作者|Aakarsh Yelisetty
编译|Flin
来源|towardsdatascience
让我们看看如何在涉及文本识别的自定义数据集上使用FAIR(Facebook AI Research)的Detectron 2进行实例检测。

你是否尝试过使用你自己选择的自定义数据集从头开始训练对象检测模型?
如果是的话,你就会知道这个过程有多乏味。如果我们选择基于区域建议的方法,如更快的R-CNN,或者我们也可以使用SSD和YOLO等一次性检测器算法,我们需要从使用特征金字塔网络和区域建议网络来构建模型。
如果我们想从头开始实现的话,它们中的任何一个都有点复杂。我们需要一个框架,在这个框架中,我们可以使用最先进的模型,例如Fast,Faster和Mask R-CNN。然而,重要的是我们需要从头开始构建一个模型,以理解其背后的数学原理。
如果我们想使用自定义数据集快速训练对象检测模型,Detectron 2就可以提供帮助。Detectron 2库的模型库中存在的所有模型都在COCO Dataset上进行了预训练。我们只需要在预先训练的模型上微调我们的自定义数据集。
Detectron 2完全重写了2018年发布的第一款Detectron。其前身是在Caffe2上编写的,Caffe2是一个深度学习框架,也得到了Facebook的支持。Caffe2和Detectron现在都不推荐使用。Caffe2现在是PyTorch的一部分,它的继承者Detectron 2完全是在PyTorch上编写的。
Detectron2旨在通过提供快速的训练并解决公司从研究到生产的过程中面临的问题,来促进机器学习的发展。
以下是Detectron 2提供的各种类型的目标检测模型。
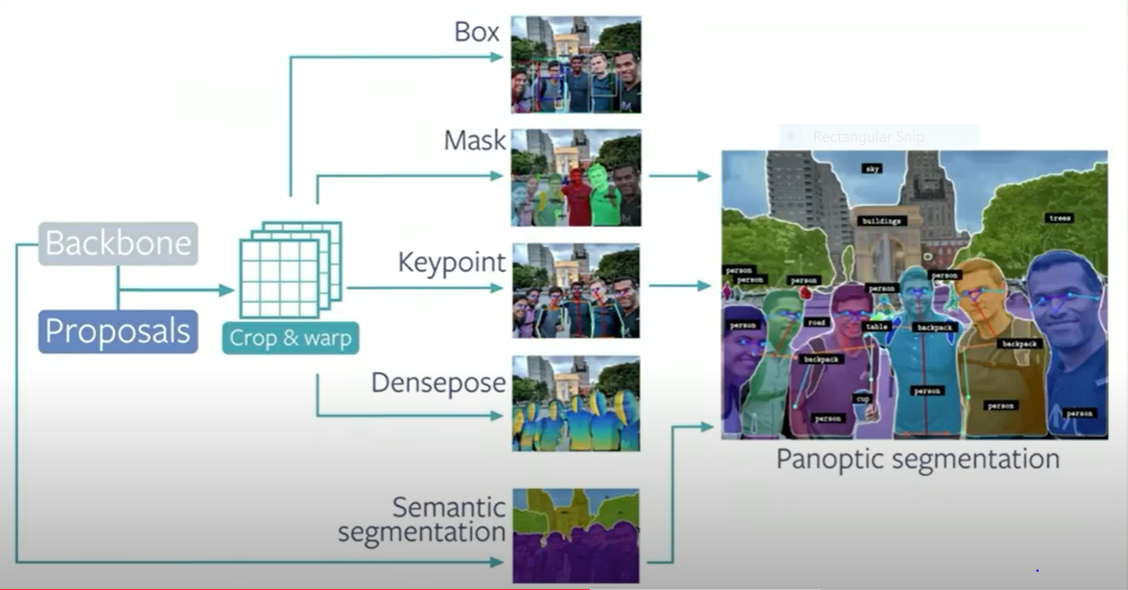
让我们直接研究实例检测。
实例检测是指对象的分类和定位,并带有边界框。在本文中,我们将使用Detectron 2的模型库中的Faster RCNN模型来识别图像中的文本语言。
请注意,我们将语言限制为2种。
我们识别北印度语和英语文本,并为其他语言提供了一个名为“Others”的类。


我们将实现一个以这种方式输出的模型。
让我们开始吧!
使用Detectron 2,可以使用七个步骤对任何自定义数据集执行对象检测。所有这些步骤都可以在此Google Colab Notebook 中轻松找到,你可以立即运行!
使用Google Colab进行这项工作很容易,因为我们可以使用GPU进行更快的训练。
步骤1:安装Detectron 2
首先安装一些依赖项,例如Torch Vision和COCO API,然后检查CUDA是否可用。CUDA有助于跟踪当前选择的GPU。然后安装Detectron2。
# install dependencies:
!pip install -U torch==1.5 torchvision==0.6 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu101/torch_stable.html
!pip install cython pyyaml==5.1
!pip install -U 'git+https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git#subdirectory=PythonAPI'
import torch, torchvision
print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())
!gcc --version
# install detectron2:
!pip install detectron2==0.1.3 -f https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/detectron2/wheels/cu101/torch1.5/index.html
步骤2:准备和注册数据集
导入一些必要的程序包。
# You may need to restart your runtime prior to this, to let your installation take effect
import detectron2
from detectron2.utils.logger import setup_logger
setup_logger()
# import some common libraries
import numpy as np
import cv2
import random
from google.colab.patches import cv2_imshow
# import some common detectron2 utilities
from detectron2 import model_zoo
from detectron2.engine import DefaultPredictor
from detectron2.config import get_cfg
from detectron2.utils.visualizer import Visualizer
from detectron2.data import MetadataCatalog
内置数据集中列出了detectron2具有内置支持的数据集。如果要使用自定义数据集,同时还要重用detectron2的数据加载器,则需要注册数据集(即,告诉detectron2如何获取数据集)。
我们使用具有三个类别的文本检测数据集:
-
英语
-
印地语
-
其他
我们将从在COCO数据集上预先训练的现有模型训练文本检测模型,该模型可在detectron2的模型库中使用。
如果你有兴趣了解从原始数据集格式到Detectron 2接受的格式的转换,请查看:
如何将数据输入模型?输入数据要求属于某些格式,如YOLO格式、PASCAL VOC格式、COCO格式等。Detectron2接受COCO格式的数据集。数据集的COCO格式由一个JSON文件组成,该文件包含图像的所有细节,如大小、注释(即边界框坐标)、与其边界框对应的标签等。例如,

这是一个JSON格式的图像。边界框表示有不同类型的格式。它必须是Detectron2的structures.BoxMode成员。这样的格式有5种。但目前,它支持 BoxMode.XYXY_ABS, BoxMode.XYWH_ABS.
我们使用第二种格式。(X,Y)表示边界框的一个坐标,W,H表示该框的宽度和高度。category_id 指的是边界框所属的类别。
然后,我们需要注册我们的数据集。
import json
from detectron2.structures import BoxMode
def get_board_dicts(imgdir):
json_file = imgdir+"/dataset.json" #Fetch the json file
with open(json_file) as f:
dataset_dicts = json.load(f)
for i in dataset_dicts:
filename = i["file_name"]
i["file_name"] = imgdir+"/"+filename
for j in i["annotations"]:
j["bbox_mode"] = BoxMode.XYWH_ABS #Setting the required Box Mode
j["category_id"] = int(j["category_id"])
return dataset_dicts
from detectron2.data import DatasetCatalog, MetadataCatalog
#Registering the Dataset
for d in ["train", "val"]:
DatasetCatalog.register("boardetect_" + d, lambda d=d: get_board_dicts("Text_Detection_Dataset_COCO_Format/" + d))
MetadataCatalog.get("boardetect_" + d).set(thing_classes=["HINDI","ENGLISH","OTHER"])
board_metadata = MetadataCatalog.get("boardetect_train")
为了验证数据加载是否正确,让我们可视化训练集中随机选择的样本的标注。
步骤3:可视化训练集
我们将从数据集的train文件夹中随机选择3张图片,并查看边界框的外观。
#Visualizing the Train Dataset
dataset_dicts = get_board_dicts("Text_Detection_Dataset_COCO_Format/train")
#Randomly choosing 3 images from the Set
for d in random.sample(dataset_dicts, 3):
img = cv2.imread(d["file_name"])
visualizer = Visualizer(img[:, :, ::-1], metadata=board_metadata)
vis = visualizer.draw_dataset_dict(d)
cv2_imshow(vis.get_image()[:, :, ::-1])
输出看起来是这样的,



第四步:训练模型
我们向前迈进了一大步。这是我们给出配置和设置模型准备接受训练的步骤。从技术上讲,我们只是在数据集上微调我们的模型,因为模型已经在COCO数据集上进行了预训练。
在Detectron2的模型库里有大量的模型可用于目标检测。在这里,我们使用faster_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x。
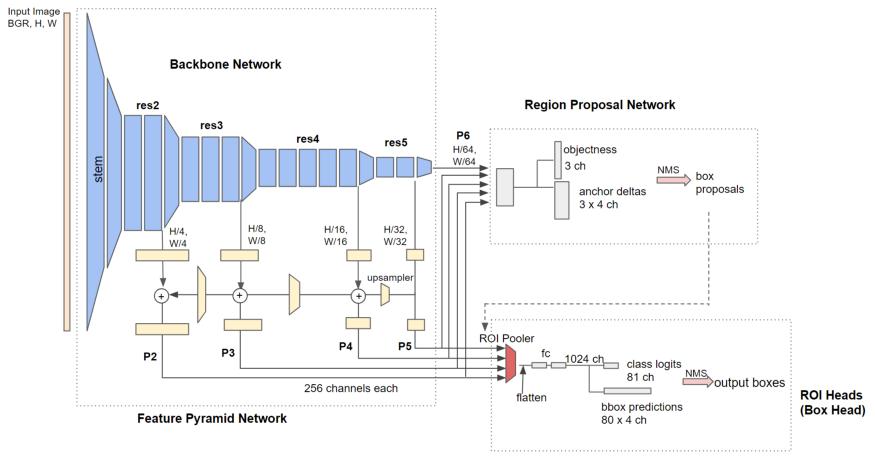
这里有一个主干网(这里是Resnet),用于从图像中提取特征,然后是一个区域建议网络,用于提出区域建议,以及一个用于收紧边界框的框头部。
你可以在我的前一篇文章中读到更多关于R-CNN如何更快工作的文章。
让我们为训练设置配置。
from detectron2.engine import DefaultTrainer
from detectron2.config import get_cfg
import os
cfg = get_cfg()
cfg.merge_from_file(model_zoo.get_config_file("COCO-Detection/faster_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml")) #Get the basic model configuration from the model zoo
#Passing the Train and Validation sets
cfg.DATASETS.TRAIN = ("boardetect_train",)
cfg.DATASETS.TEST = ("boardetect_val",)
# Number of data loading threads
cfg.DATALOADER.NUM_WORKERS = 4
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = model_zoo.get_checkpoint_url("COCO-Detection/faster_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml") # Let training initialize from model zoo
# Number of images per batch across all machines.
cfg.SOLVER.IMS_PER_BATCH = 4
cfg.SOLVER.BASE_LR = 0.0125 # pick a good LearningRate
cfg.SOLVER.MAX_ITER = 1500 #No. of iterations
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.BATCH_SIZE_PER_IMAGE = 256
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.NUM_CLASSES = 3 # No. of classes = [HINDI, ENGLISH, OTHER]
cfg.TEST.EVAL_PERIOD = 500 # No. of iterations after which the Validation Set is evaluated.
os.makedirs(cfg.OUTPUT_DIR, exist_ok=True)
trainer = CocoTrainer(cfg)
trainer.resume_or_load(resume=False)
trainer.train()
我不认为这是最好的配置。当然,其他配置的精确度也会提高。毕竟,这取决于选择正确的超参数。
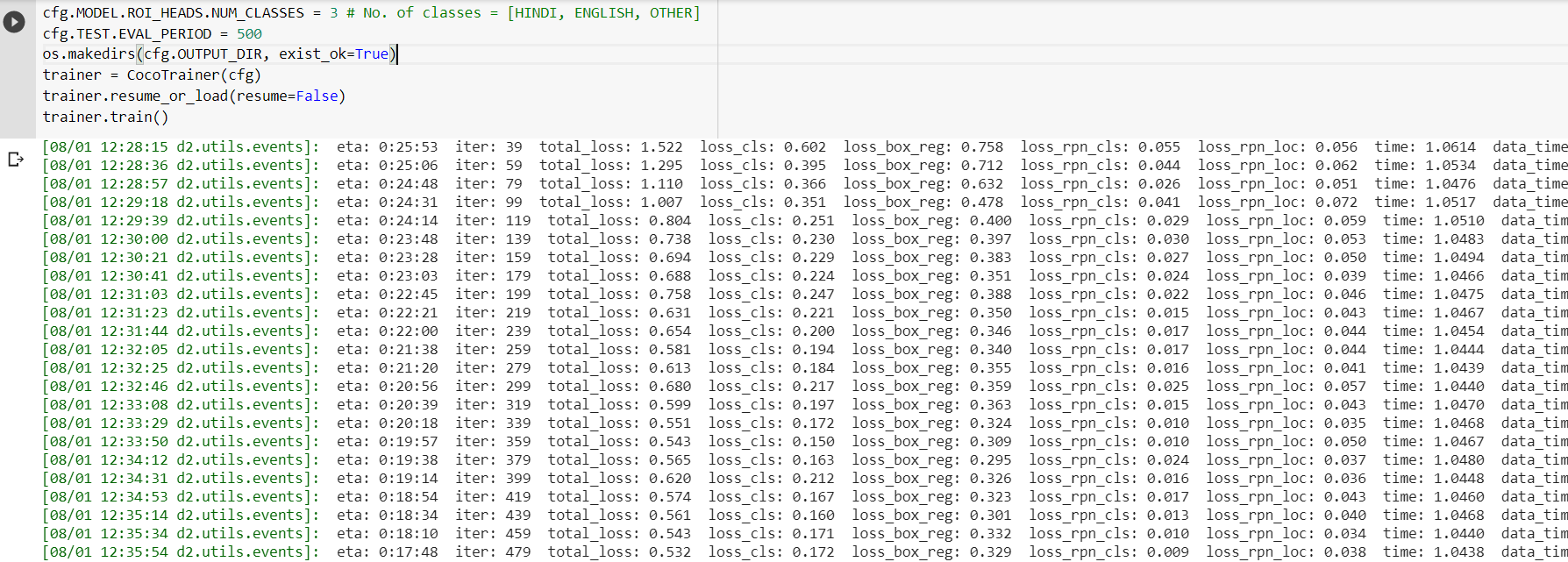
注意,这里我们还计算验证集中每500次迭代的精确度。
第五步:使用训练好的模型进行推理
现在是时候通过在验证集上测试模型来推断结果了。
成功完成训练后,输出文件夹保存在本地存储器中,其中存储最终权重。你可以保存此文件夹,以便将来根据此模型进行推断。
from detectron2.utils.visualizer import ColorMode
#Use the final weights generated after successful training for inference
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = os.path.join(cfg.OUTPUT_DIR, "model_final.pth")
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST = 0.8 # set the testing threshold for this model
#Pass the validation dataset
cfg.DATASETS.TEST = ("boardetect_val", )
predictor = DefaultPredictor(cfg)
dataset_dicts = get_board_dicts("Text_Detection_Dataset_COCO_Format/val")
for d in random.sample(dataset_dicts, 3):
im = cv2.imread(d["file_name"])
outputs = predictor(im)
v = Visualizer(im[:, :, ::-1],
metadata=board_metadata,
scale=0.8,
instance_mode=ColorMode.IMAGE
)
v = v.draw_instance_predictions(outputs["instances"].to("cpu")) #Passing the predictions to CPU from the GPU
cv2_imshow(v.get_image()[:, :, ::-1])
结果:


第6步:评估训练模型
通常,模型的评估遵循COCO评估标准。用平均精度(mAP)来评价模型的性能。
#import the COCO Evaluator to use the COCO Metrics
from detectron2.evaluation import COCOEvaluator, inference_on_dataset
from detectron2.data import build_detection_test_loader
#Call the COCO Evaluator function and pass the Validation Dataset
evaluator = COCOEvaluator("boardetect_val", cfg, False, output_dir="/output/")
val_loader = build_detection_test_loader(cfg, "boardetect_val")
#Use the created predicted model in the previous step
inference_on_dataset(predictor.model, val_loader, evaluator)
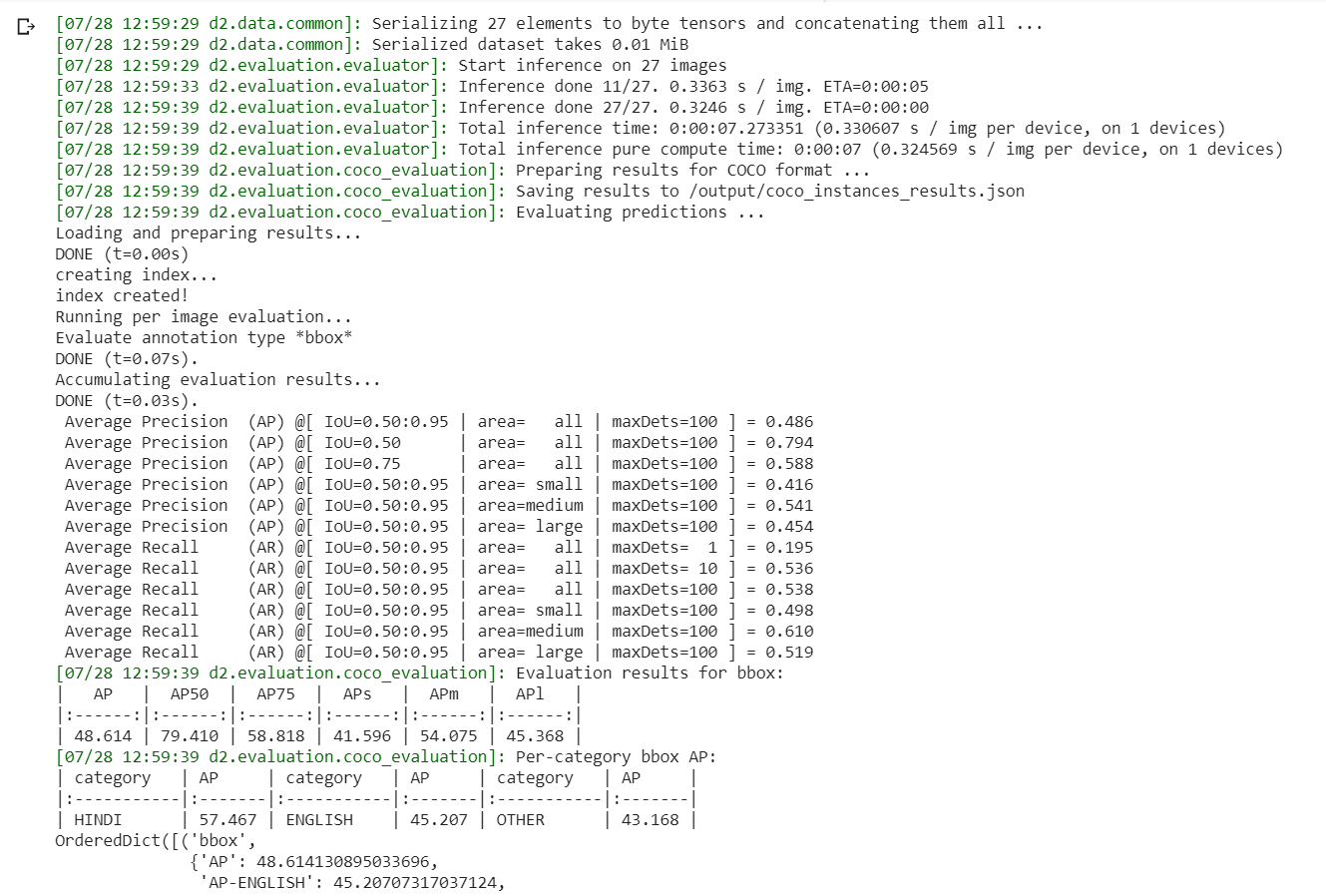
对于0.5的IoU,我们获得约79.4%的准确度,这还不错。可以通过稍微调整参数并增加迭代次数来增加。但请密切注意训练过程,因为该模型可能会过拟合。
如果你需要从保存的模型中进行推断,请浏览:https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1d0kXs-TE7_3CXldJNs1WsEshXf8Gw_5n?usp=sharing
结论
在本文中,我重点介绍了使用Detectron 2的自定义数据集进行目标检测的过程,而不是着重于获得更高的准确性。
尽管这似乎是一个非常简单的过程,但在Detectron 2的库中还有很多值得探索的地方。我们有大量的优化参数,可以进一步调整以获得更高的准确性,这完全取决于一个人的自定义数据集。
你可以从我的Github存储库下载 notebook,然后尝试在Google Colab或Jupyter Notebooks上运行它。
希望你今天学到了一些新知识。
原文链接:https://towardsdatascience.com/object-detection-in-6-steps-using-detectron2-705b92575578
欢迎关注磐创AI博客站:
http://panchuang.net/
sklearn机器学习中文官方文档:
http://sklearn123.com/
欢迎关注磐创博客资源汇总站:
http://docs.panchuang.net/