SKlearning大部分的输入数据都是M * N数组.
然而我们从数据库或文件读取得来的通常是Python内定的类型tuple或list
它们的优势就不说了,但是直接把list或tuple构成的二维数组传入scikit是会出问题的.
如:
DeprecationWarning: Passing 1d arrays as data is deprecated in 0.17 and will raise ValueError in 0.19. Reshape your data either using X.reshape(-1, 1) if your data has a single feature or X.reshape(1, -1) if it contains a single sample. DeprecationWarning)
下面贴上如何把list/tuple转为scikit使用的array
首先, 准备数据如下:
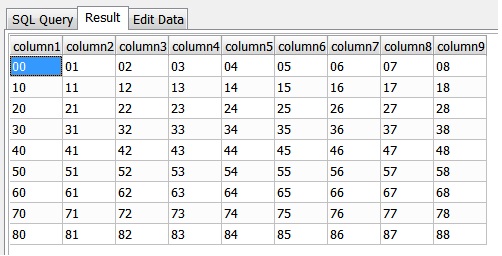
读取一行数据变为一维数组
conn = sql.connect('result_sale.db') conn.text_factory = str dataSet = conn.execute('select * from sampleData') tpRows = dataSet.fetchone() conn.close() print type(tpRows) print tpRows lstRows = list(tpRows) aryRows1 = np.array(lstRows) # 转成数组 #aryRows2 = np.array(lstRows).reshape(1, -1) # 转成1行N列 (二维数组) #aryRows3 = np.array(lstRows).reshape(-1, 1) # 转成N行1列 (二维数组) print lstRows print aryRows1
输入如下: 请留意输入的不同点 :)
('00', '01', '02', '03', '04', '05', '06', '07', '08') (tuple)
['00', '01', '02', '03', '04', '05', '06', '07', '08'] (list)
['00' '01' '02' '03' '04' '05' '06' '07' '08'] (array)
Process finished with exit code 0
一次性转换整个数据集
conn = sql.connect('result_sale.db') conn.text_factory = str dataSet = conn.execute('select * from sampleData') tpRows = dataSet.fetchall() conn.close() aryRows1 = np.array(tpRows) # 转成数组 #aryRows2 = np.array(tpRows).reshape(1, -1) # 转成1行N列 (二维数组) #aryRows3 = np.array(tpRows).reshape(-1, 1) # 转成N行1列 (二维数组) print aryRows1 #print aryRows2 #print aryRows3
输入如下:
[['00' '01' '02' '03' '04' '05' '06' '07' '08'] ['10' '11' '12' '13' '14' '15' '16' '17' '18'] ['20' '21' '22' '23' '24' '25' '26' '27' '28'] ['30' '31' '32' '33' '34' '35' '36' '37' '38'] ['40' '41' '42' '43' '44' '45' '46' '47' '48'] ['50' '51' '52' '53' '54' '55' '56' '57' '58'] ['60' '61' '62' '63' '64' '65' '66' '67' '68'] ['70' '71' '72' '73' '74' '75' '76' '77' '78'] ['80' '81' '82' '83' '84' '85' '86' '87' '88']] Process finished with exit code 0
逐条纪录转换, 可以用下标来引用数组
conn = sql.connect('result_sale.db') conn.text_factory = str dataSet = conn.execute('select * from sampleData') tpRows = dataSet.fetchall() conn.close() #aryRows = np.zeros([len(tpRows), len(tpRows[0])]) aryRows = np.ones_like(tpRows) #亦可使用 empty, empty_like, zeros, zeros_like 等方法 j=0 for row in tpRows: aryRows[j][:] = row j += 1 print aryRows
输入如下:
[['00' '01' '02' '03' '04' '05' '06' '07' '08'] ['10' '11' '12' '13' '14' '15' '16' '17' '18'] ['20' '21' '22' '23' '24' '25' '26' '27' '28'] ['30' '31' '32' '33' '34' '35' '36' '37' '38'] ['40' '41' '42' '43' '44' '45' '46' '47' '48'] ['50' '51' '52' '53' '54' '55' '56' '57' '58'] ['60' '61' '62' '63' '64' '65' '66' '67' '68'] ['70' '71' '72' '73' '74' '75' '76' '77' '78'] ['80' '81' '82' '83' '84' '85' '86' '87' '88']] Process finished with exit code 0