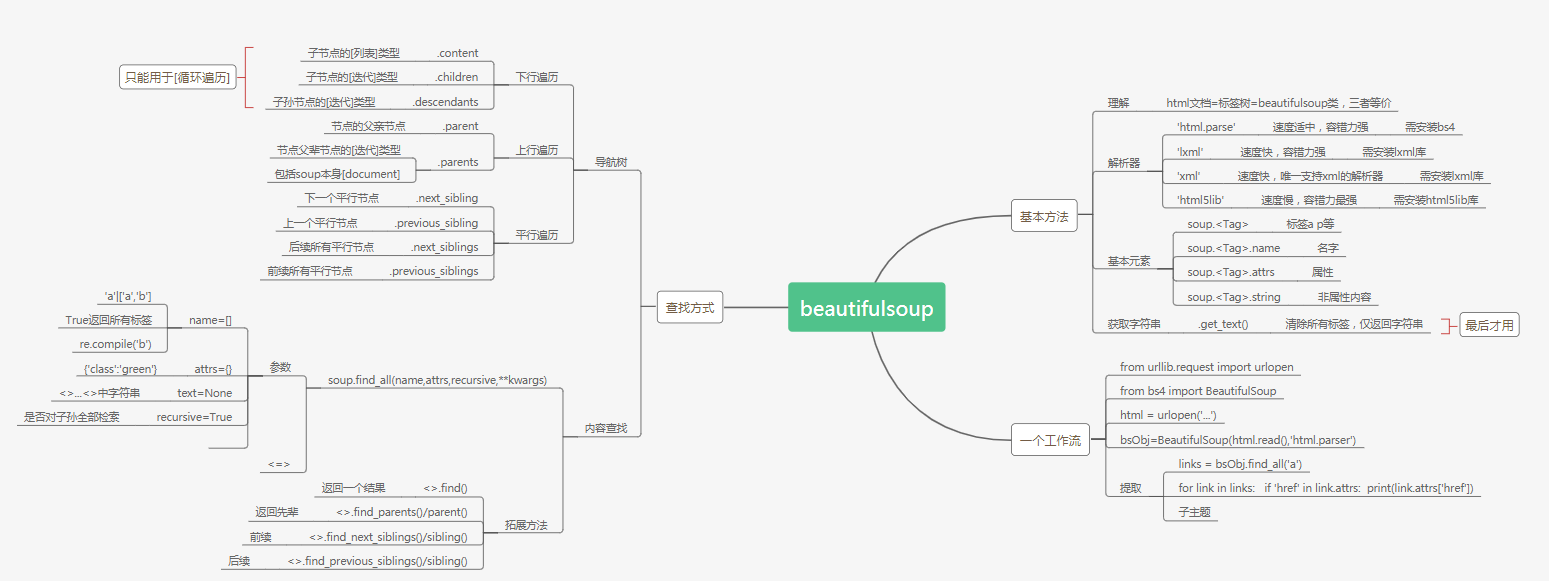
信息提取
1.通过Tag对象的属性和方法
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from urllib.request import urlopen
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
html = urlopen('https://www.cnblogs.com/pcat/p/5398997.html')
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.read().decode('utf-8'),'html.parser')#避免乱码,先utf-8解码
#print()输出第一个匹配项
print(soup)
print(soup.a)
print(soup.a.name)
print(soup.a.attrs)
print(soup.a.string)
soup.html.get_text()输出字符串,原文排版
2.通过标签树对象的find_all()方法
aS = soup.find_all('a')
for i in aS:
print(i)
#print(i.name)
#print(i.attrs)
#print(i.string)
#find_all带条件(name,attrs,string,text,recursive,可多条件匹配)
hrefs = soup.find_all(href=re.compile('pcat$'))#以pcat结尾的链接
for i in hrefs:
print(i)
#对css类名属性class进行搜索时,为避免与python保留字冲突,需用class_
a = soup.find_all(class_ = 'postDesc')
print(a)
#补充1.text匹配非属性内容。2.["a","b"]的形式,表示匹配多个值
3.通过标签树对象的find()方法
#find返回一个标签节点,find_all返回多值列表
#find
e1 =soup.find('head').find('title')#在标签名为head的tag中查找title标签
print(e1)
4.通过CSS选择器
#标签名
soup.select('p')#搜索所有标签名为p的标签
soup.select('p a')#搜索所有p标签的子孙节点中标签名为a的标签。即下N层
soup.select('p > a')#搜索所有p标签的直接子节点中标签名为a的标签。即下一层
#类名
soup.select('.blogStats ')#所有类名为blogStats的标签
soup.select('.blogStats span')#所有类名为blogStats且子孙节点中标签名为span的标签
soup.select('a.menu')#标签名为a并且类名为menu的标签
e1=soup.select('a.menu')#标签名为a并且类名为menu的标签
for i in e1:
print(i['href'])
#id
soup.select('#stats_post_count')#所有id为xxx的标签
soup.select('#navList #blog_nav_sitehome')#所有id为xxx且其子孙节点id为xxx的标签
#属性
soup.select('a[href]')#标签名为a且属性中存在href的所有标签
soup.select('a[href="https://www.cnblogs.com/pcat/"]')#标签名为a且href属性值为http://...的所有标签
soup.select('a[href^="http"]')#标签名为a且href属性以http开头的标签
soup.select('a[href$="http"]')#标签名为a且href属性以pcat结尾的标签
soup.select('a[href*="cnblogs"]')#标签名为a且href属性包含example的标签
#标签名/类名/id/属性 空格[ ] 右符号'>' 相互搭配
遍历
1.下行遍历
| <tag>.contents | 以列表形式返回Tag的所有子节点 |
| <tag>.children | 以迭代形式返回Tag的所有子节点 |
| <tag>.descendants | 以迭代形式返回Tag的所有子孙节点 |
| <tag>.strings | 以迭代形式返回Tag及其所有子孙节点的非属性字符串 |
| <tag>.stripped_strings | 以迭代形式返回Tag去除空白字符后的非属性字符串 |
c
#contents
e1=soup.ul.contents
print(type(e1))
print(len(e1))
#children
e1=soup.ul.children
for i in e1:
print(i)
#descendants
e1=soup.ul.descendants
for i in e1:
print(i)
#strings
e1=soup.ul.strings
for i in e1:
print(i)
#stripped_strings
e1=soup.ul.stripped_strings
for i in e1:
print(i)
c
2.上行遍历
| parent | 以列表形式返回tag的所有父亲节点 |
| parents | 以迭代形式返回tag的所有父辈节点 |
c
3.水平遍历
| next_sibling | 按文档顺序,返回Tag的下一个相邻兄弟节点 |
| previous_sibling | 按文档顺序,返回Tag的上一个相邻兄弟节点 |
| next_siblings | 按文档顺序,返回Tag的后续兄弟节点 |
| previous_siblings | 按文档顺序,返回Tag的前续兄弟节点 |