✅ 669. 修剪二叉搜索树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree
描述
给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改变树的根节点,所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。
示例 1:
输入:
1
/
0 2
L = 1
R = 2
输出:
1
2
示例 2:
输入:
3
/
0 4
2
/
1
L = 1
R = 3
输出:
3
/
2
/
1
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解答
思路:是递归
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int L, int R) {
if (root == null)
return root;
//下面两个if相当于删除不满足要求的节点
if (root.val < L)
return trimBST(root.right, L, R);//返回修剪过的右子树。抱有一丝丝期望,希望右子树能够满足要求,因为右子树的值大于当前根节点的值
if (root.val > R)
return trimBST(root.left, L, R);//返回修剪过的左子树,抱有一丝丝期望,希望左子树能够满足要求,因为左子树的值小于当前根节点的值
//处理正常的节点
root.left = trimBST(root.left, L, R);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, L, R);
return root;
}
写递归一定要把每步做什么,终止条件考虑清楚,思路一旦不清楚绕进去就再也出不来了
java
py
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def trimBST(self, root: TreeNode, L: int, R: int) -> TreeNode:
if root == None: return None
if (root.val < L) : return self.trimBST(root.right, L, R)
if (root.val > R) : return self.trimBST(root.left, L, R)
# for the normal ones
root.left = self.trimBST(root.left, L, root.val)# todo 为啥可以:把R 改为root.val
root.right = self.trimBST(root.right, root.val, R)
return root
'''
执行用时 :
60 ms
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
46.49%
的用户
内存消耗 :
17.5 MB
, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了
30.33%
的用户
'''
✅ 883. 三维形体投影面积
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/projection-area-of-3d-shapes
描述
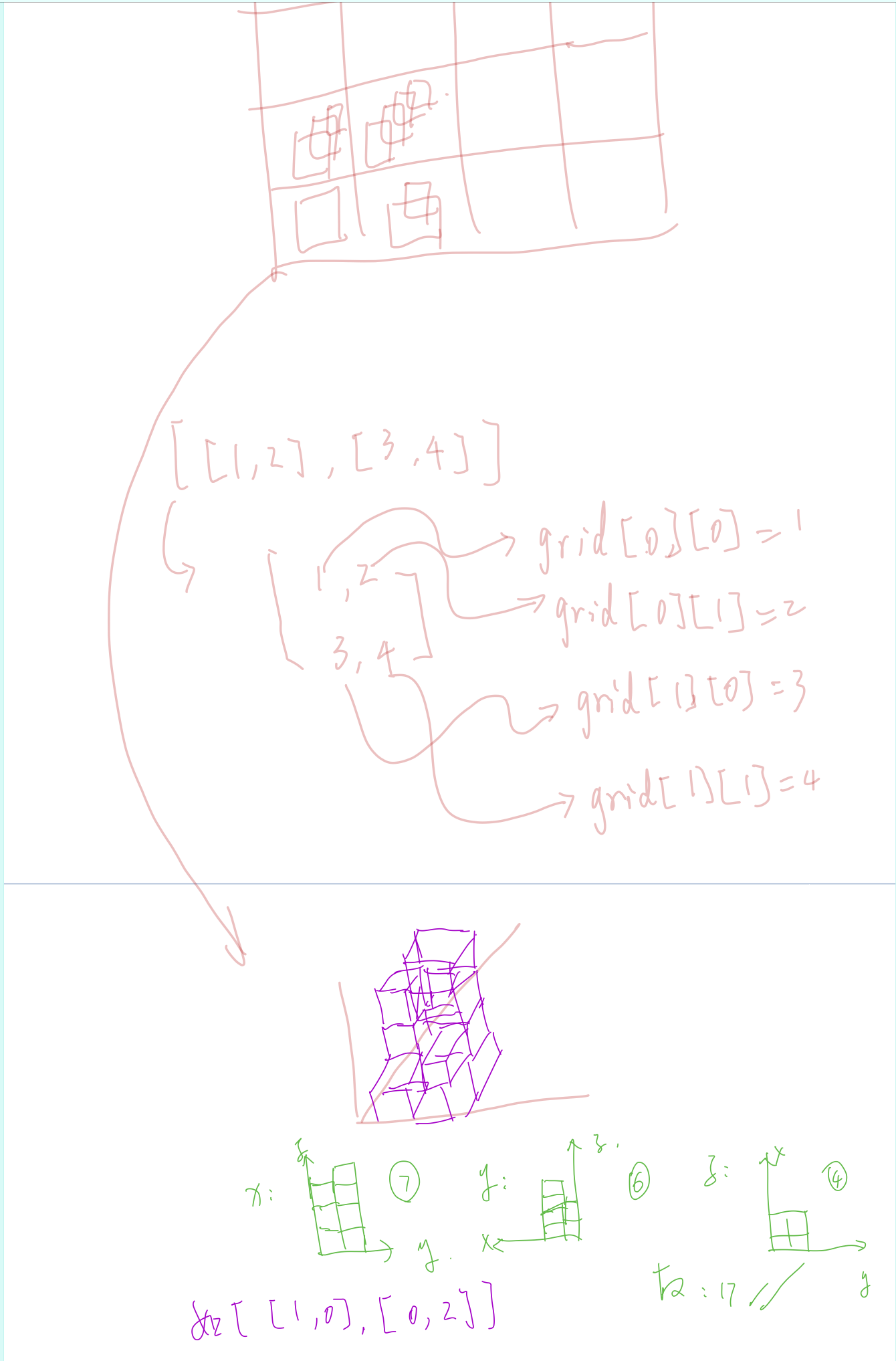
在 N * N 的网格中,我们放置了一些与 x,y,z 三轴对齐的 1 * 1 * 1 立方体。
每个值 v = grid[i][j] 表示 v 个正方体叠放在单元格 (i, j) 上。
现在,我们查看这些立方体在 xy、yz 和 zx 平面上的投影。
投影就像影子,将三维形体映射到一个二维平面上。
在这里,从顶部、前面和侧面看立方体时,我们会看到“影子”。
返回所有三个投影的总面积。
示例 1:
输入:[[2]]
输出:5
示例 2:
输入:[[1,2],[3,4]]
输出:17
解释:
这里有该形体在三个轴对齐平面上的三个投影(“阴影部分”)。
示例 3:
输入:[[1,0],[0,2]]
输出:8
示例 4:
输入:[[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
输出:14
示例 5:
输入:[[2,2,2],[2,1,2],[2,2,2]]
输出:21
提示:
1 <= grid.length = grid[0].length <= 50
0 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/projection-area-of-3d-shapes
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解答

正视图:每一行最大值之和;
侧视图:每一列最大值之和;
俯视图:柱子个数;
执行用时 : 56 ms, 在Projection Area of 3D Shapes的Python3提交中击败了90.85% 的用户
内存消耗 : 13 MB, 在Projection Area of 3D Shapes的Python3提交中击败了94.12% 的用户
class Solution:
def projectionArea(self, grid):
return sum([sum(map(max, grid)), sum(map(max, zip(*grid))), sum(v > 0 for row in grid for v in row)])
my understanding

c
int projectionArea(int** grid, int gridSize, int* gridColSize){
int i, j, xy = 0, xz = 0, yz = 0, row_max[gridSize], col_max[*gridColSize];
//init the row soldiers and col soldiers to 0
memset(row_max, 0, gridSize * sizeof(int));
memset(col_max, 0, *gridColSize * sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < gridSize; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < *gridColSize; j++) {
row_max[i] = row_max[i] > grid[i][j] ? row_max[i] : grid[i][j];
col_max[j] = col_max[j] > grid[i][j] ? col_max[j] : grid[i][j];
xy = grid[i][j] > 0 ? xy + 1 : xy;
}
}
//finish all count, then we count all size on yz and xz
for (int k = 0; k < gridSize; k++) {
yz += row_max[k];
}
for (int k = 0; k < *gridColSize; k++) {
xz += col_max[k];
}
return xy + xz + yz;
}
/*执行用时 :
24 ms
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
14.81%
的用户
内存消耗 :
7.2 MB
, 在所有 C 提交中击败了
80.00%
的用户*/
py
class Solution:
def projectionArea(self, grid):
return sum([sum(map(max, grid)), sum(map(max, zip(*grid))), sum(v > 0 for row in grid for v in row)])
py map ??
https://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-map.html
map() 会根据提供的函数对指定序列做映射。
第一个参数 function 以参数序列中的每一个元素调用 function 函数,返回包含每次 function 函数返回值的新列表。
语法
map() 函数语法:
map(function, iterable, ...)
参数
function -- 函数
iterable -- 一个或多个序列
返回值
Python 2.x 返回列表。
Python 3.x 返回迭代器。
实例
以下实例展示了 map() 的使用方法:
>>>def square(x) : # 计算平方数
... return x ** 2
...
>>> map(square, [1,2,3,4,5]) # 计算列表各个元素的平方
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
>>> map(lambda x: x ** 2, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) # 使用 lambda 匿名函数
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
# 提供了两个列表,对相同位置的列表数据进行相加
>>> map(lambda x, y: x + y, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9], [2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
[3, 7, 11, 15, 19]
python zip(*grid) ??
todo
grid = [[1,2],[3,4]]
b = zip(grid) # [([1, 2],), ([3, 4],)] todo watch me!
print(b)
c = zip(*grid)
print(c) # [(1, 3), (2, 4)]
✅ 929. 独特的电子邮件地址
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-email-addresses
描述
每封电子邮件都由一个本地名称和一个域名组成,以 @ 符号分隔。
例如,在 alice@leetcode.com中, alice 是本地名称,而 leetcode.com 是域名。
除了小写字母,这些电子邮件还可能包含 '.' 或 '+'。
如果在电子邮件地址的本地名称部分中的某些字符之间添加句点('.'),则发往那里的邮件将会转发到本地名称中没有点的同一地址。例如,"alice.z@leetcode.com” 和 “alicez@leetcode.com” 会转发到同一电子邮件地址。 (请注意,此规则不适用于域名。)
如果在本地名称中添加加号('+'),则会忽略第一个加号后面的所有内容。这允许过滤某些电子邮件,例如 m.y+name@email.com 将转发到 my@email.com。 (同样,此规则不适用于域名。)
可以同时使用这两个规则。
给定电子邮件列表 emails,我们会向列表中的每个地址发送一封电子邮件。实际收到邮件的不同地址有多少?
示例:
输入:["test.email+alex@leetcode.com","test.e.mail+bob.cathy@leetcode.com","testemail+david@lee.tcode.com"]
输出:2
解释:实际收到邮件的是 "testemail@leetcode.com" 和 "testemail@lee.tcode.com"。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-email-addresses
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解答
替换 . 为 空白。
定位到 + 以及 定位 到 @, 我们删除这两个东西 之间的东西。
经历上面2 步骤,我们将结果 加入 set,
最后返回 set.size()
re
流和正则表达式 毁天灭地。。。 todo 0223 学习 流和正则表达式
class Solution { public int numUniqueEmails(String[] emails) {
return (int) Arrays.stream(emails).map(a1 -> {
a1 = a1.replaceAll("+.*@", "@");
while (a1.matches(".*..*@.*")) {//只要循环中的a1 @号前面部分里面有.,就替换为空
a1 = a1.replaceFirst(".", "");
}
return a1;
}).distinct().count();
}
学习java 流
Java 8 Stream.distinct() 列表去重示例
https://blog.csdn.net/haiyoung/article/details/80934467
在这篇文章里,我们将提供Java8 Stream distinct()示例。 distinct()返回由该流的不同元素组成的流。distinct()是Stream接口的方法。distinct()使用hashCode()和equals()方法来获取不同的元素。因此,我们的类必须实现hashCode()和equals()方法。如果distinct()正在处理有序流,那么对于重复元素,将保留以遭遇顺序首先出现的元素,并且以这种方式选择不同元素是稳定的。在无序流的情况下,不同元素的选择不一定是稳定的,是可以改变的。distinct()执行有状态的中间操作。在有序流的并行流的情况下,保持distinct()的稳定性是需要很高的代价的,因为它需要大量的缓冲开销。如果我们不需要保持遭遇顺序的一致性,那么我们应该可以使用通过BaseStream.unordered()方法实现的无序流。
java
class Solution {
public int numUniqueEmails(String[] emails) {
if (emails.length < 1) return 0;
Set<String> myset = new HashSet<>();
for (String email: emails) {
String[] splitted = email.split("@");
String firstPart = splitted[0];
String tmp = "";
for(int i = 0; i < firstPart.length(); i++) {
if (firstPart.charAt(i) == '.') continue;
if (firstPart.charAt(i) == '+') break;
tmp += firstPart.charAt(i);
}
tmp += "@" + splitted[1];
myset.add(tmp);
}
return myset.size();
}
}
/*执行用时 :
45 ms
, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了
9.15%
的用户
内存消耗 :
41.9 MB
, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了
5.26%
的用户*/