At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
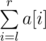 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 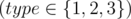 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
8 5
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
49 15 23 1 9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
注意:剪枝:若x<mod,x=x;
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 #include<cstdio> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<cmath> 7 #include<queue> 8 #include<map> 9 10 #define N 100010 11 #define M 15 12 //#define mod 1000000007 13 //#define mod2 100000000 14 #define ll long long 15 #define maxi(a,b) (a)>(b)? (a) : (b) 16 #define mini(a,b) (a)<(b)? (a) : (b) 17 18 using namespace std; 19 20 int n,q; 21 int x[N]; 22 int type; 23 int a,b,c; 24 25 struct node 26 { 27 ll sum; 28 int ma; 29 }tree[4*N]; 30 /* 31 void update(int l,int r,int i) 32 { 33 if(!tree[i].mark) return; 34 int mid=(l+r)/2; 35 tree[2*i].sum+=tree[i].mark*(ll)(mid-l+1); 36 tree[2*i+1].sum+=tree[i].mark*(ll)(r-mid); 37 tree[2*i].mark+=tree[i].mark; 38 tree[2*i+1].mark+=tree[i].mark; 39 tree[i].mark=0; 40 41 }*/ 42 43 ll query(int tl,int tr,int l,int r,int i) 44 { 45 if(tl>r || tr<l) 46 return 0; 47 if(tl<=l && r<=tr) 48 return tree[i].sum; 49 // update(l,r,i); 50 int mid=(l+r)/2; 51 52 return query(tl,tr,l,mid,2*i)+query(tl,tr,mid+1,r,2*i+1); 53 } 54 /* 55 void addd(int tl,int tr,int l,int r,int i,int val) 56 { 57 if(tl>r || tr<l) 58 return; 59 if(tl<=l && tr>=r){ 60 tree[i].sum+=val*(ll)(r-l+1); 61 tree[i].mark+=val; 62 return; 63 } 64 update(l,r,i); 65 int mid=(l+r)/2; 66 addd(tl,tr,l,mid,2*i,val); 67 addd(tl,tr,mid+1,r,2*i+1,val); 68 tree[i].sum=tree[2*i].sum+tree[2*i+1].sum; 69 }*/ 70 71 void modefiyMod(int tl,int tr, int l, int r,int i,int mod) 72 { 73 if(tree[i].ma<mod) return; 74 if(l==r){ 75 tree[i].sum=tree[i].ma=tree[i].sum%mod; 76 return; 77 } 78 else{ 79 int mid=(l+r)/2; 80 if(tr<=mid){ 81 modefiyMod(tl,tr,l,mid,i*2,mod); 82 } 83 else if(tl>mid){ 84 modefiyMod(tl,tr,mid+1,r,i*2+1,mod); 85 } 86 else{ 87 modefiyMod(tl,tr,l,mid,i*2,mod); 88 modefiyMod(tl,tr,mid+1,r,i*2+1,mod); 89 } 90 tree[i].sum=tree[2*i].sum+tree[2*i+1].sum; 91 tree[i].ma=max(tree[2*i].ma,tree[2*i+1].ma); 92 } 93 } 94 95 void setVal(int i, int l, int r,int x,int v) 96 { 97 if(l==r){ 98 tree[i].sum=tree[i].ma=v; 99 return; 100 } 101 else{ 102 int mid=(l+r)/2; 103 if(x<=mid){ 104 setVal(i*2,l,mid,x,v); 105 } 106 else{ 107 setVal(i*2+1,mid+1,r,x,v); 108 } 109 tree[i].sum=tree[2*i].sum+tree[2*i+1].sum; 110 tree[i].ma=max(tree[2*i].ma,tree[2*i+1].ma); 111 } 112 } 113 114 void build_tree(int l,int r,int i) 115 { 116 if(l==r){ 117 tree[i].sum=x[l]; 118 tree[i].ma=x[l]; 119 return; 120 } 121 int mid=(l+r)/2; 122 build_tree(l,mid,2*i); 123 build_tree(mid+1,r,2*i+1); 124 tree[i].sum=tree[2*i].sum+tree[2*i+1].sum; 125 tree[i].ma=max(tree[2*i].ma,tree[2*i+1].ma); 126 } 127 128 int main() 129 { 130 int i; 131 //freopen("data.in","r",stdin); 132 //scanf("%d",&T); 133 //for(int cnt=1;cnt<=T;cnt++) 134 //while(T--) 135 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&q)!=EOF) 136 { 137 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&x[i]); 138 memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree)); 139 build_tree(1,n,1); 140 while(q--){ 141 scanf("%d",&type); 142 if(type==1){ 143 scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); 144 ll ans=query(a,b,1,n,1); 145 printf("%I64d ",ans); 146 147 } 148 else if(type==2){ 149 scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); 150 modefiyMod(a, b, 1, n, 1, c); 151 } 152 else{ 153 scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); 154 setVal(1, 1, n, a, b); 155 } 156 } 157 } 158 159 return 0; 160 }