VOC2007数据集格式:
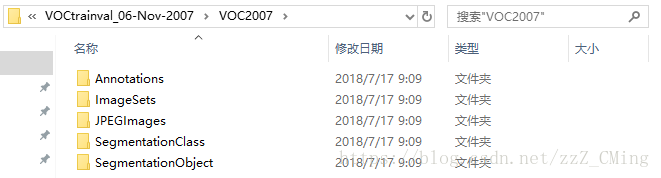
VOC2007详细介绍在这里,提供给大家有兴趣作了解。而制作自己的数据集只需用到前三个文件夹,所以请事先建好这三个文件夹放入同一文件夹内,同时ImageSets文件夹内包含Main文件夹
JPEGImages:用于存放训练、测试的图片(图片格式最好为.jpg)
Annatations:用于存放.xml格式的文件,也就是图片对应的标签,每个.xml文件都对应于JPEGImages文件夹的一张图片
ImageSets:内含Main文件夹,在…/ImageSets/Main文件夹下包含test.txt、train.txt、val.txt、trainval.txt四个文件,生成的方式第二步有详细说明
第一步
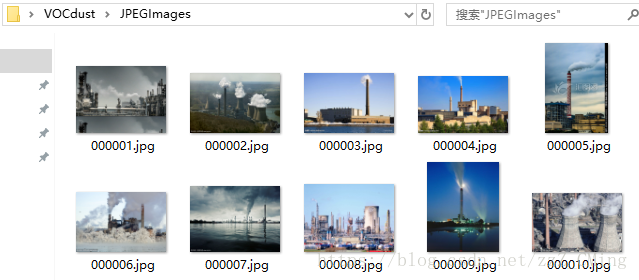
下载图片,存入JPEGImages文件夹——你可以直接从各种渠道下载得到所需要的图片集,存入到JPEGImages文件夹下,命名格式统一为“00xxxx.jpg”,如下图:
第二步
使用labelImg工具给图片打标签——这是最重要的一步。如果你的python已经pip install lxml下载了lxml,
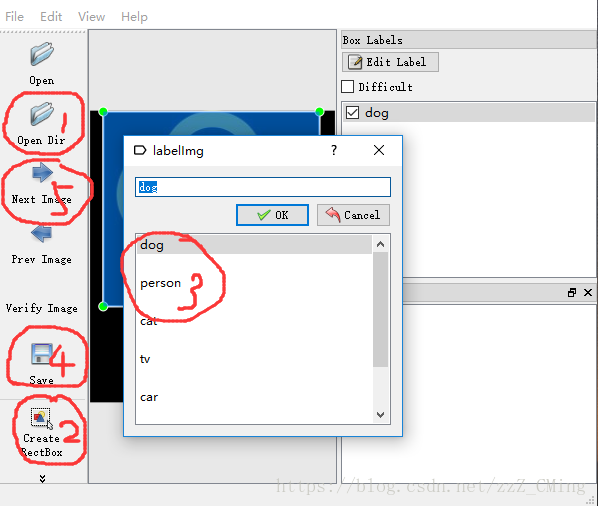
labelImg工具简单的使用步骤就是:
打开单个文件,或者打开一个图片文件夹
给目标物体建立box边框
对box边框内的物体贴上标签
把一张图片内所有目标物都打上各自标签后,再保存生成.xml文件,注意存入Annatations文件夹,文件名也要与当前图片保存一致
然后next下一张图片继续打标签,直到所有图片内物体都打上了标签,最后exit
第三步
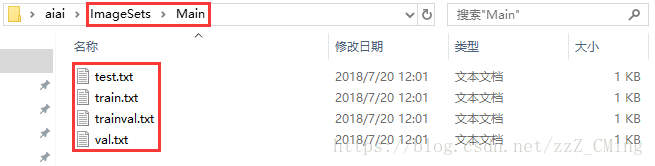
生成Main文件夹下的.txt文件——在主目录下运行以下代码既可生成test.txt、train.txt、val.txt、trainval.txt四个文件,请注意每一个path地址是否正确(其实这四个txt文件在后续并没有什么用处)
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 # -*- author:zzZ_CMing CSDN address:https://blog.csdn.net/zzZ_CMing 3 # -*- 2018/07/18; 15:19 4 # -*- python3.5 5 import os 6 import random 7 8 trainval_percent = 0.7 9 train_percent = 0.8 10 xmlfilepath = 'Annotations' 11 txtsavepath = 'ImageSets/Main' 12 total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath) 13 14 num = len(total_xml) 15 list = range(num) 16 tv = int(num*trainval_percent) 17 tr = int(tv*train_percent) 18 trainval = random.sample(list,tv) 19 train = random.sample(trainval,tr) 20 21 ftrainval = open(txtsavepath+'/trainval.txt', 'w') 22 ftest = open(txtsavepath+'/test.txt', 'w') 23 ftrain = open(txtsavepath+'/train.txt', 'w') 24 fval = open(txtsavepath+'/val.txt', 'w') 25 26 for i in list: 27 name = total_xml[i][:-4]+' ' 28 if i in trainval: 29 ftrainval.write(name) 30 if i in train: 31 ftrain.write(name) 32 else: 33 fval.write(name) 34 else: 35 ftest.write(name) 36 37 ftrainval.close() 38 ftrain.close() 39 fval.close() 40 ftest .close() 41 print('Well Done!!!')
运行完成,得到如下文件:可以打开看一看,内容就是各个图片的索引,意味着哪些图片用做训练,哪些用做测试。
第四步
用.xml标签,生成.tfrecord文件
说明:SSD框架所用到的标签文件并不直接是.xml格式文件,而是.tfrecord文件
特别注意:要在主目录提前建好tfrecords_文件夹,不然会报错找不到目标文件夹
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 # -*- author:zzZ_CMing CSDN address:https://blog.csdn.net/zzZ_CMing 3 # -*- 2018/07/17; 13:18 4 # -*- python3.5 5 """ 6 特别注意: path地址是否正确、要在主目录下提前创建“tfrecords_”文件夹 7 """ 8 9 import os 10 import sys 11 import random 12 import numpy as np 13 import tensorflow as tf 14 import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET # 操作xml文件 15 16 # 我的标签定义只有两类,要根据自己的图片而定 17 VOC_LABELS = { 18 'none': (0, 'Background'), 19 'aiaitie': (1, 'Product') 20 } 21 22 # 图片和标签存放的文件夹. 23 DIRECTORY_ANNOTATIONS = 'Annotations/' 24 DIRECTORY_IMAGES = 'JPEGImages/' 25 26 # 随机种子. 27 RANDOM_SEED = 4242 28 SAMPLES_PER_FILES = 3 # 每个.tfrecords文件包含几个.xml样本 29 30 31 # 生成整数型,浮点型和字符串型的属性 32 def int64_feature(value): 33 if not isinstance(value, list): 34 value = [value] 35 return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=value)) 36 37 def float_feature(value): 38 if not isinstance(value, list): 39 value = [value] 40 return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=value)) 41 42 def bytes_feature(value): 43 if not isinstance(value, list): 44 value = [value] 45 return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=value)) 46 47 # 图片处理 48 def _process_image(directory, name): 49 # Read the image file. 50 filename = directory + DIRECTORY_IMAGES + name + '.jpg' 51 image_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(filename, 'rb').read() 52 53 # Read the XML annotation file. 54 filename = os.path.join(directory, DIRECTORY_ANNOTATIONS, name + '.xml') 55 tree = ET.parse(filename) 56 root = tree.getroot() 57 58 # Image shape. 59 size = root.find('size') 60 shape = [int(size.find('height').text), 61 int(size.find('width').text), 62 int(size.find('depth').text)] 63 # Find annotations. 64 bboxes = [] 65 labels = [] 66 labels_text = [] 67 difficult = [] 68 truncated = [] 69 for obj in root.findall('object'): 70 label = obj.find('name').text 71 labels.append(int(VOC_LABELS[label][0])) 72 labels_text.append(label.encode('ascii')) # 变为ascii格式 73 74 if obj.find('difficult'): 75 difficult.append(int(obj.find('difficult').text)) 76 else: 77 difficult.append(0) 78 if obj.find('truncated'): 79 truncated.append(int(obj.find('truncated').text)) 80 else: 81 truncated.append(0) 82 83 bbox = obj.find('bndbox') 84 a = float(bbox.find('ymin').text) / shape[0] 85 b = float(bbox.find('xmin').text) / shape[1] 86 a1 = float(bbox.find('ymax').text) / shape[0] 87 b1 = float(bbox.find('xmax').text) / shape[1] 88 a_e = a1 - a 89 b_e = b1 - b 90 if abs(a_e) < 1 and abs(b_e) < 1: 91 bboxes.append((a, b, a1, b1)) 92 93 return image_data, shape, bboxes, labels, labels_text, difficult, truncated 94 95 # 转化样例 96 def _convert_to_example(image_data, labels, labels_text, bboxes, shape, 97 difficult, truncated): 98 xmin = [] 99 ymin = [] 100 xmax = [] 101 ymax = [] 102 for b in bboxes: 103 assert len(b) == 4 104 # pylint: disable=expression-not-assigned 105 [l.append(point) for l, point in zip([ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax], b)] 106 # pylint: enable=expression-not-assigned 107 108 image_format = b'JPEG' 109 example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={ 110 'image/height': int64_feature(shape[0]), 111 'image/width': int64_feature(shape[1]), 112 'image/channels': int64_feature(shape[2]), 113 'image/shape': int64_feature(shape), 114 'image/object/bbox/xmin': float_feature(xmin), 115 'image/object/bbox/xmax': float_feature(xmax), 116 'image/object/bbox/ymin': float_feature(ymin), 117 'image/object/bbox/ymax': float_feature(ymax), 118 'image/object/bbox/label': int64_feature(labels), 119 'image/object/bbox/label_text': bytes_feature(labels_text), 120 'image/object/bbox/difficult': int64_feature(difficult), 121 'image/object/bbox/truncated': int64_feature(truncated), 122 'image/format': bytes_feature(image_format), 123 'image/encoded': bytes_feature(image_data)})) 124 return example 125 126 # 增加到tfrecord 127 def _add_to_tfrecord(dataset_dir, name, tfrecord_writer): 128 image_data, shape, bboxes, labels, labels_text, difficult, truncated = 129 _process_image(dataset_dir, name) 130 example = _convert_to_example(image_data, labels, labels_text, 131 bboxes, shape, difficult, truncated) 132 tfrecord_writer.write(example.SerializeToString()) 133 134 135 # name为转化文件的前缀 136 def _get_output_filename(output_dir, name, idx): 137 return '%s/%s_%03d.tfrecord' % (output_dir, name, idx) 138 139 140 def run(dataset_dir, output_dir, name='voc_train', shuffling=False): 141 if not tf.gfile.Exists(dataset_dir): 142 tf.gfile.MakeDirs(dataset_dir) 143 144 path = os.path.join(dataset_dir, DIRECTORY_ANNOTATIONS) 145 filenames = sorted(os.listdir(path)) # 排序 146 if shuffling: 147 random.seed(RANDOM_SEED) 148 random.shuffle(filenames) 149 150 i = 0 151 fidx = 0 152 while i < len(filenames): 153 # Open new TFRecord file. 154 tf_filename = _get_output_filename(output_dir, name, fidx) 155 with tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tf_filename) as tfrecord_writer: 156 j = 0 157 while i < len(filenames) and j < SAMPLES_PER_FILES: 158 sys.stdout.write(' Converting image %d/%d ' % (i + 1, len(filenames))) # 终端打印,类似print 159 sys.stdout.flush() # 缓冲 160 161 filename = filenames[i] 162 img_name = filename[:-4] 163 _add_to_tfrecord(dataset_dir, img_name, tfrecord_writer) 164 i += 1 165 j += 1 166 fidx += 1 167 168 print(' Finished converting the Pascal VOC dataset!') 169 170 171 # 原数据集路径,输出路径以及输出文件名,要根据自己实际做改动 172 dataset_dir = "C:/Users/Admin/Desktop/" 173 output_dir = "./tfrecords_" 174 name = "voc_train" 175 176 def main(_): 177 run(dataset_dir, output_dir, name) 178 179 if __name__ == '__main__': 180 tf.app.run()
得到的.tfrecords文件如下:
