总结一下java中获取与泛型相关的信息的知识,不如说是使用方法.网上也有很多类似的优秀文章,这里主要做一个知识的总结.通过反射获取泛型信息的常见例子:
//bean
package testProject;
public class Person {
private String nameString = "233";
public String getNameString() {
return nameString;
}
public void setNameString(String nameString) {
this.nameString = nameString;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [nameString=" + nameString + "]";
}
}
//基本dao
public abstract class BaseDao<T> {
private Class<T> clazz = null;
{
Type type = getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
if( type instanceof ParameterizedType ){
ParameterizedType pType = (ParameterizedType)type;
Type claz = pType.getActualTypeArguments()[0];
if( claz instanceof Class ){
this.clazz = (Class<T>) claz;
}
}
}
public T getEntity() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException{
return this.clazz.newInstance();
}
}
//实现
public class PersonDao extends BaseDao<Person> {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
PersonDao pDao = new PersonDao();
System.out.println( pDao.getEntity().toString() );
}
}
//结果:Person [nameString=233]
在java的java.lang.reflect 包中有一个Type接口. 具体子类如下.
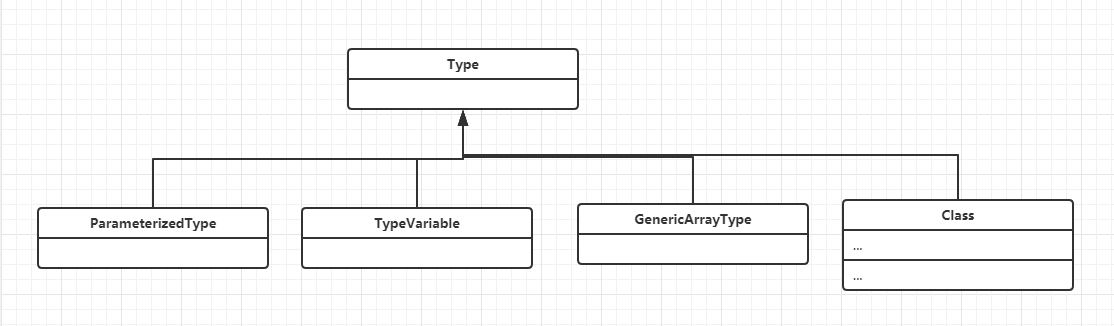
一般java中包含泛型信息的地方包括类( class<T> MyClass )方法( public <T> void test(T t){ } )字段( public List<T> list,public T t),继承的父类中包含( class MyClass1 extends MyClass<String>{} )等.
java将这些泛型信息进行了分类,包括包含泛型信息的类型,不包含泛型信息的类型,泛型数组类型,以及对泛型参数(T,V等泛型参数)信息类等.所有这些分类统一用Type接口作为抽象
class HaveGenericClass<T>{} class NoGenericClass{} public class TypeTest<T> { private List<String> list; private T t; private List list1; private List<T> list2; private HaveGenericClass haveGenericClassWithoutGeneric; private HaveGenericClass<String> haveGenericClassWithGeneric; private NoGenericClass noGenericClass; private int var; private List<T>[] listTArr; private List<String>[] listStringArr; private List[] listArr; private T[] tArr; private int[] intArr; private HaveGenericClass[] haveGenericClassWithoutGenericArr; private HaveGenericClass<T>[] haveGenericClassWithGenericArr; private HaveGenericClass<String>[] haveGenericClassWithGenericArr2; private NoGenericClass[] noGenericClassArr; private <U> U genericMethod(U u,String s){ return u; } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { Field[] fields = TypeTest.class.getDeclaredFields(); for( Field f: fields ){ Type t = f.getGenericType(); printType(f.getName(), t); } Method genericMethod = TypeTest.class.getDeclaredMethod("genericMethod",Object.class,String.class); Type[] types = genericMethod.getGenericParameterTypes(); Parameter[] ps = genericMethod.getParameters(); for(Parameter p : ps){ Type type = p.getParameterizedType(); printType(p.getName(), type); System.out.println( p.getType() ); } } public static void printType(String name, Type type){ if( type instanceof Class ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : Class"); }else if( type instanceof ParameterizedType ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : ParameterizedType"); }else if( type instanceof GenericArrayType ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : GenericArrayType"); }else if( type instanceof TypeVariable ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : TypeVariable"); } } }
运行结果如下:
the type of list is : ParameterizedType
the type of t is : TypeVariable
the type of list1 is : Class
the type of list2 is : ParameterizedType
the type of haveGenericClassWithoutGeneric is : Class
the type of haveGenericClassWithGeneric is : ParameterizedType
the type of noGenericClass is : Class
the type of var is : Class
the type of listTArr is : GenericArrayType
the type of listStringArr is : GenericArrayType
the type of listArr is : Class
the type of tArr is : GenericArrayType
the type of intArr is : Class
the type of haveGenericClassWithoutGenericArr is : Class
the type of haveGenericClassWithGenericArr is : GenericArrayType
the type of haveGenericClassWithGenericArr2 is : GenericArrayType
the type of noGenericClassArr is : Class
the type of arg0 is : TypeVariable
class java.lang.Object
the type of arg1 is : Class
class java.lang.String
从上面的测试中可以看到,带有泛型信息的类型可以划分到ParameterizedType类型,类似( List<String>,List<T>等).包含泛型信息的数组则可以划分到GenericArrayType分类,其余不包含泛型信息的类型可以划分到Class类型(可以认为不包含泛型的类型也是一种参数化类型(参数化类型 举个例子就是 class person<T>{ }这样子),只不过这种参数化类型的泛型信息为零(没有泛型信息的参数化类型)),因此Class类也实现Type接口.下面就介绍有一下这4个类的方法和如何获取(仅限我所知道的).
1.ParameterizedType
public interface ParameterizedType extends Type { //获取<>中的实际类型 Type[] getActualTypeArguments(); //获取<>前的实际类型 Type getRawType(); //如果这个类是某个类的所属,返回这个所属的类,否则返回null Type getOwnerType(); }
Type[] getActualTypeArguments();
获取<>中的实际类型,该方法只脱去最外层的<>.
class People<U,V,T>{} public class TypeTest<T> { private People<String,List<String>,T> People; public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { Type t = TypeTest.class.getDeclaredField("People").getGenericType(); ParameterizedType pt = (ParameterizedType)t; Type[] types = pt.getActualTypeArguments(); for( int i = 0; i < types.length; i++ ){ printType(types[i].toString(), types[i]); } } public static void printType(String name, Type type){ if( type instanceof Class ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : Class"); }else if( type instanceof ParameterizedType ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : ParameterizedType"); }else if( type instanceof GenericArrayType ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : GenericArrayType"); }else if( type instanceof TypeVariable ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : TypeVariable"); } } }
执行结果为
the type of class java.lang.String is : Class
the type of java.util.List<java.lang.String> is : ParameterizedType
the type of T is : TypeVariable
可以看到第二个泛型参数的类型是ParameterizedType,也真是List<String>所对应的类型.另外第三个泛型参数的类型为TypeVariable,泛型参数(T,V等泛型参数)信息类(我是这么解释和理解的)之后会提到.
2.getRawType()
获取声明泛型的实际的类或接口,也就是<>前面的那个值
3.getOwnerType()
如果该类是内部类,那么该方法可以获取外部类,否则返回null, 举个例子
public class TypeTest<T> { private People<String,List<String>,T> People; private class Inner<U>{} private Inner<String> inner; public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { Type t = TypeTest.class.getDeclaredField("inner").getGenericType(); ParameterizedType pt = (ParameterizedType)t; Type t1 = pt.getOwnerType(); if( t1 instanceof ParameterizedType ){ ParameterizedType pt1 = (ParameterizedType)t1; System.out.println( pt1.getRawType() ); } }
}
结果:
class testProject.TypeTest
2.GenericArrayType
泛型数组类型,类似(List<String>[] T[]等).
public interface GenericArrayType extends Type { Type getGenericComponentType(); }
返回泛型数组中元素的Type类型,即List<String>[] 中的 List<String>(ParameterizedTypeImpl),T[] 中的T(TypeVariableImpl),List<String>[][]中的List<String>[]();
public class TypeTest<T> { private List<String>[] lists; private T[] ts; private List<String>[][] listss; public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { Type lists = ((GenericArrayType)TypeTest.class.getDeclaredField("lists").getGenericType()).getGenericComponentType(); Type ts = ((GenericArrayType)TypeTest.class.getDeclaredField("ts").getGenericType()).getGenericComponentType(); Type listss = ((GenericArrayType)TypeTest.class.getDeclaredField("listss").getGenericType()).getGenericComponentType(); printType("lists", lists); printType("ts",ts ); printType("listss",listss ); } public static void printType(String name, Type type){ if( type instanceof Class ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : Class"); }else if( type instanceof ParameterizedType ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : ParameterizedType"); }else if( type instanceof GenericArrayType ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : GenericArrayType"); }else if( type instanceof TypeVariable ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : TypeVariable"); } } }
执行结果如下:
the type of lists is : ParameterizedType
the type of ts is : TypeVariable
the type of listss is : GenericArrayType
3.TypeVariable
泛型的类型变量,可以认为是List<T>中的T,Map<K,V>中的K,V等
3.1 getBounds()
获取类型变量上限,如果没有上限(即 class Person<T>{},这里的类型变量T 没有上限),那么上限为Object
public class TypeTest<T extends String & Comparable<String>> {//继承String,实现接口Comparable<String>,可以用&连接多个接口 private List<String>[] lists; private T[] ts; private List<String>[][] listss; public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { TypeVariable tv[] = TypeTest.class.getTypeParameters(); Type[] ts = tv[0].getBounds(); for( Type t : ts ){ System.out.println( t ); } } }
执行结果如下:
class java.lang.String
java.lang.Comparable<java.lang.String>
3.2 getGenericDeclaration()
获取声明该类型变量的类比如( TypeTest<T> 中的TypeTest )
public class TypeTest<T> { private List<String>[] lists; private List<String>[][] listss; public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { TypeVariable tv[] = TypeTest.class.getTypeParameters(); System.out.println( tv[0].getGenericDeclaration() ); } }
执行结果:
class testProject.TypeTest
3.3 getName()
获取类型变量在源码中定义的名称
public class TypeTest<T> { private List<String>[] lists; private List<String>[][] listss; public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { TypeVariable tv[] = TypeTest.class.getTypeParameters(); System.out.println( tv[0].getName() ); } }
执行结果:
T
//补充一点
泛型的声明包括在类上方法上或者构造函数上,并不能再字段上声明泛型.
在类上声明:
class Person<T>{
private T t; //字段可以使用声明的泛型
}
在构造函数上声明:
class TypeTest{
public <U> TypeTest(){}
}
在方法上声明:
class TypeTest{
public <T> void test(T t){}
}
但不能直接在字段上声明, 比如
class Person{
private T t;//错误
}
这样的使用方法不正确.
由此及彼,在获取泛型变量的方式上,java提供了一个GenericDeclaration接口
public interface GenericDeclaration{ TypeVariable<?>[] getTypeParameters(); }
用于获取泛型变量,
而实现该接口的继承体现如下
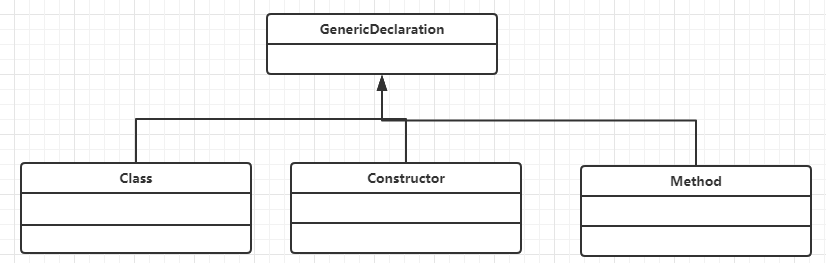
其中并不包含Field类.
4.Class
Class描述类的字节码信息(即.class文件的信息),包括所描述的类的字段信息,方法信息,注解信息,也包括与泛型有关的信息. 下面只介绍和泛型有关的方法.
public final class Class<T> extends Object implements Serializable,GenericDeclaration,Type,AnnotatedElement
4.1 getTypeParameters
TypeVariable<?>[] getTypeParameters()
返回类上的泛型信息( 比如Person<T,U>{},则返回TypeVariable数值标识泛型变量T,U ,如果没有泛型信息则数组长度为零)
class People<T,V,S>{ } class Chinese extends People<String,Integer,Double>{ } public class TypeTest<T> { public <U> TypeTest(){ } private List<String>[] lists; private List<String>[][] listss; public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { TypeVariable[] tv = People.class.getTypeParameters(); System.out.println( tv.length ); for( TypeVariable t : tv ){ System.out.println( t ); } TypeVariable[] tv1 = Chinese.class.getTypeParameters(); System.out.println( tv1.length ); for( TypeVariable t : tv1 ){ System.out.println( t ); } } }
执行结果如下:
3
T
V
S
0
4.2 getGenericSuperClass();
返回该类的父类的泛型类型 比如( class Chinese extendis People<String,Integer,Double>{},返回的是People<String,Integer,Double>,如果没有父类,返回的是Objec的Class实例 )
4.3 getGenericInterfaces();
返回该类的实现的接口们的泛型类型 比如(class Chinese extends People<String,Integer,Double> implements SpeakChinese<String>,UseChopsticks<Double>{},返回的是SpeakChinese<String>,UseChopsticks<Double>,如果没有实现的接口,返回的Type数组长度为0)
代码如下:
interface Walk<R>{} interface SpeakChinese<H>{} interface UseChopsticks<M>{} class People<T,V,S> implements Walk<Short>{ } class Chinese extends People<String,Integer,Double> implements SpeakChinese<String>,UseChopsticks<Double>{ } class Mars extends People<String,Double,List<String>>{ } public class TypeTest<T> { public <U> TypeTest(){ } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { printType(People.class.getGenericSuperclass().toString(), People.class.getGenericSuperclass()); printType(Chinese.class.getGenericSuperclass().toString(), Chinese.class.getGenericSuperclass()); Type[] types = Chinese.class.getGenericInterfaces(); System.out.println( types.length ); for(Type t: types){ printType(t.toString(), t); } Type[] types1 = Mars.class.getGenericInterfaces(); System.out.println( types1.length ); for( Type t : types1 ){ printType( t.toString(),t ); } } public static void printType(String name, Type type){ if( type instanceof Class ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : Class"); }else if( type instanceof ParameterizedType ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : ParameterizedType"); }else if( type instanceof GenericArrayType ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : GenericArrayType"); }else if( type instanceof TypeVariable ){ System.out.println("the type of " + name + " is : TypeVariable"); } } }
执行结果如下:
the type of class java.lang.Object is : Class
the type of testProject.People<java.lang.String, java.lang.Integer, java.lang.Double> is : ParameterizedType
2
the type of testProject.SpeakChinese<java.lang.String> is : ParameterizedType
the type of testProject.UseChopsticks<java.lang.Double> is : ParameterizedType
0
以上就是4种类型的介绍.
另外 还有一个接口继承自Type接口
WildcardType
用于描述包含通配符的泛型变量的信息. 比如List<? extends String> 或者 List<? super Integer>等
public interface WildcardType extends Type{ Type[] getLowerBounds(); Type[] getUpperBounds(); }
getLowerBounds()
获取泛型变量的下界,
getUpperBounds()
获取泛型变量的上界.
public class TypeTest<T> { private List<? extends String> upperBoundsList; private List<? super Integer> lowerBoundsList; public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException { Field upperBoundsList = TypeTest.class.getDeclaredField("upperBoundsList"); ParameterizedType pt = (ParameterizedType)upperBoundsList.getGenericType(); Type[] types = pt.getActualTypeArguments(); System.out.println( ((WildcardType)types[0]).getUpperBounds()[0] ); Field lowerBoundsList = TypeTest.class.getDeclaredField("lowerBoundsList"); ParameterizedType pt1 = (ParameterizedType)lowerBoundsList.getGenericType(); Type[] types1 = pt1.getActualTypeArguments(); System.out.println( ((WildcardType)types1[0]).getLowerBounds()[0] ); } }
执行结果如下:
class java.lang.String
class java.lang.Integer
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
以上为本人查阅资料参考网上文章所写,
不能保证完全正确,
也并非面面俱到.
表述方式并不是偏向于专业化(如有疑惑的地方可留言),如有错误,望指正.
参考文档:
http://tool.oschina.net/apidocs/apidoc?api=jdk_7u4
http://www.jianshu.com/p/e8eeff12c306