好吧,我都要吐了。
接连三个例子都是类似的套路,使用某个查询参数类的实例,结合对应的Task类,对返回值进行取值、显示。
这个例子是Identify识别,使用了TileLayer这种图层,数据来自Server的MapServer。
结果演示
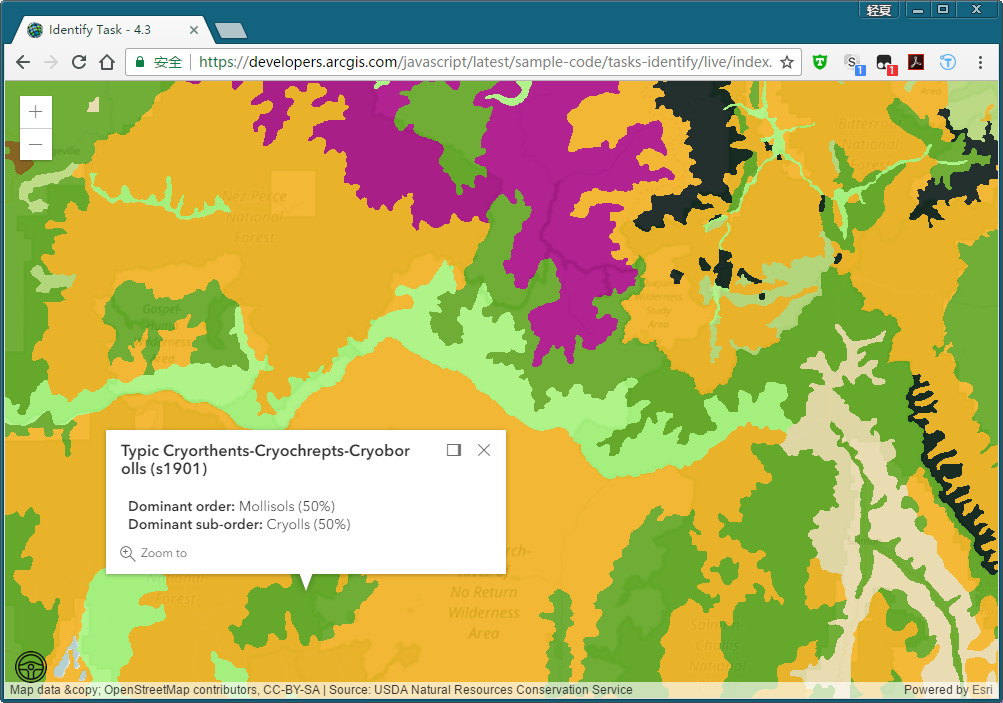
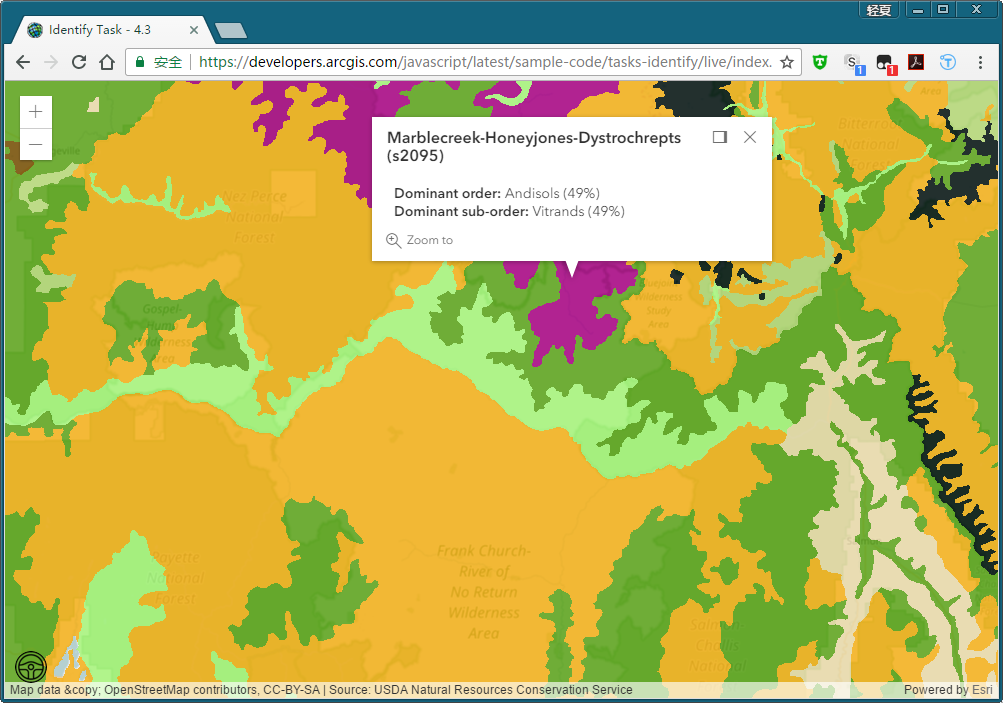
戳不同的地方会有不同的识别结果。
我对TileLayer不是很了解,这一例仅针对有了解的同学,做一个IdentifyTask的解释。
IdentifyTask/IdentifyParameter/IdentifyResult三个类
既然是一样的套路,那么先对这三个类有了解的话就会好说很多吧。
IdentifyTask

当前,IdentifyTask不能在SceneView和dynamic layers中使用。有关Identify是什么,请【点我】
其执行成功的返回值包括有一个IdentifyResult[]。
IdentifyParameters
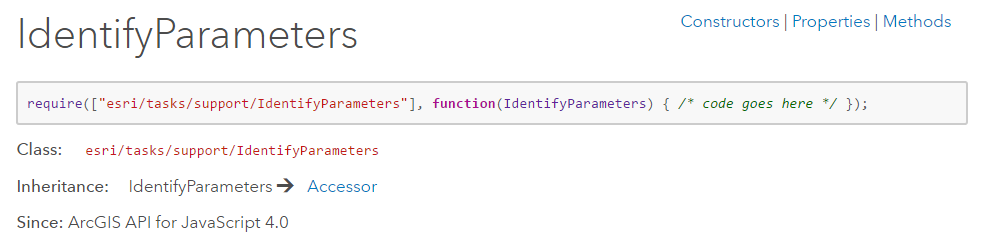
本例中用到的属性有:tolerance(Number)、mapExtent(Extent类)、layerId(Number[])、layerOption(String)、width(Number)、height(Number)、geometry(Geometry类);
分别意义是:屏幕像素与应被识别的几何体之间的距离;地图外框;需要被识别的图层的ID号;哪些图层需要被识别(默认顶层图层),是个枚举量;view的长宽。
IdentifyResult
本例中用到IdentifyResult的属性有:
layerName(String类)、feature(Geometry类)
后者是识别得到的几何体,前者是包括后者的图层的图层名。
给出引用
require([ "esri/Map", "esri/views/MapView", "esri/layers/TileLayer", "esri/tasks/IdentifyTask", "esri/tasks/support/IdentifyParameters", "dojo/_base/array", "dojo/on", "dojo/dom", "dojo/domReady!" ], function( Map, MapView, TileLayer, IdentifyTask, IdentifyParameters, arrayUtils, on, dom ) }
不解释,和前两篇类似。
函数参数骨架
function(Map, MapView, TileLayer, IdentifyTask, IdentifyParameters, arrayUtils, on, dom){ var identifyTask, params; var soilURL = "https://services.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/rest/services/Specialty/Soil_Survey_Map/MapServer";
var parcelsLyr = new TileLayer({...}); var map = new Map({...}); map.add(parcelsLyr); var view = new MapView({...}); view.then(function(){...}); //每次点击地图时,就会处理一次的方法体 function executeIdentifyTask(event){...} }
看起来也不是很复杂的样子,嗯,时间不早了,先吃个晚饭,晚上回来继续写完第七章。
好的我吃完了,咱们继续学习Identify这个例子。
首先是根据soilURL这个MapServer地址生成一个TileLayer,名为parcelsLyr,把它添加到实例化的Map中。
在MapView对象创建完成后,紧接着一个异步操作,下面就对MapView对象的回调函数进行解释:
view.then(function() { on(view, "click", executeIdentifyTask); identifyTask = new IdentifyTask(soilURL); params = new IdentifyParameters(); params.tolerance = 3; params.layerIds = [0, 1, 2]; params.layerOption = "top"; params.width = view.width; params.height = view.height; });
每当点击view的时候,触发click事件executeIdentifyTask()。
然后就实例化一个IdentifyTask对象和一个IdentifyParameters对象,并对IdentifyParameters对象赋值(属性)。
于是这个例子最大头的executeIdentifyTask()方法体就是核心了,先把它骨架化:
function executeIdentifyTask(event) { params.geometry = event.mapPoint; params.mapExtent = view.extent; dom.byId("viewDiv").style.cursor = "wait"; identifyTask.execute(params)
.then(function(response) {..这里很长..}) .then(showPopup); function showPopup(response){...} }
首先呢,获取一些必要的参数,传递给IdentifyParameters(geometry属性和mapExtent属性)
然后执行IdentifyTask的execute()方法,这个方法有两个异步操作,第一个异步操作的回调函数非常的长,还得继续往下拆。
第二个回调函数待第一个回调函数完成后,显示一个弹窗。
那么【第一个回调函数】继续拆解如下:
.then(function(response) { var results = response.results; return arrayUtils.map(results, function(result) { var feature = result.feature; var layerName = result.layerName; feature.attributes.layerName = layerName; if (layerName === 'Soil Survey Geographic') { feature.popupTemplate = {...}; } else if (layerName === 'State Soil Geographic') { feature.popupTemplate = {...}; } else if (layerName === 'Global Soil Regions') { feature.popupTemplate = {...}; } return feature; }); })
从response中获取results属性,该属性为Object数组,装箱为IdentifyResult类型的数组。(同上例)
紧接着返回arrayUtils.map方法遍历results(IdentifyResult数组)得到的feature集合(Geometry类型)。
arrayUtils.map()方法遍历得到的是Geometry数组。
这个map()方法里做了什么呢?
首先,获取IdentifyResult数组其中的IdentifyResult元素中的一个属性——feature(Graphic类型),然后对不同的IdentifyResult对象的LayerName,设置feature不同的弹窗模板。
————是不是很乱?
1. 遍历IdentifyResult[]中的每一个IdentifyResult;//别问我IdentifyResult[]怎么来的,从response中来的。见上一篇博客。
2. 对于每一个IdentifyResult,它有两个属性:feature(Graphic类型)和layerName(String类型);
3. 对于每一个IdentifyResult,如果layerName不同,那么对应的feature的弹窗信息格式(即popupTemplate)肯定不同;
4. 三个分支,对不同layerName的IdentifyResult,其feature就设置不同的popupTemplate;
5. 返回此IdentifyResult的feature。
这一层回调函数就算OK了。因为feature是Graphic类型的,所以map返回的就是Graphic[]类型的。
题外话,其实ESRI这样写很绕,虽然充分利用了JS的灵活和强大,但是代码解读起来就非常困难,函数能作为变量到处嵌套。
【第二个回调函数】
.then(showPopup); function showPopup(response) { if (response.length > 0) { view.popup.open({ features: response, location: event.mapPoint }); } dom.byId("viewDiv").style.cursor = "auto"; }
这回终于把回调函数写出来了。
第二层回调函数的response参数是什么呢?
可以看到,把response赋给了popup的features属性了,可知response是Graphic[]类型的,这与上一个then返回的值一致。
这样,就能利用第一个回调函数中设置好的popupTemplate进行不同格式的弹窗了。
关于第一个回调函数的弹窗popupTemplate不作详细解释了,因为这已经够绕了。我在文末给出整个js代码以供需要的同学参考。
总结一下
本例,仍然是对某某Result中的Graphic或者Geometry的属性进行读取或者操作。
和上两篇是类似的,空间查询的重点就是某某Task和某某Parameters和某某Result的交叉使用:
某某Task.execute(某某Parameters)
.then(回调函数处理某某Result)
.then(..)....
至于怎么处理这个Result中的feature,官方的例子写的很明确了,但是值类型就很隐晦。
因为JS的弱类型性,导致这些值类型十分模糊,所以绕、晕也是正常的,我已经尽我所能把每个关键的地方的值类型进行解释和说明了,希望大家能看懂我的胡言乱语。
好了,第七章空间查询的内容并不是很多,这几个Task肯定很有用,我在写完第八章空间查询后会对其进行一个比较全面的解释。
第八章见!
附上这例子的全代码:

<script> require([ "esri/Map", "esri/views/MapView", "esri/layers/TileLayer", "esri/tasks/IdentifyTask", "esri/tasks/support/IdentifyParameters", "dojo/_base/array", "dojo/on", "dojo/dom", "dojo/domReady!" ], function( Map, MapView, TileLayer, IdentifyTask, IdentifyParameters, arrayUtils, on, dom ) { var identifyTask, params; // URL to the map service where the identify will be performed var soilURL = "https://services.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/rest/services/Specialty/Soil_Survey_Map/MapServer"; // Add the map service as a TileLayer for fast rendering // Tile layers are composed of non-interactive images. For that reason we'll // use IdentifyTask to query the service to add interactivity to the app var parcelsLyr = new TileLayer({ url: soilURL, opacity: 0.85 }); var map = new Map({ basemap: "osm" }); map.add(parcelsLyr); var view = new MapView({ map: map, container: "viewDiv", center: [-120.174, 47.255], zoom: 7 }); view.then(function() { // executeIdentifyTask() is called each time the view is clicked on(view, "click", executeIdentifyTask); // Create identify task for the specified map service identifyTask = new IdentifyTask(soilURL); // Set the parameters for the Identify params = new IdentifyParameters(); params.tolerance = 3; params.layerIds = [0, 1, 2]; params.layerOption = "top"; params.width = view.width; params.height = view.height; }); // Executes each time the view is clicked function executeIdentifyTask(event) { // Set the geometry to the location of the view click params.geometry = event.mapPoint; params.mapExtent = view.extent; dom.byId("viewDiv").style.cursor = "wait"; // This function returns a promise that resolves to an array of features // A custom popupTemplate is set for each feature based on the layer it // originates from identifyTask.execute(params).then(function(response) { var results = response.results; return arrayUtils.map(results, function(result) { var feature = result.feature; var layerName = result.layerName; feature.attributes.layerName = layerName; if (layerName === 'Soil Survey Geographic') { feature.popupTemplate = { // autocasts as new PopupTemplate() title: "{Map Unit Name}", content: "<b>Dominant order:</b> {Dominant Order} ({Dom. Cond. Order %}%)" + "<br><b>Dominant sub-order:</b> {Dominant Sub-Order} ({Dom. Cond. Suborder %}%)" + "<br><b>Dominant Drainage Class:</b> {Dom. Cond. Drainage Class} ({Dom. Cond. Drainage Class %}%)" + "<br><b>Farmland Class:</b> {Farmland Class}" }; } else if (layerName === 'State Soil Geographic') { feature.popupTemplate = { // autocasts as new PopupTemplate() title: "{Map Unit Name}", content: "<b>Dominant order:</b> {Dominant Order} ({Dominant %}%)" + "<br><b>Dominant sub-order:</b> {Dominant Sub-Order} ({Dominant Sub-Order %}%)" }; } else if (layerName === 'Global Soil Regions') { feature.popupTemplate = { // autocasts as new PopupTemplate() title: layerName, content: "<b>Dominant order:</b> {Dominant Order}" + "<br><b>Dominant sub-order:</b> {Dominant Sub-Order}" }; } return feature; }); }).then(showPopup); // Send the array of features to showPopup() // Shows the results of the Identify in a popup once the promise is resolved function showPopup(response) { if (response.length > 0) { view.popup.open({ features: response, location: event.mapPoint }); } dom.byId("viewDiv").style.cursor = "auto"; } } }); </script>
