前言
相信大家在刚开始体验 Springboot 的时候一定会经常碰到这个页面,也就是访问一个不存在的页面的默认返回页面。
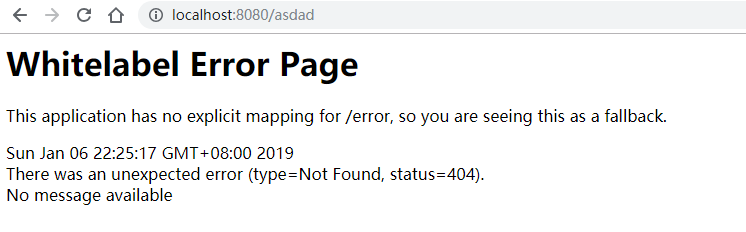
{
"timestamp":"2019-01-06 22:26:16",
"status":404,
"error":"Not Found",
"message":"No message available",
"path":"/asdad"
}
很明显,SpringBoot 根据 HTTP 的请求头信息进行了不同的响应处理。HTTP 相关知识可以参考此处。
1. SpringBoot 异常处理机制
追随 SpringBoot 源码可以分析出默认的错误处理机制。
// org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
// 绑定一些错误信息 记为 1
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes(
this.serverProperties.getError().isIncludeException());
}
// 默认处理 /error 记为 2
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
this.errorViewResolvers);
}
// 错误处理页面 记为3
@Bean
public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer() {
return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, this.dispatcherServletPath);
}
@Configuration
static class DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration {
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration(ApplicationContext applicationContext,
ResourceProperties resourceProperties) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
}
// 决定去哪个错误页面 记为4
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(DispatcherServlet.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() {
return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext,
this.resourceProperties);
}
}
结合上面的注释,上面代码里的四个方法就是 Springboot 实现默认返回错误页面主要部分。
1.1. errorAttributes
errorAttributes直译为错误属性,这个方法确实如此,直接追踪源代码。
代码位于:
// org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorAttributes
这个类里为错误情况共享很多错误信息,如。
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
errorAttributes.put("status", status);
errorAttributes.put("error", HttpStatus.valueOf(status).getReasonPhrase());
errorAttributes.put("errors", result.getAllErrors());
errorAttributes.put("exception", error.getClass().getName());
errorAttributes.put("message", error.getMessage());
errorAttributes.put("trace", stackTrace.toString());
errorAttributes.put("path", path);
这些信息用作共享信息返回,所以当我们使用模版引擎时,也可以像取出其他参数一样轻松取出。
1.2. basicErrorControll
直接追踪 BasicErrorController 的源码内容可以发现下面的一段代码。
// org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.BasicErrorController
@Controller
// 定义请求路径,如果没有error.path路径,则路径为/error
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
// 如果支持的格式 text/html
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
// 获取要返回的值
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(
request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
// 解析错误视图信息,也就是下面1.4中的逻辑
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
// 返回视图,如果没有存在的页面模版,则使用默认错误视图模版
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 如果是接受所有格式的HTTP请求
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request,
isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
// 响应HttpEntity
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
}
由上可知,basicErrorControll 用于创建用于请求返回的 controller类,并根据HTTP请求可接受的格式不同返回对应的信息,所以在使用浏览器和接口测试工具测试时返回结果存在差异。
1.3. ererrorPageCustomizer
直接查看方法里的new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, this.dispatcherServletPath);
//org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer
/**
* {@link WebServerFactoryCustomizer} that configures the server's error pages.
*/
private static class ErrorPageCustomizer implements ErrorPageRegistrar, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties properties;
private final DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath;
protected ErrorPageCustomizer(ServerProperties properties,
DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
this.properties = properties;
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
}
// 注册错误页面
// this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath())
@Override
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
//getPath()得到如下地址,如果没有自定义error.path属性,则去/error位置
//@Value("${error.path:/error}")
//private String path = "/error";
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(this.dispatcherServletPath
.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath()));
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage);
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
由上可知,当遇到错误时,如果没有自定义 error.path 属性,则请求转发至 /error.
1.4. conventionErrorViewResolver
根据上面的代码,一步步深入查看 SpringBoot 的默认错误处理实现,查看看 conventionErrorViewResolver方法。下面是 DefaultErrorViewResolver 类的部分代码,注释解析。
// org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorViewResolver
// 初始化参数,key 是HTTP状态码第一位。
static {
Map<Series, String> views = new EnumMap<>(Series.class);
views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx");
views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx");
SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views);
}
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
// 使用HTTP完整状态码检查是否有页面可以匹配
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
// 使用 HTTP 状态码第一位匹配初始化中的参数创建视图对象
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 拼接错误视图路径 /eroor/[viewname]
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
// 使用模版引擎尝试创建视图对象
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders
.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
// 没有模版引擎,使用静态资源文件夹解析视图
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 遍历静态资源文件夹,检查是否有存在视图
for (String location : this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) {
try {
Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
return null;
}
而 Thymeleaf 对于错误页面的解析实现。
//org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider
public class ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider
implements TemplateAvailabilityProvider {
@Override
public boolean isTemplateAvailable(String view, Environment environment,
ClassLoader classLoader, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent("org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine",
classLoader)) {
String prefix = environment.getProperty("spring.thymeleaf.prefix",
ThymeleafProperties.DEFAULT_PREFIX);
String suffix = environment.getProperty("spring.thymeleaf.suffix",
ThymeleafProperties.DEFAULT_SUFFIX);
return resourceLoader.getResource(prefix + view + suffix).exists();
}
return false;
}
}
从而我们可以得知,错误页面首先会检查模版引擎文件夹下的 /error/HTTP状态码 文件,如果不存在,则检查去模版引擎下的/error/4xx或者 /error/5xx 文件,如果还不存在,则检查静态资源文件夹下对应的上述文件。
2. 自定义异常页面
经过上面的 SpringBoot 错误机制源码分析,知道当遇到错误情况时候,SpringBoot 会首先返回到模版引擎文件夹下的 /error/HTTP状态码 文件,如果不存在,则检查去模版引擎下的/error/4xx或者 /error/5xx 文件,如果还不存在,则检查静态资源文件夹下对应的上述文件。并且在返回时会共享一些错误信息,这些错误信息可以在模版引擎中直接使用。
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
errorAttributes.put("status", status);
errorAttributes.put("error", HttpStatus.valueOf(status).getReasonPhrase());
errorAttributes.put("errors", result.getAllErrors());
errorAttributes.put("exception", error.getClass().getName());
errorAttributes.put("message", error.getMessage());
errorAttributes.put("trace", stackTrace.toString());
errorAttributes.put("path", path);
因此,需要自定义错误页面,只需要在模版文件夹下的 error 文件夹下防止4xx 或者 5xx 文件即可。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>[[${status}]]</title>
<!-- Bootstrap core CSS -->
<link href="/webjars/bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body >
<div class="m-5" >
<p>错误码:[[${status}]]</p>
<p >信息:[[${message}]]</p>
<p >时间:[[${#dates.format(timestamp,'yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss ')}]]</p>
<p >请求路径:[[${path}]]</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
随意访问不存在路径得到。
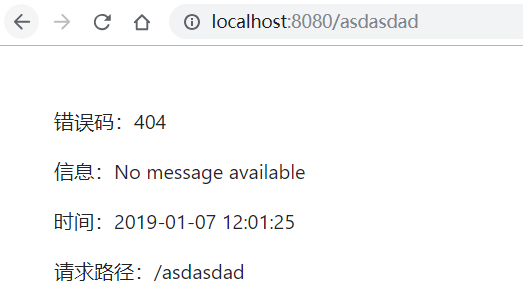
3. 自定义错误JSON
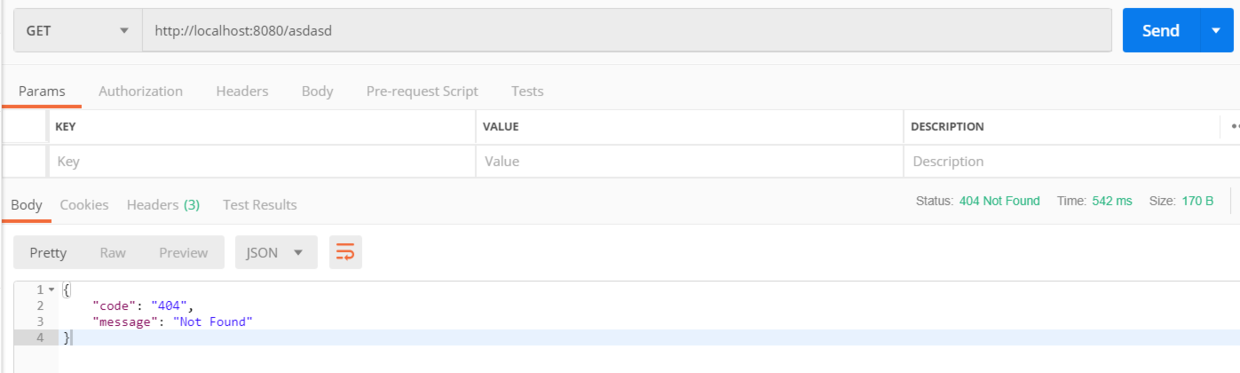
根据上面的 SpringBoot 错误处理原理分析,得知最终返回的 JSON 信息是从一个 map 对象中转换出来的,那么,只要能自定义 map 中的值,就可以自定义错误信息的 json 格式了。直接重写 DefaultErrorAttributes类的 getErrorAttributes 方法即可。
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* <p>
* 自定义错误信息JSON值
*
* @Author niujinpeng
* @Date 2019/1/7 15:21
*/
@Component
public class ErrorAttributesCustom extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
String code = map.get("status").toString();
String message = map.get("error").toString();
HashMap<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("code", code);
hashMap.put("message", message);
return hashMap;
}
}
使用 postman 请求测试。
4. 统一异常处理
使用 @ControllerAdvice 结合@ExceptionHandler 注解可以实现统一的异常处理,@ExceptionHandler 注解的类会自动应用在每一个被 @RequestMapping 注解的方法。当程序中出现异常时会层层上抛
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import net.codingme.boot.domain.Response;
import net.codingme.boot.enums.ResponseEnum;
import net.codingme.boot.utils.ResponseUtill;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* <p>
* 统一的异常处理
*
* @Author niujinpeng
* @Date 2019/1/7 14:26
*/
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandle {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Response handleException(Exception e) {
log.info("异常 {}", e);
if (e instanceof BaseException) {
BaseException exception = (BaseException) e;
String code = exception.getCode();
String message = exception.getMessage();
return ResponseUtill.error(code, message);
}
return ResponseUtill.error(ResponseEnum.UNKNOW_ERROR);
}
}
请求异常页面得到响应如下。
{
"code": "-1",
"data": [],
"message": "未知错误"
}
文章代码已经上传到 GitHub Spring Boot Web开发 - 错误机制。
<完>
欢迎点赞关注!
本文原发于个人博客:https://www.codingme.net 转载请注明出处
