本次实现了openmv4圆形、矩形、直线的形状识别
圆形识别:
代码如下:x_margin保持不变,更改threshold的阈值
1、threshold=500,x_margin=10
import sensor, image, time sensor.reset() #复位摄像头 sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # grayscale is faster sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) #160*120 sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) clock = time.clock() while(True): clock.tick() #捕获帧率 img = sensor.snapshot().lens_corr(1.8) #畸变矫正,但是会影响帧率 # Circle对象有四个值: x, y, r (半径), 和 magnitude。 # magnitude是检测圆的强度。越高越好 # roi 是一个用以复制的矩形的感兴趣区域(x, y, w, h)。x和y是以左下角为圆心的(0,0) # ROI 即图像矩形。操作范围仅限于roi区域内的像素。 # x_stride 是霍夫变换时需要跳过的x像素的数量。若已知圆较大,可增加 # x_stride 。简述为有效两点之间的距离跨度 # y_stride 是霍夫变换时需要跳过的y像素的数量。若已知直线较大,可增加 # y_stride 。 # threshold 控制从霍夫变换中监测到的圆。只返回大于或等于阈值的圆。 # 应用程序的阈值正确值取决于图像。注意:一条圆的大小是组成圆所有 # 索贝尔滤波像素大小的总和。 # x_margin 控制所检测的圆的合并。 圆像素为 x_margin 、 y_margin 和 # r_margin的部分合并。 #以设定的x_margin为边界,大于它的合并为一个圆,小于它则消失 # y_margin 控制所检测的圆的合并。 圆像素为 x_margin 、 y_margin 和 # r_margin 的部分合并。 # r_margin 控制所检测的圆的合并。 圆像素为 x_margin 、 y_margin 和 # r_margin 的部分合并。 # r_min,r_max和r_step控制测试圆的半径。 # threshold = 3500比较合适。如果视野中检测到的圆过多,请增大阈值; # 相反,如果视野中检测到的圆过少,请减少阈值。 #注意:物体阈值大于设定的threshold,或物体的像素大于x—_margin才能被框中(y_margin和r_margin理论上也行,但是实现不了) for c in img.find_circles(threshold = 2000, x_margin = 10, y_margin = 10, r_margin = 10, r_min = 10, r_max = 100, r_step = 2): img.draw_circle(c.x(), c.y(), c.r(), color = (255, 0, 0)) print(c) #image.find_circles[roi,x_stride=2,y_stride=1,threshold=2000,x_margin=10,y_margin=10,r_margin=10,r_min=2,r_max,r_step=2) #返回圆的x位置。返回圆的y位置。返回圆的半径。返回圆的模(magnitude)。----对应于c print("FPS %f" % clock.fps())
运行结果:密密麻麻的圆
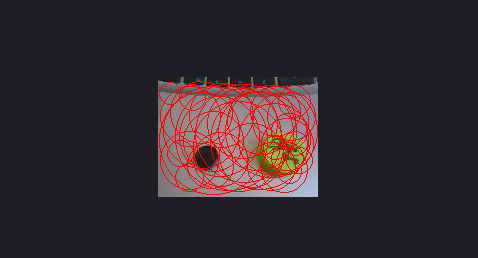
2、threshold=2000,x_margin=10
运行结果:识别了两个圆

3、threshold=3000,x_margin=10
运行结果:只识别了一个圆

threshold的阈值,更改x_margin:
1、x_margin=10,threshold=2000
运行结果:识别了两个圆

2、x_margin=1000,threshold=2000
运行结果:只识别了一个圆

修改threshold或x_margin都能改变识别的范围
矩形识别:
代码如下:
import sensor, image, time sensor.reset() sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # 灰度更快(160x120 max on OpenMV-M7) sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) clock = time.clock() while(True): clock.tick() img = sensor.snapshot() # 下面的`threshold`应设置为足够高的值,以滤除在图像中检测到的具有 # 低边缘幅度的噪声矩形。最适用与背景形成鲜明对比的矩形。 for r in img.find_rects(threshold = 10000): img.draw_rectangle(r.rect(), color = (255, 0, 0)) for p in r.corners(): img.draw_circle(p[0], p[1], 5, color = (0, 255, 0)) print(r) print("FPS %f" % clock.fps())
运行结果:将矩形和它的 四个角分别框起来
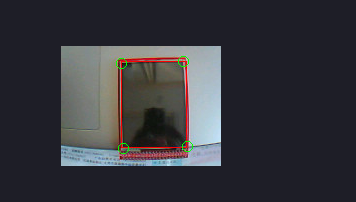
线段识别:
代码如下:
enable_lens_corr = False # turn on for straighter lines...打开以获得更直的线条… import sensor, image, time sensor.reset() sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) #灰度更快 sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) clock = time.clock() # 所有的线对象都有一个`theta()`方法来获取它们的旋转角度。 # 您可以根据旋转角度来过滤线条。 min_degree = 0 max_degree = 179 # 所有线段都有 `x1()`, `y1()`, `x2()`, and `y2()` 方法来获得他们的终点 # 一个 `line()` 方法来获得所有上述的四个元组值,可用于 `draw_line()`. while(True): clock.tick() img = sensor.snapshot() if enable_lens_corr: img.lens_corr(1.8) # for 2.8mm lens... # `threshold` controls how many lines in the image are found. Only lines with # edge difference magnitude sums greater than `threshold` are detected... # `threshold`控制从霍夫变换中监测到的直线。只返回大于或等于阈值的 # 直线。应用程序的阈值正确值取决于图像。注意:一条直线的大小是组成 # 直线所有索贝尔滤波像素大小的总和。 # `theta_margin`和`rho_margin`控件合并相似的直线。如果两直线的 # theta和ρ值差异小于边际,则它们合并。 for l in img.find_lines(threshold = 1000, theta_margin = 25, rho_margin = 25): if (min_degree <= l.theta()) and (l.theta() <= max_degree): img.draw_line(l.line(), color = (255, 0, 0)) # print(l) print("FPS %f" % clock.fps())
运行结果:通过theta_margin和rho_margin控件合并相似的直线

注意:通过theta_margin和rho_margin控件合并相似的直线,这样可以防止直线太散乱
正是步行者,一步步登峰!