大纲:
6.1创建字符串
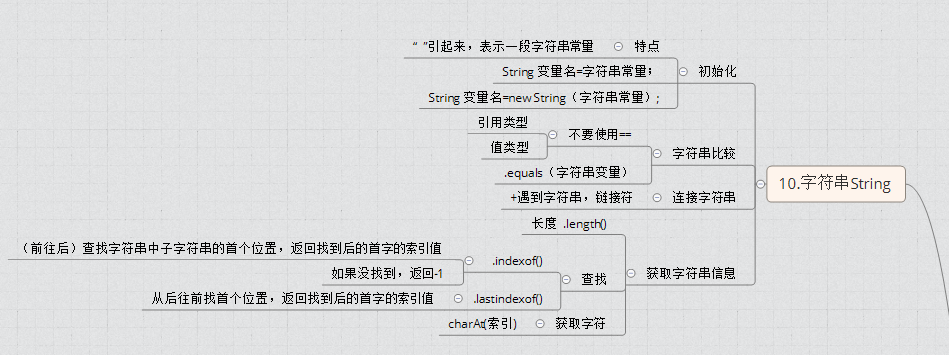
定义:String类即字符串类型,并不是JAVA的基本数据类型,但可以像基本数据类型一样用,用双引号括起来进行声明。在JAVA中用String类的构造类型方法来创建字符串变量。常用构造方法如下:
1.String()
一个String对象,可以表示一个空字符序列。
<例>:String s=new String();
2. String(char a[])
用一个字符数组a创建String对象。
<例>:char a[]=new char{'我','爱','你'};
String s=new String(a);
//等价于:String s=new String(“我爱你”);
3.String(char a[],int offset,int length)
提取字符数组a中的一部分创建一个字符串对象。参数offset表示开始截取字符串的位置,length表示截取字符串的长度。
<例>:char a[]={'s','t','r','i','n','g'};
String s=String(a,1,3);
//等价于:String s={“tri”};
6.2字符串操作
定义:对于已经声明的字符串,可以对其进行相应的操作,String类中包含很多方法。
6.2.1字符串连接
1.多个字符串连接
连接多个字符串时,在每两个连接的字符串之间用“+”相连,“+”就是字符串的连接符,连接后生成一个新的字符串。
<例>:String s1=new String ("hello");
String s2=new String ("word");
String s=s1+" "+s2;
运行结果:hello word
2.连接其他数据类型
在字符串和其他数据类型连接时,同时使用"+"连接符,连接之后的返回值是字符串.
<例>:int booktime=4;
float computer=2.5f;
System.out.println("我每天花"+booktime+"个小时看书,用"+computer+"个小时上机操作.");
6.2.2获取字符串信息
1.获取字符串长度
str.length();方法
***str:指的是字符串对象
***返回值:int类型的字符串长度
String a="hello world";
System.out.println(a.length);//输出11.
***空格也算长度
2.获取指定字符的索引位置
str.indexOf(substr);//返回字符首次出现位置的索引
str.lastindexOf(substr);//返回字符最后出现位置的索引
str:任意字符串对象
substr:要搜索的字符
在计算机中,返回的String对象索引都是从0开始的.
3.获取指定索引位置的字符
使用String类的charAt()方法可获取指定索引处的索引下的字符,返回字符的索引,
格式: str.charAt(int index);
*** str:任意字符串
*** index:整型值,用于指定要返回的字符的下标.
*** 返回值:返回指定索引位置的字符.
<例>:String s="hello world";
char s1=s.charAt(0);
System.out.println(s1);//输出:h
6.2.3判断字符串
判断字符串主要是判断字符串是否相等,判断字符串是否以指定的字符串开始或结尾.这里讲的是判断字符串是否相等.
(1) equals()方法
使用equals方法对字符串进行比较时严格区分大小写的,再此条件下,如果两个字符串扔具有相同的字符和长度,则返回true,否则返回folse.
语法:str.equals(String otherstr)
***str:参与比较的一个字符串对象
***otherstr:参加比较的另一个字符串对象
***返回值:返回boolean类型.
(2) equalslgnoreCase()方法
使用equalslgnoreCase方法对字符串进行比较时忽略区分大小写的,再此条件下,如果两个字符串扔具有相同的字符和长度,则返回true,否则返回folse.
语法:str.equalslgnoreCase(String otherstr)
***str:参与比较的一个字符串对象
***otherstr:参加比较的另一个字符串对象
***返回值:返回boolean类型.
在字符串比较中,不允许使用"==",这是严重错误.
package 基本数据类型; public class String字符串 { public static void main(String[] args) { //String 不同定义方法意义不同 String str="字符串常量"; String str1=new String("字符串常量");//构造方法, String str2=new String("字符串常量");//new开辟新的内存空间 String str3="字符串常量"; System.out.println(str); System.out.println(str1); System.out.println(str2); System.out.println(str==str1);//返回false,因为定义方式不同,意义不同 System.out.println(str==str2);//返回false,因为定义方式不同,意义不同 System.out.println(str1==str2);//返回false,因为定义方式不同,意义不同 System.out.println(str==str3);//返回true,因为定义方式相同,意义相同 //==运算实际比较的是内存地址是否相等,本质不是不是比较值,用new时不适用 //解决方法 .equals System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true,这个才是表示字符串是否相等 System.out.println(str.equals(str1)); //字符串信息 //.length()字符串长度,带括号的是方法,不带括号的是属性 System.out.println("str字符串长度="+str.length()); //传入参数 char[]c=new char[]{'我','很','好'}; String str4=new String(c); System.out.println(str4); //.indexOf从(前往后)查找字符串中子字符串的首个位置,返回找到后的首字的索引值 //有再多也返回第一个 .indexOf System.out.println("常字的位置="+str.indexOf("常")); //返回第一个字的位置 System.out.println("常字的位置="+str.indexOf("串常量")); //如果字符串中查找不到,返回-1 判断包含某个字符串,<0没有,>=0包含 System.out.println("常字的位置="+str.indexOf("xxx")); //.lastIndexOf检索从(后往前)查找位置,但是返回索引值仍是从0开始 System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("常")); //获取字符 char c1=str.charAt(0); System.out.println(c1); } } 答案: 字符串常量 字符串常量 字符串常量 false false false true true true str字符串长度=5 我很好 常字的位置=3 常字的位置=2 常字的位置=-1 3 字