GCC 内联汇编
在MIT6.828的实验中,有几处用到了很底层的函数,都以内联汇编的形式存在,例如
static inline uint32_t
read_esp(void)
{
uint32_t esp;
asm volatile("movl %%esp,%0" : "=r" (esp));
return esp;
}
static inline uint32_t
read_ebp(void)
{
uint32_t ebp;
asm volatile("movl %%ebp,%0" : "=r" (ebp));
return ebp;
}
因此这篇博客对于内联汇编的基本用法做一个总结。
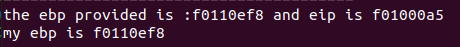
首先是一般的形式,只能使用全局变量来传递数据,例如如下程序(插入在kern/monitor.c):
uint32_t test_val=0;
int mon_backtrace(int argc, char **argv, struct Trapframe *tf)
{
uint32_t *ebp=(uint32_t*)read_ebp();
cprintf("the ebp provided is :%8x and eip is %8x
",ebp,ebp[1]);
// you could use simple asm if you use global variables
asm volatile(
"push %eax
"
"mov %ebp,%eax
"
"mov %eax,test_val
"
"popl %eax
"
);
cprintf("my ebp is %8x
",(uint32_t*)test_val);
return 0;
}
运行结果如下
这里就跟普通的汇编一样的使用方式,注意关键字volatile是为了防止被优化,还有每行汇编语句后面的
。又或者如这段程序
int32_t eip=0;
int main()
{
//basic inline assembly
//global variable can be use
asm volatile(
"push %eax
"
"call .testpop
"
".testpop:
"
"pop %ebx
"
"movl %ebx,%eax
"
"movl %eax,eip
"
"pop %eax
"
);
printf("the eip is :%x
",eip);
asm volatile(
"push %eax
"
"movl %ebp,%eax
"
"movl %eax,eip
"
"pop %eax
"
);
printf("the ebp is :%x
",eip);
return 0;
}
如果只能使用全局变量,必然会有很多不方便。为了能使用局部变量,需要使用扩展的内联汇编。扩展的内联汇编形式如下
asm("assembly code"
:output location
:input orperands
:changed registers
);
其中
output location :输出的放哪儿
input operands :哪些输入
changed registers:改变了哪些寄存器
并且输入和输出部分都是如下形式
"constraint"(variable)
约束符主要是限制寄存器的使用
a use %eax %ax or %al
b use %ebx,%bx,or %bl
c use %ecx,%cx,or %cl
d use %edx,%dx,or %dl
S use %esi or %si
D use %edi or %si
r use any available register
q use one of %eax,%ebx,%ecx or %edx
A use %eax&%edx for 64-bit value
f use float register
m use memory location of variable
同时可以加上修饰符
+ read & write
= only write
来看一段程序
uint32_t ebp;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"push %%eax
"
"mov %%ebp,%%eax
"
"mov %%eax,%%edx
"
"pop %%eax "
:"=d"(ebp)
:
:"%eax"
);
printf("the ebp is %8x
",(uint32_t*)ebp);
这里"=d"(ebp)意思是输出使用寄存器%edx,并且把结果放到变量ebp中。没有输入所以省略,但是冒号不能省。这个过程改变了%eax。注意的是,编译器默认输入输出中涉及的寄存器都被改变,因此不能再将这部分寄存器写到改变部分去。注意汇编代码中的寄存器%eax要写成%%eax,每条语句完要写
。
再来看一段程序
int xa=6;
int xb=2;
int result_1;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"add %%ebx,%%eax
"
"movl $2,%%ecx
"
"mul %%ecx
"
"movl %%eax,%%edi
"
"movl %%eax,%%edx"
:"=d"(result_1)
:"a"(xa),"b"(xb)
:"%ecx","%edi"
);
printf("the result is %d
",result_1);
:"=d"(result_1)输出使用%edx,放到result_1这个变量中;
:"a"(xa),"b"(xb)输入变量xa的值放到%eax中,xb的值放到%ebx中;
:"%ecx","%edi"这个过程还改变了%ecx和%edi。
再来看一个例子
int data1=10;
int data2=20;
int result;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"imul %%edx ,%%ecx
"
"movl %%ecx ,%%eax
"
:"=a"(result)
:"d"(data1),"c"(data2)
);
printf("10*20 is %d
",result);
有了上面的例子,这个应该就很好理解了。然而在我们看别人写的内联汇编中,有时会出现%0,%1这种。这叫占位符,就是代表第几个操作数所在的寄存器,例如看如下代码
// %0 is the register to store result
// %1 is the register to store data1
// %2 is the register to store data2
__asm__ __volatile__(
"imul %1 ,%2
"
"movl %2 ,%0
"
:"=r"(result)
:"r"(data1),"r"(data2)
);
printf("10*20 is %d
",result);
这里使用了限定符r就是,让编译器自己选择可用的寄存器。注意这里改变的寄存器列表为空,需要连带冒号一起省略。
同时,也可以用输入变量来接受结果,结合占位符,有如下代码
__asm__ __volatile__(
"imul %1 ,%0
"
:"=r"(data2)
:"r"(data1),"0"(data2)
);
输入和输出都是data2。
但是,如果输入输出过多,还用数字就会显得不太好,因此gcc也有一个方便的做法
data1=10;
data2=20;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"imul %[value1] ,%[value2]
"
:[value2]"=r"(data2)
:[value1]"r"(data1),"0"(data2)
);
printf("10*20 is %d
",data2);
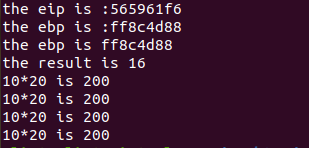
全文的测试代码如下:
//test_asm.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
int32_t eip=0;
int main()
{
//basic inline assembly
asm volatile(
"push %eax
"
"call .testpop
"
".testpop:
"
"pop %ebx
"
"movl %ebx,%eax
"
"movl %eax,eip
"
"pop %eax
"
);
printf("the eip is :%x
",eip);
asm volatile(
"push %eax
"
"movl %ebp,%eax
"
"movl %eax,eip
"
"pop %eax
"
);
printf("the ebp is :%x
",eip);
uint32_t ebp;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"push %%eax
"
"mov %%ebp,%%eax
"
"mov %%eax,%%edx
"
"pop %%eax "
:"=d"(ebp)
:
:"%eax"
);
printf("the ebp is %8x
",(uint32_t*)ebp);
int xa=6;
int xb=2;
int result_1;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"add %%ebx,%%eax
"
"movl $2,%%ecx
"
"mul %%ecx
"
"movl %%eax,%%edi
"
"movl %%eax,%%edx"
:"=d"(result_1)
:"a"(xa),"b"(xb)
:"%ecx","%edi"
);
printf("the result is %d
",result_1);
int data1=10;
int data2=20;
int result;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"imul %%edx ,%%ecx
"
"movl %%ecx ,%%eax
"
:"=a"(result)
:"d"(data1),"c"(data2)
);
printf("10*20 is %d
",result);
__asm__ __volatile__(
"imul %1 ,%2
"
"movl %2 ,%0
"
:"=r"(result)
:"r"(data1),"r"(data2)
);
printf("10*20 is %d
",result);
// you could refer them
// 0 means use the first register to store the input and output
__asm__ __volatile__(
"imul %1 ,%0
"
:"=r"(data2)
:"r"(data1),"0"(data2)
);
printf("10*20 is %d
",data2);
// you could rename
// [name] "constraint"(variable)
data1=10;
data2=20;
__asm__ __volatile__(
"imul %[value1] ,%[value2]
"
:[value2]"=r"(data2)
:[value1]"r"(data1),"0"(data2)
);
printf("10*20 is %d
",data2);
return 0;
}
编译指令: gcc -O0 -m32 test_asm.c -o test
结果如下