转载自: http://m.blog.csdn.net/blog/Enjoying_Science/42008801
题目链接:http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/problem/viewProblem.action?id=49880
题意:7数码问题。在2×4的棋盘上,摆有7个棋子,每个棋子上标有1至7的某一数字,不同棋子上标的数字不相同。棋盘上还有一个空格(用0表示),与空格相邻(上下左右)的棋子可以移到空格中,该棋子原先位置成为空格。给出一个初始状态(保证可以转移到最终状态),找出一种从初始状态转变成给定最终状态的移动棋子步数最少的移动步骤。
输入:多组输入,每组8个数,表示初始状态前四个数为第一行从左到右,后四个数为第二行从左到右。
输出:至少需要多少步可以从输入状态到达最终状态(0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7)
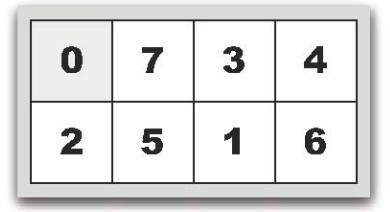 (图1)
(图1)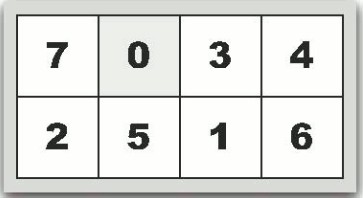 (图2)
(图2) (图3)
(图3)
分析:
乍一看这题没从入手,但只要采取逆向思维,还是可以用广度优先搜索解决。先不考虑如何用最小步数从输入状态到达最终状态,所有结果的最终状态都是(01234567),那么反过来想,只要求出最终状态到达所有结果时的最小步数并记录下来,接下来就是查表了。0表示空位置,对空位置周围的格子采用广度优先的方式移动到0,并记录下最小步数的结果即可。如上图所示,图1,可以选择让7移动过来变成图2,也可以选择让2移动过来变成图3。我们要做的只不过是不断重复这种选择,直至穷举所有情况并记录结果。
我主要是用一个map<string, int>来表示(01234567)到string 的最小步数int,只要当前结果还不存在,就加入map,必然能够穷尽状态。另外,在移动格子问题上,因为我采用string来表示当前状态,那么移动方向上下左右分别就是当前位置-4, +4, -1, +1。需要注意的是,位置3不能移动到位置4.
思路:与前几题的bfs不同,这次的bfs没有明确的移动对象,看似任意一个数都可以当成对象移动。这时我们只需要抓住一个格子就行,比如我们把0作为移动对象,那么0在地图中漫游所有的格子得到的肯定就是问题的解空间。由于题目的输入是多个case,如果对每个case都运行一遍bfs就会TLE。这时我们祭出dp技能,只需要一次bfs就将解空间算出来,以后每个case只要到解空间中去找就行了。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <map> 5 #include <queue> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 map<string, int> dp; 9 int direction[4] = { 1, -1, 4, -4 }; 10 11 //************************************ 12 // Method: bfs 13 // FullName: bfs 14 // Access: public 15 // Returns: void 16 // Qualifier: 让0漫游整个字串 17 //************************************ 18 void bfs() 19 { 20 queue<string> que; 21 que.push("01234567"); 22 dp["01234567"] = 0; 23 while (!que.empty()) 24 { 25 string now = que.front(); que.pop(); 26 // p是'0'的位置 27 int p = 0; 28 for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++j) 29 { 30 if (now[j] == '0') 31 { 32 p = j; 33 break; 34 } 35 } 36 37 for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) 38 { 39 int n = p + direction[i]; 40 if (0 <= n && n < 8 && 41 !(p == 3 && i == 0) && // 右上角不能再往右了 42 !(p == 4 && i == 1)) // 左下角不能再往左了 43 { 44 string next = now; 45 swap(next[p], next[n]); 46 if (dp.find(next) == dp.end()) 47 { 48 dp[next] = dp[now] + 1; 49 que.push(next); 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 ///////////////////////////SubMain////////////////////////////////// 57 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 58 { 59 60 bfs(); 61 string line; 62 while (getline(cin, line)) 63 { 64 line.erase(remove(line.begin(), line.end(), ' '), line.end()); 65 cout << dp[line] << endl; 66 } 67 68 return 0; 69 } 70 ///////////////////////////End Sub//////////////////////////////////

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <map> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 typedef pair<string, int> P; 10 11 const int INF = 100000000; 12 13 //输入 14 string a; 15 16 //移动方向 17 int op[4] = {-1, 1, -4, 4}; 18 19 map<string, int> dp; //保存从string变到"01234567"的int 20 21 //计算从"01234567"转换到其他序列所需的最小步数 22 void bfs(){ 23 //初始化 24 queue<P> que; 25 que.push(P("01234567", 0)); 26 dp["01234567"] = 0; 27 //宽度优先搜索 28 while(!que.empty()){ 29 P p = que.front(); 30 que.pop(); 31 string s = p.first; 32 int cur = p.second; 33 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){ 34 //构造下一次交换 35 int next = cur + op[i]; 36 string str = s; 37 swap(str[cur], str[next]); 38 map<string, int>::iterator it = dp.find(str); 39 //判断是否可移动以及是否访问过 40 if(0 <= next && next < 8 41 && !(cur == 3 && next == 4) && !(cur == 4 && next == 3) 42 && it == dp.end()){ 43 44 que.push(P(str, next)); 45 dp[str] = dp[s] + 1; 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 51 void solve(){ 52 //删除空格 53 a.erase(remove(a.begin(), a.end(), ' '), a.end()); 54 cout<<dp[a]<<endl; 55 } 56 57 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]){ 58 //先逆向构造所有情况,后直接读取输入用例的结果 59 bfs(); 60 while(getline(cin, a)){ 61 solve(); 62 } 63 return 0; 64 }
用find函数来定位数据出现位置,它返回的一个迭代器,当数据出现时,它返回数据所在位置的迭代器,如果map中没有要查找的数据,它返回的迭代器等于end函数返回的迭代器
