今天打算从数据库中取数据,并展示到视图中。不多说,先上图:
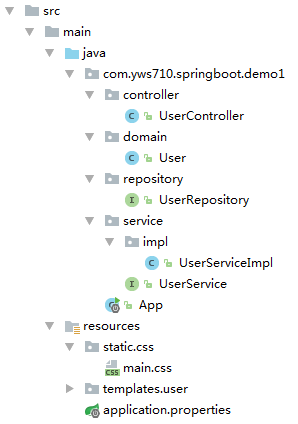
第一步:添加依赖。打开pom.xml文件,添加必要的依赖,完整代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.yws710.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>demo1</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-data-jpa -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用Freemarker替代JSP做页面渲染 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
第二步:配置数据源(前提是数据库已经建好了)。在classpath:resources目录下新建一个名为application.properties的文件。在文件中添加如下内容:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbootdemo1 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=update
这是今天仅有的配置信息。
第三步:domain层。创建实体类,在domain包中新建一个User类:
package com.yws710.springboot.demo1.domain;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
@Entity
@Table(name="t_user")
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String name;
private Date birthday;
private BigDecimal salary;
public User(){}
public User(int id, String name, Date birthday, BigDecimal salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.birthday = birthday;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public BigDecimal getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(BigDecimal salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
第四步:dao层。在repository包中新建一个UserRepository接口:
package com.yws710.springboot.demo1.repository;
import com.yws710.springboot.demo1.domain.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {
}
神奇的Spring Data JPA,自从用了它,我连最简单的查询语句都不会写了。
第五步:service层。在service包中创建UserService接口,以及它的实现类UserServiceImpl。
package com.yws710.springboot.demo1.service;
import com.yws710.springboot.demo1.domain.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
List<User> userList();
}
package com.yws710.springboot.demo1.service.impl;
import com.yws710.springboot.demo1.domain.User;
import com.yws710.springboot.demo1.repository.UserRepository;
import com.yws710.springboot.demo1.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public List<User> userList() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
}
第六步:控制层。在controller包中创建UserController类:
package com.yws710.springboot.demo1.controller;
import com.yws710.springboot.demo1.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/list")
public ModelAndView userList() throws Exception {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("userList", userService.userList());
mv.setViewName("/user/list");
return mv;
}
}
第七步:视图层。在classpath:resources中创建一个名为templates的文件夹,这是Spring Boot默认的视图文件存放位置,创建一个user目录,在user中建立一个名为list.ftl的文件(Freemarker模板文件),文件内容如下:
为了展示静态资源的访问,特地在classpath:resources中创建了一个static文件夹。你猜的没错,这就是Spring Boot默认的静态资源存放位置(其实默认的位置有三个,详见Spring Boot官方文档),main.css文件就存放在static中的css文件夹中。注意模板文件中引用css文件的写法(感觉自己好啰嗦)。
第八步:创建启动类。在demo1包中新建一个App类:
package com.yws710.springboot.demo1;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
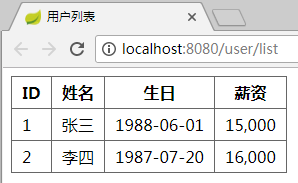
第九步:运行App类中的main方法。在浏览器中输入 http://localhost:8080/user/list,页面显示结果如下:
最后啰嗦一句,注意项目结构图中各文件的位置。
收工,明天打算使用日志和阿里巴巴的数据连接池Druid。
