whether it was replaced. If the advisor wasn't found in the * list of advisors, this method returns {@code false} and does nothing. * @throws AopConfigException in case of invalid advice */ boolean replaceAdvisor(Advisor a, Advisor b) throws AopConfigException; /** * Add the given AOP Alliance advice to the tail of the advice (interceptor) chain. * <p>This will be wrapped in a DefaultPointcutAdvisor with a pointcut that always * applies, and returned from the {@code getAdvisors()} method in this wrapped form. * <p>Note that the given advice will apply to all invocations on the proxy, * even to the {@code toString()} method! Use appropriate advice implementations * or specify appropriate pointcuts to apply to a narrower set of methods. * @param advice advice to add to the tail of the chain * @throws AopConfigException in case of invalid advice * @see #addAdvice(int, Advice) * @see org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor */ void addAdvice(Advice advice) throws AopConfigException; /** * Add the given AOP Alliance Advice at the specified position in the advice chain. * <p>This will be wrapped in a {@link org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor} * with a pointcut that always applies, and returned from the {@link #getAdvisors()} * method in this wrapped form. * <p>Note: The given advice will apply to all invocations on the proxy, * even to the {@code toString()} method! Use appropriate advice implementations * or specify appropriate pointcuts to apply to a narrower set of methods. * @param pos index from 0 (head) * @param advice advice to add at the specified position in the advice chain * @throws AopConfigException in case of invalid advice */ void addAdvice(int pos, Advice advice) throws AopConfigException; /** * Remove the Advisor containing the given advice. * @param advice the advice to remove * @return {@code true} of the advice was found and removed; * {@code false} if there was no such advice */ boolean removeAdvice(Advice advice); /** * Return the index (from 0) of the given AOP Alliance Advice, * or -1 if no such advice is an advice for this proxy. * <p>The return value of this method can be used to index into * the advisors array. * @param advice AOP Alliance advice to search for * @return index from 0 of this advice, or -1 if there's no such advice */ int indexOf(Advice advice); /** * As {@code toString()} will normally be delegated to the target, * this returns the equivalent for the AOP proxy. * @return a string description of the proxy configuration */ String toProxyConfigString(); }
该接口主要定义了代理类的工厂基本的行为,比如说添加Advisor,添加Advise,删除与替换Adivsor等
Adivise:
通知接口,该接口没有方法定义,其常见的子接口有BeforeAdvise,AfterAdvise,MethodInterceptor等
PointCut:
切点接口,该接口定义如下:

/* * Copyright 2002-2012 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.aop; /** * Core Spring pointcut abstraction. * * <p>A pointcut is composed of a {@link ClassFilter} and a {@link MethodMatcher}. * Both these basic terms and a Pointcut itself can be combined to build up combinations * (e.g. through {@link org.springframework.aop.support.ComposablePointcut}). * * @author Rod Johnson * @see ClassFilter * @see MethodMatcher * @see org.springframework.aop.support.Pointcuts * @see org.springframework.aop.support.ClassFilters * @see org.springframework.aop.support.MethodMatchers */ public interface Pointcut { /** * Return the ClassFilter for this pointcut. * @return the ClassFilter (never {@code null}) */ ClassFilter getClassFilter(); /** * Return the MethodMatcher for this pointcut. * @return the MethodMatcher (never {@code null}) */ MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher(); /** * Canonical Pointcut instance that always matches. */ Pointcut TRUE = TruePointcut.INSTANCE; }
Pointcut由ClassFilter和MethodMatcher构成。它通过ClassFilter定位到某些特定类上,通过MethodMatcher定位到某些特定方法上,这样Pointcut就拥有了描述某些类的某些特定方法的能力。
Advisor:
代表一般切面,它仅包含一个Advice,我们说过,因为Advice包含了横切代码和连接点的信息,所以Advior本身就是一个简单的切面,只不过它代表的横切的连接点是所有目标类的所有方法,因为这个横切面太宽泛,所以一般不会直接使用。
2.2、源码分析
我们先来看看ProxyFactoryBean的相关方法
getObject方法:
/** * Return a proxy. Invoked when clients obtain beans from this factory bean. * Create an instance of the AOP proxy to be returned by this factory. * The instance will be cached for a singleton, and create on each call to * {@code getObject()} for a proxy. * @return a fresh AOP proxy reflecting the current state of this factory */ @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { initializeAdvisorChain(); if (isSingleton()) { return getSingletonInstance(); } else { if (this.targetName == null) { logger.warn("Using non-singleton proxies with singleton targets is often undesirable. " + "Enable prototype proxies by setting the 'targetName' property."); } return newPrototypeInstance(); } }
这里面我们关注一下getSingletonInstance方法:
/** * Return the singleton instance of this class's proxy object, * lazily creating it if it hasn't been created already. * @return the shared singleton proxy */ private synchronized Object getSingletonInstance() { if (this.singletonInstance == null) { this.targetSource = freshTargetSource(); if (this.autodetectInterfaces && getProxiedInterfaces().length == 0 && !isProxyTargetClass()) { // Rely on AOP infrastructure to tell us what interfaces to proxy. Class<?> targetClass = getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new FactoryBeanNotInitializedException("Cannot determine target class for proxy"); } setInterfaces(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(targetClass, this.proxyClassLoader)); } // Initialize the shared singleton instance. super.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); this.singletonInstance = getProxy(createAopProxy()); } return this.singletonInstance; }
在这里我们关在关注一下getProxy(AopProxy aopProxy)方法,AopProxy是一个接口:

/* * Copyright 2002-2012 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.aop.framework; /** * Delegate interface for a configured AOP proxy, allowing for the creation * of actual proxy objects. * * <p>Out-of-the-box implementations are available for JDK dynamic proxies * and for CGLIB proxies, as applied by {@link DefaultAopProxyFactory}. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @see DefaultAopProxyFactory */ public interface AopProxy { /** * Create a new proxy object. * <p>Uses the AopProxy's default class loader (if necessary for proxy creation): * usually, the thread context class loader. * @return the new proxy object (never {@code null}) * @see Thread#getContextClassLoader() */ Object getProxy(); /** * Create a new proxy object. * <p>Uses the given class loader (if necessary for proxy creation). * {@code null} will simply be passed down and thus lead to the low-level * proxy facility's default, which is usually different from the default chosen * by the AopProxy implementation's {@link #getProxy()} method. * @param classLoader the class loader to create the proxy with * (or {@code null} for the low-level proxy facility's default) * @return the new proxy object (never {@code null}) */ Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader); }
该接口有如下实现类:JdkDynamicAopProxy , CglibAopProxy , ObjenesisCglibAopProxy。
那么在这里我们看一下JdkDynamicAopProxy的源码,我只贴出其中一个关键部分:
@Override public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true); findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this); }
那么我们可以看出:JDK的动态代理是AOP的实现方式之一
三、基于AOP的核心类与接口实现代理
1、先定义基本的JavaBean:

package org.hzgj.spring.study; @Aop public class Water { private int capacity; public int getCapacity() { return capacity; } public void setCapacity(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; } public void test() { System.out.println("test"); } @Aop public void test1() { System.out.println("test1"); } }
2、自定义注解

package org.hzgj.spring.study; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE}) public @interface Aop { }
3、定义JavaBean的代理

package org.hzgj.spring.study; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation; import org.springframework.aop.framework.AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean; import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor; import org.springframework.aop.support.annotation.AnnotationMatchingPointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * */ @Component public class WaterProxyFactoryBean extends AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean { public WaterProxyFactoryBean() { super.setTarget(new Water()); } @Override protected Object createMainInterceptor() { AnnotationMatchingPointcut pointcut = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(Aop.class, Aop.class); DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, (MethodInterceptor) invocation -> { System.out.println(1); return invocation.proceed(); }); return advisor; } }
该类继承AbstractSingletonProxyFactoryBean,然后需要重写createMainInterceptor,我在这里定义了一个DefaultPointcutAdvisor与扫描注解的PointCut,至此切点,通知,代理都有了,那么AOP最基本的条件也就具备了
4、主程序

package org.hzgj.spring.study; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); Water water = applicationContext.getBean(Water.class); water.test1(); } }
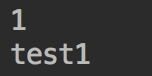
运行成功时会得到如下结果: