$ color{#0066ff}{ 题目描述 }$
半月的夜空中,寄托了多少人与人之间的思念啊
曦月知道,这些思念会汇集成一个字符串(S(n = |S|))
由于思念汇集的过于复杂,因此曦月希望提炼出所有的思念
我们定义(Y_S(i))表示对于字符串(S)而言,长度为(i)的子串中,字典序最小的,左端点最小的左端点的值
比如对于串(S = "baa"),(Y_S(1) = 2, Y_S(2) = 2, Y_S(3) = 1)
曦月会告知你(S)串,你只需要告诉曦月(Y_S(i)(1 le i le n))即可
(color{#0066ff}{输入格式})
第一行,两个参数,分别是(sigma in {10, 26, 10^7})和(n)
如果(sigma = 26),那么第二行将是一个长为(n)的小写字母字符串(S)
其他情况下,第二行将输入(n)个位于([0, sigma]内)的整数
(color{#0066ff}{输出格式})
输出一行,第iii个数表示(Y_S(i))的值
(color{#0066ff}{输入样例})
26 11
remoonqaqac
26 11
txdydkwqaqa
10000000 17
9 9 8 2 4 4 3 5 3 1 9 2 6 0 8 1 7
(color{#0066ff}{输出样例})
8 10 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 1
9 9 9 5 5 5 5 3 3 1 1
14 14 14 14 10 10 10 10 4 4 4 4 4 4 3 2 1
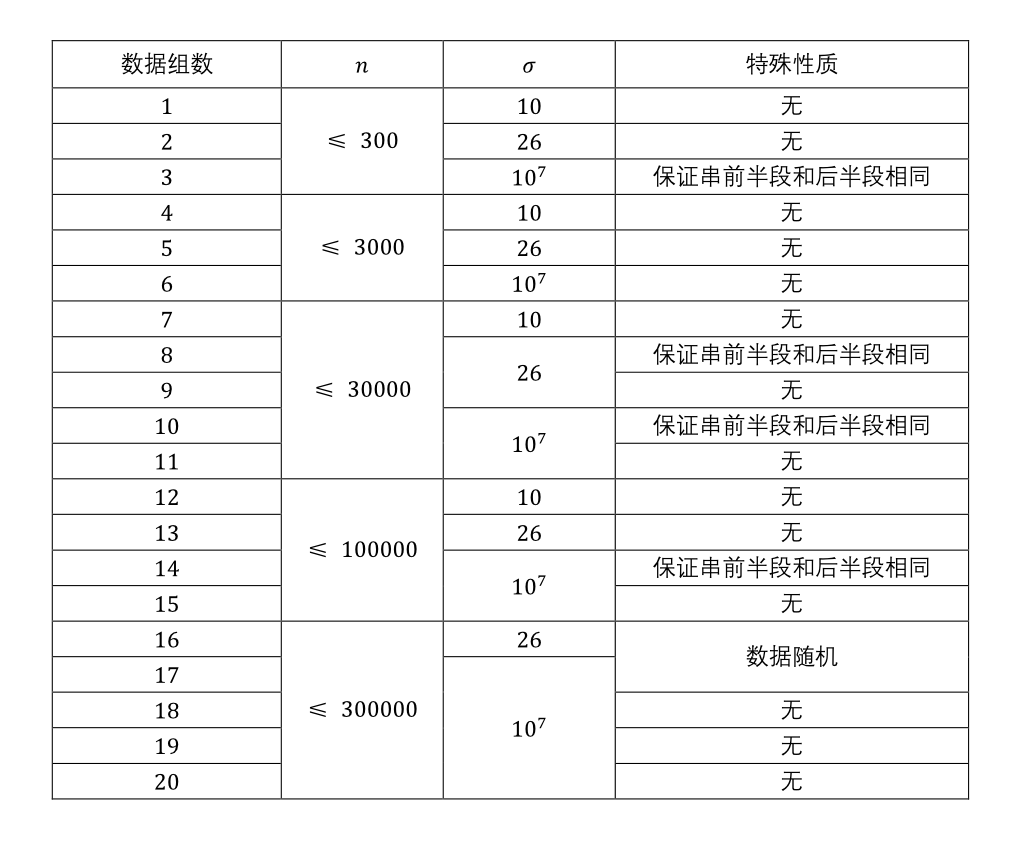
(color{#0066ff}{数据范围与提示})
(color{#0066ff}{题解})
建立后缀自动机,要求左端点最小,你需要维护左端点,所以倒着插入,建立后缀树
这样树上的点代表的是某一后缀的前缀
后缀自动机上每个点维护一个pos为起始位置l
然后考虑后缀树上的一条边,它对应的字串长度就是$[父亲len+1,自己的len] $,那么对于这一区间的答案就可以用自己子树的pos最小值来更新
至于字典序最小?,我们可以dfs出后缀树中每个节点是它父亲的那个儿子,然后考虑倒着覆盖,当前字典序是最优的,把原来的覆盖掉,用线段树维护答案就行了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
LL in() {
char ch; LL x = 0, f = 1;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))(ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(x = ch ^ 48; isdigit(ch = getchar()); x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return x * f;
}
const int maxn = 3e5 + 10;
const int inf = 0x7fffffff;
struct Tree {
protected:
struct node {
node *ch[2];
int l, r, val, tag;
node(int l = 0, int r = 0, int val = 0, int tag = -1): l(l), r(r), val(val), tag(tag) {
ch[0] = ch[1] = NULL;
}
void trn(int v) { val = tag = v; }
void dwn() {
if(tag == -1) return;
ch[0]->trn(tag);
ch[1]->trn(tag);
tag = -1;
}
int mid() { return (l + r) >> 1; }
}*root;
void build(node *&o, int l, int r) {
o = new node(l, r);
if(l == r) return;
build(o->ch[0], l, o->mid());
build(o->ch[1], o->mid() + 1, r);
}
void lazy(node *o, int l, int r, int val) {
if(l > r) return;
if(l <= o->l && o->r <= r) return o->trn(val);
o->dwn();
if(l <= o->mid()) lazy(o->ch[0], l, r, val);
if(r > o->mid()) lazy(o->ch[1], l, r, val);
}
void out(node *o) {
if(o->l == o->r) return (void)(printf("%d ", o->val));
o->dwn();
out(o->ch[0]); out(o->ch[1]);
}
public:
void build(int n) { build(root, 1, n); }
void lazy(int l, int r, int val) { lazy(root, l, r, val); }
void out() { out(root); }
}tree;
struct SAM {
protected:
struct node {
std::map<int, node*> ch, treech;
node *fa;
int len, pos;
node(int len = 0, int pos = 0): len(len), pos(pos) {
fa = NULL;
ch.clear(), treech.clear();
}
}pool[maxn << 1], *tail, *root, *lst;
int s[maxn];
char ls[maxn];
void extend(int c, int id) {
node *o = new(tail++) node(lst->len + 1, id), *v = lst;
for(; v && !v->ch[c]; v = v->fa) v->ch[c] = o;
if(!v) o->fa = root;
else if(v->len + 1 == v->ch[c]->len) o->fa = v->ch[c];
else {
node *n = new(tail++) node(v->len + 1, v->ch[c]->pos), *d = v->ch[c];
n->ch = d->ch, n->fa = d->fa, d->fa = o->fa = n;
for(; v && v->ch[c] == d; v = v->fa) v->ch[c] = n;
}
lst = o;
}
void getmin(node *o) {
for(std::pair<int, node*> i : o->treech) {
getmin(i.second);
o->pos = std::min(o->pos, i.second->pos);
}
}
void getans(node *o) {
tree.lazy((o->fa? o->fa->len + 1 : 1), o->len, o->pos);
for(std::map<int, node*>::reverse_iterator it = o->treech.rbegin(); it != o->treech.rend(); it++)
getans(it->second);
}
public:
SAM() {
tail = pool;
root = lst = new(tail++) node();
}
void init(int bel, int len) {
if(bel == 26) {
scanf("%s", ls + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++) s[i] = ls[i] - 'a';
}
else {
for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++) s[i] = in();
}
for(int i = len; i >= 1; i--) extend(s[i], i);
}
void build() {
for(node *o = pool + 1; o != tail; o++)
o->fa->treech[s[o->pos + o->fa->len]] = o;
}
void getmin() { getmin(root); }
void getans() { getans(root); }
}s;
int main() {
int val = in(), n = in();
s.init(val, n);
tree.build(n);
s.build();
s.getmin();
s.getans();
tree.out();
return 0;
}