广度优先搜索算法(英语:Breadth-First-Search,缩写为BFS),又译作宽度优先搜索,是一种图形搜索算法。
简单的说,BFS是从根节点开始,沿着树的宽度遍历树的节点。如果所有节点均被访问,则算法中止。
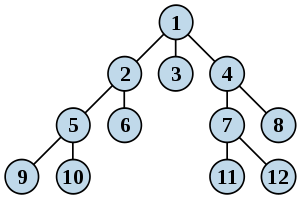 |
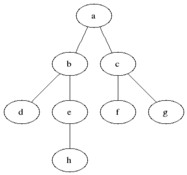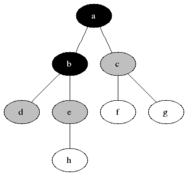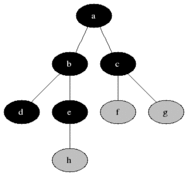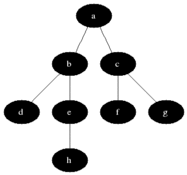 |
时间与空间复杂度:
| 时间复杂度: |  |
| 空间复杂度: |  |
树的BSF:
- 首先将根节点放入队列中。
- 从队列中取出第一个节点,并检验它是否为目标。
- 如果找到目标,则结束搜索并回传结果。
- 否则将它所有尚未检验过的直接子节点加入队列中。
- 若队列为空,表示整个树都检查过了—亦即树中没有欲搜索的目标。结束搜索并回传“找不到目标”。
- 重复步骤2。
/* * 树的广度优先搜索 * 省去了初始化树的部分 */ struct Node { int self; // 结点值 Node *left; // 左结点 Node *right; // 右结点 }; int target = 5; const int TREE_SIZE = 9; std::queue<Node *> unvisited; Node nodes[TREE_SIZE]; Node *current; void bfs(){ unvisited.push(&nodes[0]); // 根节点入队 while (!unvisited.empty()) { current = unvisited.front(); unvisited.pop(); if(current->self==target){ // do something return ; } if (current->left != NULL) unvisited.push(current->left); // 左结点入队 if (current->right != NULL) unvisited.push(current->right); // 右结点入队 cout << current->self << endl; } }
图的BFS:
- 首先将起始结点放入队列中。
- 从队列中取出第一个节点,并检验它是否为目标。
- 如果找到目标,则结束搜索并回传结果。
- 否则将它所有尚未检验过的邻居结点加入队列中。
- 若队列为空,表示整张图都检查过了—亦即图中没有欲搜索的目标。结束搜索并回传“找不到目标”。
- 重复步骤2。
/* * 广度优先遍历 * 图采用邻接矩阵存储 * locateVex() - 计算顶点的下标 * createGraph() - 创建图 * bfs() - 广度优先遍历图 */ #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 100; queue<char> q; bool visited[MAXN]; typedef struct Graph { char vexs[MAXN]; //顶点表 int arcs[MAXN][MAXN]; //邻接矩阵 int vexnum, arcnum; //当前的顶点数和边数 } Graph; int locateVex(Graph &graph, char v) { for (int i = 0; i < graph.vexnum; i++) if (graph.vexs[i] == v) return i; return 0; } int createGraph(Graph &graph) { int i, j, k; char v1, v2; cout << "please input the number of vertices and the number of edges:" << endl; cin >> graph.vexnum >> graph.arcnum; // 读入顶点信息 cout << "please input vertex information:" << endl; for (i = 0; i < graph.vexnum; i++) cin >> graph.vexs[i]; // 初始化邻接矩阵边,0表示顶点i和j之间无边 for (i = 0; i < graph.vexnum; i++) for (j = 0; j < graph.vexnum; j++) graph.arcs[i][j] = 0; // 读入边集信息 cout << "please input the edge information:" << endl; for (k = 0; k < graph.arcnum; k++) { cin >> v1 >> v2; i = locateVex(graph, v1); //找到顶点i的下标 j = locateVex(graph, v2); //找到顶点j的下标 graph.arcs[i][j] = graph.arcs[j][i] = 1; } return 1; } void bfs(Graph &graph, char v0) { int cur, cur_index; int index0 = locateVex(graph, v0); visited[index0] = 1; q.push(v0); cout << "the result is:" << endl; while (!q.empty()) { cur = q.front(); q.pop(); // 将栈顶元素出栈 cur_index = locateVex(graph, cur); //得到顶点对应下标 cout << graph.vexs[cur_index] << " "; for (int i = 0; i < graph.vexnum; i++) { if (graph.arcs[cur_index][i] && !visited[i]) { q.push(graph.vexs[i]); //将顶点入队 visited[i] = 1; //顶点已被访问 } } } } int main() { Graph graph; createGraph(graph); bfs(graph, 'a'); return 0; }