描述:
假设南京鼓楼区的移动电话基站为如下操作:把该区域分成一个正方形,形成一个 S * S 的 矩阵,行和列的编号为从 0 到 S-1。正方形的每个块为一个基站。 基站内的活跃手机数量 可能会发生变化,因为手机会从一个块移动到另一个块,或者开机和关机。 在这时,每个 基站会向主基站报告活跃手机数量的变化以及矩阵变化位置的行和列。 编写一个程序,接收这些报告,并回答有关任何矩阵中当前活跃手机总数的查询。
输入: 每一次输入会在单独的一行上,包含一个整数指令和多个整数参数。
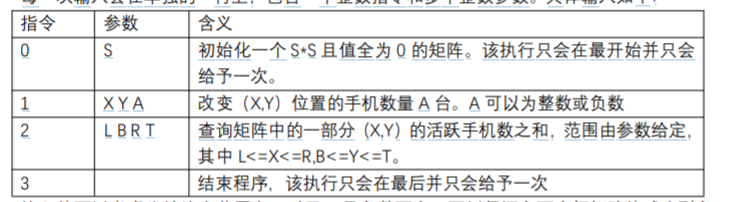
输入值可以考虑为始终在范围内,对于 A 是负数而言,可以保证它不会把矩阵值减小到负 数。索引查询从 0 开始,例如,对于大小为 4*4 的表,我们有 0<=X<=3 且 0<=Y<=3。
表的大小:1 * 1 <= S * S <= 1024 * 1024
每个基站中的值 V(任何时间):0 <= V <= 32767
更新的活跃手机数量:-32768 <= A <= 32767
输入的指令数:3 <= U <= 60002
整个表中的最大电话数:M = 2 ^ 30
输出:
您的程序不应该对除 2 之外的指令的行返回任何内容。如果指令是 2,那么您的程序应该通 过将答案写为包含单个整数的标准输出。
样例输入:
0 4
1 1 2 3
2 0 0 2 2
1 1 1 2
1 1 2 -1
2 1 1 2 3
3
样例输出: 3 4
分析:主要仔细看输入输出的描述。其中根据输入,知道入参,包含四中指令,0 开始创建矩阵,二维数组来实现,记录个位置手机数量。3指令,表示结束。1指令对指定位置上的手机数量进行改变,整数为增加,负数为减少,第一次为该位置上的手机数量。2指令输出部分区域的手机数量。
附上测试案例:
1 import static org.junit.Assert.*; 2 3 import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; 4 import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; 5 import java.io.InputStream; 6 import java.io.PrintStream; 7 8 import org.junit.After; 9 import org.junit.Before; 10 import org.junit.Test; 11 12 public class MobilePhoneTest1 { 13 14 String sep; 15 MobilePhone mp; 16 PrintStream console = null; 17 ByteArrayInputStream in = null; 18 ByteArrayOutputStream out = null; 19 InputStream input = null; 20 21 @Before 22 public void setUp() throws Exception { 23 mp = new MobilePhone(); 24 out = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 25 input = System.in; 26 console = System.out; 27 System.setOut(new PrintStream(out)); 28 sep = System.getProperty("line.separator"); 29 } 30 31 @After 32 public void tearDown() throws Exception { 33 System.setIn(input); 34 out.close(); 35 System.setOut(console); 36 } 37 38 @Test(timeout=4000) 39 public void test1() { 40 in = new ByteArrayInputStream(("0 4" + sep + "1 1 2 3" + sep +"2 0 0 2 2" + sep + "1 1 1 2" + sep + "1 1 2 -1" + sep + "2 1 1 2 3" + sep +"3").getBytes()); 41 System.setIn(in); 42 mp.entrance(); 43 String ans = out.toString(); 44 assertEquals("3" + sep + "4"+sep, ans); 45 } 46 47 @Test(timeout=4000) 48 public void test2() { 49 in = new ByteArrayInputStream(("0 9" + sep + "1 2 5 55" + sep +"2 0 3 5 7" + sep + "1 3 3 77" + sep + "2 0 0 6 5" + sep +"3").getBytes()); 50 System.setIn(in); 51 mp.entrance(); 52 String ans = out.toString(); 53 assertEquals("55" + sep + "132"+sep, ans); 54 } 55 56 @Test(timeout=4000) 57 public void test3() { 58 in = new ByteArrayInputStream(("0 110" + sep + "1 77 66 233" + sep +"2 0 0 0 0" + sep + "1 11 22 112" + sep + "1 11 22 112" + sep + "1 3 5 -17" + sep + "2 21 34 5 9" + sep +"3").getBytes()); 59 System.setIn(in); 60 mp.entrance(); 61 String ans = out.toString(); 62 assertEquals("0" + sep + "224"+sep, ans); 63 } 64 65 @Test(timeout=4000) 66 public void test4() { 67 in = new ByteArrayInputStream(("0 255" + sep + "1 128 64 196" + sep +"2 167 173 47 53" + sep + "2 133 247 150 232" + sep + "2 152 167 201 37" + sep +"3").getBytes()); 68 System.setIn(in); 69 mp.entrance(); 70 String ans = out.toString(); 71 assertEquals("196" + sep + "0" + sep+ "0" + sep, ans); 72 } 73 74 @Test(timeout=4000) 75 public void test5() { 76 in = new ByteArrayInputStream(("0 777" + sep + "1 7 7 77" + sep +"2 7 7 7 7" + sep + "1 6 6 -66" + sep + "1 111 111 111" + sep + "2 17 27 37 47" + sep + "2 57 67 77 87" + sep + "2 97 107 127 137" + sep +"3").getBytes()); 77 System.setIn(in); 78 mp.entrance(); 79 String ans = out.toString(); 80 assertEquals("77" + sep + "0" + sep + "0" + sep + "111" + sep, ans); 81 } 82 }
解题代码:
1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 4 5 public class MobilePhone { 6 7 static int [][] juzheng =null; 8 9 public static void entrance() { 10 String input = getSystemIn(); 11 String [] instructions = input.split("/"); 12 for(int i=0;i<instructions.length;i++){ 13 String instruction = instructions[i]; 14 String [] content = instruction.split(" "); 15 String zhiling = "";//0,1,2,3 16 if(content!=null){ 17 zhiling = content[0]; 18 if("0".equals(zhiling) && i==0){ 19 int s = Integer.parseInt(content[1]);//矩阵大小 20 juzheng=new int[s][s]; 21 }else if("1".equals(zhiling)){ 22 int x = Integer.parseInt(content[1]); 23 int y = Integer.parseInt(content[2]); 24 int num = Integer.parseInt(content[3]); 25 if(juzheng[x][y]==0){ 26 juzheng[x][y]=num; 27 28 }else{ 29 juzheng[x][y]=juzheng[x][y]+num; 30 } 31 32 }else if("2".equals(zhiling)){ 33 int l= Integer.parseInt(content[1]); 34 int b= Integer.parseInt(content[2]); 35 int r= Integer.parseInt(content[3]); 36 int t= Integer.parseInt(content[4]); 37 int sum=0; 38 int L,B,R,T; 39 if(l<r){ 40 L =l; 41 R =r; 42 }else { 43 L =r; 44 R =l; 45 } 46 if(b<t){ 47 B =b; 48 T =t; 49 }else { 50 B =t; 51 T =b; 52 } 53 for (int m=L;m<R+1;m++){ 54 for (int n=B;n<T+1;n++){ 55 sum=sum+juzheng[m][n]; 56 } 57 58 } 59 60 System.out.println(sum); 61 }else if("3".equals(zhiling)){ 62 return; 63 } 64 } 65 66 67 } 68 69 } 70 71 /** 72 * 将输入流转换为字符串 73 * @return 74 */ 75 private static String getSystemIn(){ 76 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 77 String str = null; 78 String res = "" ; 79 try { 80 81 int b; 82 while(( str=br.readLine()) != null){ 83 res=res+"/"+str; 84 } 85 86 } catch (IOException e) { 87 e.printStackTrace(); 88 } 89 return res.substring(1,res.length()); 90 } 91 92 93 94 95 }