spring web mvc 处理流程
Architecture 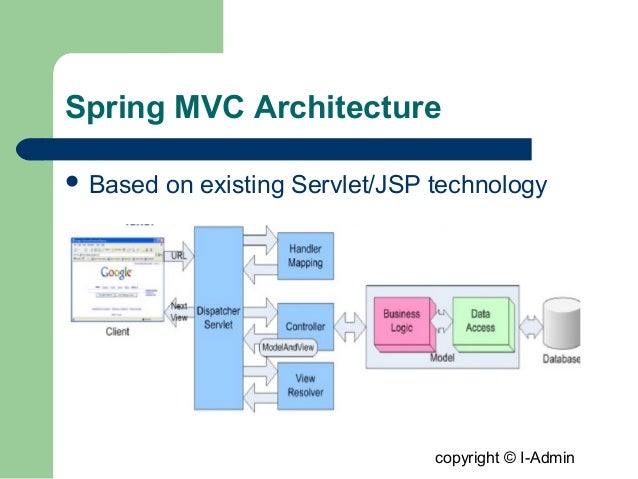
web.xml (webapp必要配置)
作用:spring web mvc 使用dispatcherServlet 分发request,一般我们都需要一个web.xml 来定义这项工作。
servlet-mapping 中定义工作包括:
- servlet-name :用于匹配名字到 [servlet-name]-servlet.xml (默认的规则:路径位于:/WEBContent/WEB-INF/[servlet-name]-servlet.xml)
- url-pattern : 定义哪些url 需要servlet去处理
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
-
其他:
- context-param 的 contextConfigLocation:如果不适用默认规则:自己指定路径来设置Spring容器加载配置文件路径, 如下例子使用applicationContext.xml 可以多个xml
<init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml, /WEB-INF/part2.xml</param-value> </init-param>- listener-class : 为了能在加载spring 的 bean 配置,设置 Listener
- listen-class 为org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
<listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener </listener-class> </listener>
servlet 定义的比较固定:
- servlet-class : 定义哪种具体的servlet class(org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet) 去做
- servlet-name :与 web.xml 的servlet-mapping 对应的 servlet-name
dispatcher-servlet.xml / [servlet-name]-servlet.xml (webapp 非必要配置)
作用:初始化 bean
比较典型的例子:
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/jsp/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
applicationContext.xml (webapp 非必要配置)
bean 的class 是 org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
如果需要初始化bean 对象的成员属性property,则定义其具体属性property name & value
dispatcher-servlet.xml 与 applicationContext.xml 的差别:
共同:两者对webapp 其实都是非必须
applicationContext.xml 定义bean 的 root webapp context
dispatcher-servlet.xml 定义的bean 给一个叫dispatcher(可以是其他名字)的 webapp context
据说 普通webapp context 可以引用 root webapp context
也即:dispatcher-servlet.xml 可以引用applicationContext.xml 定义 context。但反之不行
吐槽:
这么多xml 真的挺烦的,而且还有pom.xml。而且xml 都是比较冗长,使用习惯了其他如nodejs的动态语言,写起来会真的对这些冗长的配置很恼火。
对于pom.xml, gradle 可以稍微释放 xml
对于上述这么多xml,spring-boot 可以释放 这些这么多配置的问题。尤其在:我只不过是想写个简单的rest、单一职责的微服务而已。
另外一方面,这么多xml,IDE是有工具去做简化这些工作的。譬如:
- pom.xml 的下载管理是可以通过IDE dependencies tab -> Add 去搜做的。
- Spring Bean configuration file(beans.xml)是可以通过IDE beans tab -> New Bean 去配置的。
然而还是觉得比较麻烦。。。
参考:Spring - MVC Framework Tutorial(http://www.tutorialspoint.com/spring/spring_web_mvc_framework.htm)
spring mvc architecture(http://www.slideshare.net/RaviKantSoni2/spring-framework-3-session1)
Spring的web.xml配置
(http://book.51cto.com/art/200909/151039.htm)
explain dispatcher-servlet.xml, applicationContext.xml, web.xml (https://www.quora.com/How-will-you-explain-dispatcher-servlet-xml-applicationContext-xml-web-xml-and-spring-servlet-xml-to-a-NOVICE-J2EE-Java-programmer-and-relationship-between-these-xmls-in-a-Spring-Web-App)
difference between ApplicationContext and WebApplicationContext (http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11708967/what-is-the-difference-between-applicationcontext-and-webapplicationcontext-in-s)