多网卡的情况下发送二层包需要配置网卡
三层包不需要配置接口
发包方法:
sr() 发送三层数据包,等待接收一个或者多个数据包的响应 sr1() 发送三层数据包,只会接收一个数据包的响应 srp() 发送二层数据包,然后一直等待回应 srp1() 发送二层发送数据包,只返回第一个答案 send() 只发送三层数据包,系统自动处理路由和两层信息 sendp() 只发送二层数据包 带p字母的都是发送二层数据包,必须要写以太网头部Ether(),而且如果是多接口一定要指定接口 不带p字母都是发送三层数据包,不需要填Ether头部,不需要指定接口
hwdst表示硬件MAC
verbose=False 表示关闭scapy自身的回显
通过Scapy看ARP结构:
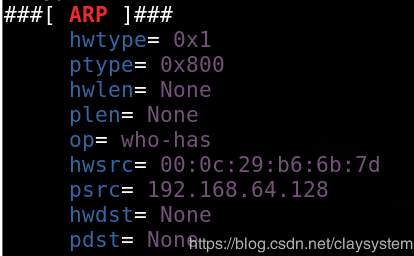
hwdst表示硬件MAC
verbose=False 表示关闭scapy自身的回显
srp返回包结构分析:

Demo:
#!/usr/bin/python3
from scapy.all import *
localmac = '00:0c:29:b6:6b:7d'
localip = '192.168.64.128'
destip = '192.168.64.129'
intername ='eth0'
result_raw = srp(Ether(src=localmac,dst='FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF')/ARP(op=1,hwsrc=localmac,hwdst='00:00:00:00:00:00',psrc=localip,pdst=destip),iface = intername,timeout=1,verbose=False)
print("srp返回的类型",type(result_raw));
print("srp返回的信息:",result_raw);
print("=================================");
print("读取tuple中的第一个元素:",result_raw[0]);
print("类型:",type(result_raw[0]));
print("通过res方法将这个scapy内置的类转换成一个由tuple组成的list");
print("=================res======================")
print(result_raw[0].res);
print("=================end======================");
#res返回的是一个list 可是这个list中只有一个tuple阿 [0] [0]指的是什么数据阿
print("通过getlayer(ARP).fields函数将结果转换为字典");
print(result_raw[0].res[0][1].getlayer(ARP).fields)
输出结果:
srp返回的类型 <class 'tuple'>
srp返回的信息: (<Results: TCP:0 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:1>, <Unanswered: TCP:0 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:0>)
=================================
读取tuple中的第一个元素: <Results: TCP:0 UDP:0 ICMP:0 Other:1>
类型: <class 'scapy.plist.SndRcvList'>
通过res方法将这个scapy内置的类转换成一个由tuple组成的list
=================res======================
[(<Ether dst=FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF src=00:0c:29:b6:6b:7d type=0x806 |<ARP op=who-has hwsrc=00:0c:29:b6:6b:7d psrc=192.168.64.128 hwdst=00:00:00:00:00:00 pdst=192.168.64.129 |>>
, <Ether dst=00:0c:29:b6:6b:7d src=00:0c:29:05:66:e5 type=0x806 |<ARP hwtype=0x1 ptype=0x800 hwlen=6 plen=4 op=is-at hwsrc=00:0c:29:05:66:e5 psrc=192.168.64.129 hwdst=00:0c:29:b6:6b:7d pdst=192.168.64.128 |<Padding load='x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00' |>>>)]
=================end======================
通过getlayer(ARP).fields函数将结果转换为字典
{'hwtype': 1, 'ptype': 2048, 'hwlen': 6, 'plen': 4, 'op': 2, 'hwsrc': '00:0c:29:05:66:e5', 'psrc': '192.168.64.129', 'hwdst': '00:0c:29:b6:6b:7d', 'pdst': '192.168.64.128'}
根据赛题构造一个ARP包:
scapy:
arpPkt = Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")/ARP(pdst='192.168.64.129',hwdst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff") 参数解释: Ether()以太网包 dst=广播地址 ARP()ARP包 pdst=目标IP地址 hwdst=广播地址
演示scapy中ARP包结构:
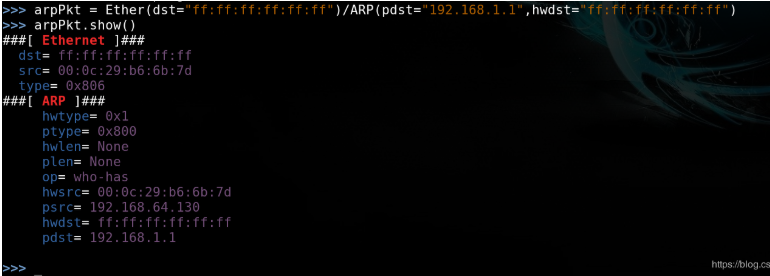
发送ARP包:
res = srp1(arpPkt,timeout=1,verbose=False) 参数解释: srp1 : Send and receive packets at layer 2 and return only the first answer 翻译来就是 在第2层发送和接收数据包,只返回第一个答案 timeout:设置超时时间 verbose:设置scapy的回显,False表示关闭 默认是开启的
查看srp1返回包的类型,这个比较关键
type(res); <class 'scapy.layers.l2.Ether'>
可以发现这里返回包结构的数据类型是:scapy.layers.l2.Ether,之前使用srp接收数据包的类型是scapy.plist.SndRcvList
返回包的结构:
>>> res.show()
###[ Ethernet ]###
dst= 00:0c:29:b6:6b:7d
src= 00:0c:29:05:66:e5
type= 0x806
###[ ARP ]###
hwtype= 0x1
ptype= 0x800
hwlen= 6
plen= 4
op= is-at
hwsrc= 00:0c:29:05:66:e5
psrc= 192.168.64.129
hwdst= 00:0c:29:b6:6b:7d
pdst= 192.168.64.130
###[ Padding ]###
load= 'x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00x00'
>>>
参数解释:
这里有一点需要注意,这个包是目标机器接收我们发送的arp包后返回来的包,怎么说呢,就是我们目标机器发给我们的一个包
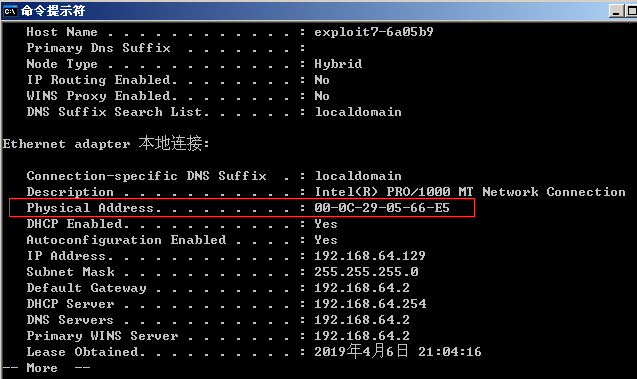
所以这里的参数 pdst是我们自身的ip,hwdst是我们自身的mac地址,不能看包结构名是dst就觉得是目标的
而psrc是目标ip的ip地址,hwsrc是目标机器的mac地址 这点比较重要 太多数据很容易萌萌
验证结果是正确的:
有了上面发送单个IP的基础来看下赛题:
#encoding=utf-8 from scapy.all import * import sys def worker(): ip_list=[] for ipFix in range(1,Flag1): ip = Flag2 + str(ipFix) arpPkt = Flag6(dst=Flag3)/ARP(pdst=ip, hwdst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff") res = Flag5(arpPkt, timeout=1, verbose=False) if res: #print "IP: " + res.psrc + " MAC: " + res.hwsrc ip_list.append(res.psrc) return Flag4 if __name__=="__main__": fp = open('/root/ip.txt','w') ip_list = worker() for ip in ip_list: fp.write(ip+' ') print('over scan') fp.close() #Flag1 = 255 #Flag2 = "192.168.48." #Flag3 = "FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF" 广播地址 #Flag4 = ip_list 返回这个list #Flag5 = srp1发包函数 #Flag6 = Ether 二层发包需要添加以太网头部 逻辑分析: 1.可写方式的打开一个文件/root/ip.txt 2.worker函数分析: 1.创建一个空的list 2.用for in range 1-255 循环 3.然后字符串拼接成192.168.1.x的ip 4.使用srp1构造arp数据包 5.发送arp数据包返回结果存在res中 6.如果res中成功接收到值,添加到list中 7.循环完1-255 返回存活主机的list 3.将worker返回的list写入1打开的文件 OK.
为了巩固自己对这个库的认识和py代码能力的掌握,我写了一个小玩具~
多线程arp扫描:
#!/usr/bin/python3 from scapy.all import * import sys import time import threading import optparse #增加多线程 为了线程同步 加了3个全局变量 liveHost_list = [] #存活主机 live_count = 0; #存活主机数量 liveHostPrint_list = [] #打印的时候用 def printBanner(): banner = ''' _ ____ ____ ____ / | _ | _ / ___| ___ __ _ _ __ _ __ ___ _ __ / _ | |_) | |_) \___ / __/ _` | '_ | '_ / _ '__| / ___ | _ <| __/ ___) | (_| (_| | | | | | | | __/ | /_/ \_\_| \_\_| |____/ \___\__,_|_| |_|_| |_|\___|_| v1.0 by r4bbit ''' print(banner); def get_current_time(): year = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d',time.localtime()); minute = time.strftime('%H-%M-%S',time.localtime()); return year+minute #返回时间 def arp_scan(ip): global liveHostPrint_list global live_count ; global liveHost_list start_time = time.time(); #构造arp数据包 time.sleep(0.001) arpPkt = Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")/ARP(pdst=ip,hwdst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff"); #发送arp数据包 resPkt = srp1(arpPkt,timeout=1,verbose=False); #如果resPkt中返回的有包 if resPkt: # print("[+] " + resPkt.psrc+" is Live"+" MAC:"+resPkt.hwsrc); #这里需要注意 因为是接受的包 所以需要打印出的是发送包的源ip和源mac liveHost_list.append(resPkt.psrc); #存储到傻吊list中 print_tmp = "IP:"+resPkt.psrc+" MAC:"+resPkt.hwsrc liveHostPrint_list.append(print_tmp); live_count +=1; #else: # print("[-] "+ip+" Not Alive"); def main(): printBanner(); global liveHost_list; global live_count; global liveHostPrint_list; parser = optparse.OptionParser("usage -i <192.168.1> 主要是我菜不会用netaddr库"); parser.add_option('-i',dest='target_ips',type='string',help='ip no'); (options,arg) = parser.parse_args() if(options.target_ips == None): print(parser.usage); exit(0); else: target_ips = options.target_ips start_time = time.time(); for ip in range(1,255): ip_str = target_ips+"."+str(ip); scan_thread = threading.Thread(target=arp_scan,args=(ip_str,)); scan_thread.start(); end_time = time.time(); #创建文件夹 #如果文件夹不存在 #扫描完成打印结果 然后存储文件 for ip in liveHostPrint_list: print(ip); print("Scan Done. Live Host Num:%d Use Time:%f s " % (live_count,end_time-start_time)); if not os.path.exists(target_ips): os.mkdir(target_ips) log_name = get_current_time(); fp = open("./"+target_ips+"/"+log_name+".arp","w"); print("Scan Log in "+target_ips); for i in liveHost_list: fp.write(i+" "); fp.close(); if __name__ == '__main__': main()
