一、搭建Hibernate环境
1.在src目录下创建hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件
PS:文件的名字不能改!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- configure the database setting -->
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">1234</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</property>
<!-- configure the hibernate setting -->
<!-- transaction is supported by org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect</property>
<!-- show sql in the console -->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!-- create and update the database automaticlly -->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!-- javax.persistence.validation.mode默认情况下是auto的,就是说如果不设置的话它是会自动去你的classpath下面找一个
bean-validation**包,但是找不到,所以beanvalitionFactory错误 -->
<property name="javax.persistence.validation.mode">none</property>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
2. 编写实体类,以Person类为例
package test.Hibernate.model;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Person {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Set<String> getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Set<String> address) {
this.address = address;
}
private int id;
private String name;
private Set<String> address = new HashSet<String>();
}
3.编写Person.hbm.xml实体类配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!--
Mapping file autogenerated by MyEclipse Persistence Tools
-->
<hibernate-mapping package="test.Hibernate.model">
<class name="Person" table="person">
<id column="id" name="id" type="int">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name" length="50" type="string"></property>
<set name="address" table="address">
<key column="personId"></key>
<element column="address" type="string" length="50"></element>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
4.在hibernate.cfg.xml中加入映射信息
<mapping resource="test/Hibernate/model/Person.hbm.xml" />
5.使用MyEclipse生成SessionFactory
package test.Hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.HibernateException;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
/**
* Configures and provides access to Hibernate sessions, tied to the
* current thread of execution. Follows the Thread Local Session
* pattern, see {@link http://hibernate.org/42.html }.
*/
public class SessionFactory {
/**
* Location of hibernate.cfg.xml file.
* Location should be on the classpath as Hibernate uses
* #resourceAsStream style lookup for its configuration file.
* The default classpath location of the hibernate config file is
* in the default package. Use #setConfigFile() to update
* the location of the configuration file for the current session.
*/
private static final ThreadLocal<Session> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Session>();
private static org.hibernate.SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private static Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
private static ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry;
static {
try {
configuration.configure();
serviceRegistry = new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("%%%% Error Creating SessionFactory %%%%");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private SessionFactory() {
}
/**
* Returns the ThreadLocal Session instance. Lazy initialize
* the <code>SessionFactory</code> if needed.
*
* @return Session
* @throws HibernateException
*/
public static Session getSession() throws HibernateException {
Session session = (Session) threadLocal.get();
if (session == null || !session.isOpen()) {
if (sessionFactory == null) {
rebuildSessionFactory();
}
session = (sessionFactory != null) ? sessionFactory.openSession()
: null;
threadLocal.set(session);
}
return session;
}
/**
* Rebuild hibernate session factory
*
*/
public static void rebuildSessionFactory() {
try {
configuration.configure();
serviceRegistry = new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("%%%% Error Creating SessionFactory %%%%");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Close the single hibernate session instance.
*
* @throws HibernateException
*/
public static void closeSession() throws HibernateException {
Session session = (Session) threadLocal.get();
threadLocal.set(null);
if (session != null) {
session.close();
}
}
/**
* return session factory
*
*/
public static org.hibernate.SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
/**
* return hibernate configuration
*
*/
public static Configuration getConfiguration() {
return configuration;
}
}
6.编写测试类
package test.Hibernate.dao;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.junit.Test;
import test.Hibernate.SessionFactory.SessionFactory;
import test.Hibernate.model.Person;
public class PersonDao {
@Test
public void add(){
Session session = SessionFactory.getSession();
Transaction tr = session.beginTransaction();
//----------------------------------------------
Person p = new Person();
p.setName("test");
p.getAddress().add("firstAddr");
p.getAddress().add("secondAddr");
p.getAddress().add("thirdAddr");
p.getAddress().add("fourthAddr");
session.save(p);
//----------------------------------------------
tr.commit();
SessionFactory.closeSession();
}
@Test
public void get(){
Session session = SessionFactory.getSession();
Transaction tr = session.beginTransaction();
//----------------------------------------------
Person p = (Person)session.get(Person.class, 2);
System.out.println(p);
//----------------------------------------------
tr.commit();
SessionFactory.closeSession();
}
}
二、主键生成策略
identity:使用数据库的自动增长策略,不是所有数据库都支持,比如oracle就不支持。
sequence:在 DB2,PostgreSQL,Oracle,SAP DB,McKoi 中使用序列(sequence)在使用Oracle数据库时可以使用这一个。
hilo:使用高低位算法生成主键值。只需要一张额外表,所有的数据都支持。
native:根据底层数据库的能力选择 identity、sequence 或者 hilo中的一个。
assigned:手工指定主键值。
uuid:由Hibernate自动生成UUID并指定为主键值。
三、Hibernate映射关系配置
1.一对一映射(以主键关联作为示例)User与IdCard(有外键方)的XML配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!--
Mapping file autogenerated by MyEclipse Persistence Tools
-->
<hibernate-mapping package="test.Hibernate.model">
<class name="User" table="user">
<id name="id" type="int" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" type="string" column="name"/>
<set name="address" table="address">
<key column="userId"></key>
<element column="address" type="string"></element>
</set>
<one-to-one name="idCard" class="IdCard" cascade="all"></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!--
Mapping file autogenerated by MyEclipse Persistence Tools
-->
<hibernate-mapping package="test.Hibernate.model">
<class name="IdCard" table="idCard">
<id name="id" type="int" column="id">
<generator class="foreign">
<param name="property">user</param>
</generator>
</id>
<property name="number" type="string" column="number"/>
<one-to-one name="user" class="User" constrained="true"></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
2.一对多,多对一(以Father和Children为例)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="test.Hibernate.model">
<class name="Father" table="father">
<id name="id" type="int" column="id" >
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" type="string" column="name"/>
<set name="children" cascade="all">
<key column="fatherId"></key>
<one-to-many class="Children"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="test.Hibernate.model">
<class name="Children" table="children">
<id name="id" type="int" column="id" >
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" type="string" column="name"/>
<many-to-one name="father" class="Father" column="fatherId"></many-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
3.多对多(以Student和Teacher为例)
PS:有一方的set集合要标明inverse=true(后面会讲)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!--
Mapping file autogenerated by MyEclipse Persistence Tools
-->
<hibernate-mapping package="test.Hibernate.model">
<class name="Student" table="student">
<id name="id" type="int" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" type="string" column="name" length="20"/>
<set name="teachers" table="student_teacher" inverse="false" >
<key column="studentId"></key>
<many-to-many class="Teacher" column="teacherId"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!--
Mapping file autogenerated by MyEclipse Persistence Tools
-->
<hibernate-mapping package="test.Hibernate.model">
<class name="Teacher" table="teacher">
<id name="id" type="int" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name" type="string" length="20"></property>
<set name="students" table="student_teacher" inverse="true" cascade="all">
<key column="teacherId"></key>
<many-to-many class="Student" column="studentId"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
四、inverse和cascade的区别(个人总结,有不对还望指正)
1.inverse=false在一对多删除时是把孩子的外键设置为null,然后删除父亲,孩子不删除,而casecade=all在一对多删除时是把孩子的外键设置为null,然后删除父亲,然后再删除孩子
2.many to many的时候由一方维护,所以一方要设置inverse=false,但是inverse=true的另一方直接删除会出错,这个时候可以用casecade完成级联删除
3.inverse=false只用于set等集合属性,在one to one关系中可以用casecade完成级联删除
五、使用C3P0连接池
1.需要额外导入3个jar包

2.在hibernate.cfg.xml中加入C3P0配置信息
<!-- C3P0连接池设定-->
<!-- 使用c3p0连接池 配置连接池提供的供应商-->
<property name="connection.provider_class">org.hibernate.connection.C3P0ConnectionProvider</property>
<!--在连接池中可用的数据库连接的最少数目 -->
<property name="c3p0.min_size">5</property>
<!--在连接池中所有数据库连接的最大数目 -->
<property name="c3p0.max_size">20</property>
<!--设定数据库连接的过期时间,以秒为单位,
如果连接池中的某个数据库连接处于空闲状态的时间超过了timeout时间,就会从连接池中清除 -->
<property name="c3p0.timeout">120</property>
<!--每3000秒检查所有连接池中的空闲连接 以秒为单位-->
<property name="c3p0.idle_test_period">3000</property>
六、HQL语句
@Test
public void HQLSearch(){
Session session = SessionFactory.getSession();
Transaction tr = session.beginTransaction();
//-----------------------------------------
//common search with where
// String hql= "select e.id,e.name from User e where e.id>=5 and e.id<=9";
// Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
// List list = query.list();
// for(Object o : list){
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString((Object[])o));
// }
//paging search
// String hql= "select e.id,e.name from User e";
// Query query = session.createQuery(hql);
// query.setFirstResult(0);
// query.setMaxResults(10);
// List list = query.list();
// for(Object o : list){
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString((Object[])o));
// }
//search with parameters
// String hql= "select e.id,e.name from User e where id>=? and id<=?";
// Query query = session.createQuery(hql)
// .setParameter(0, 1)
// .setParameter(1, 3);
// List list = query.list();
// for(Object o : list){
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString((Object[])o));
// }
//search with parameters whose type is collection
// String hql= "select e.id,e.name from User e where id in (:ids)";
// Query query = session.createQuery(hql)
// .setParameterList("ids",new Object[]{1,2,3,8} );
// List list = query.list();
// for(Object o : list){
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString((Object[])o));
// }
//-----------------------------------------
tr.commit();
SessionFactory.closeSession();
}
七、DML语句
@Test
public void DML(){
Session session = SessionFactory.getSession();
Transaction tr = session.beginTransaction();
//-----------------------------------------
User u = (User)session.get(User.class, 11);
String sql = "update User set name=? where id>?";
int result = session.createQuery(sql)
.setParameter(0, "updated")
.setParameter(1, 10)
.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("count of update:"+result);
//the object's status in session was not updated when the object in database have been changed,so if you want
//to get the updated object in session,you should use method "refresh".
session.refresh(u);
System.out.println(u);
//-----------------------------------------
tr.commit();
SessionFactory.closeSession();
}
八、开启二级缓存
1. 需要导入以下jar包
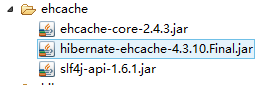
2.在hibernate.cfg.xml中加入以下配置
<!-- 使用二级缓存,默认是未打开的。 -->
<!-- 指定要使用的缓存的提供商,这也就打开了二级缓存-->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<!-- 开启使用查询缓存 -->
<property name="cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
<!-- 指定要使用二级缓存的实体类 -->
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="test.Hibernate.model.Person" />
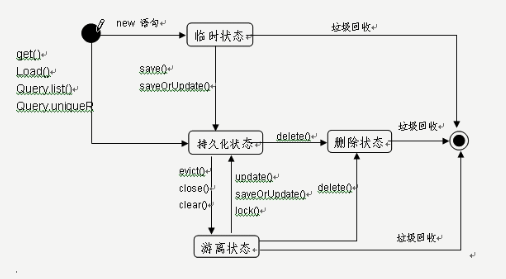
九、Hibernate对象状态及转化