STL的基本使用之关联容器:map和multiMap的基本使用
-
简介
- map 和 multimap 内部也都是使用红黑树来实现,他们存储的是键值对,并且会自动将元素的key进行排序。两者不同在于map 不允许key重复,而multiSet 允许key重复
-
头文件 #include< map >
-
构造函数及析构函数

-
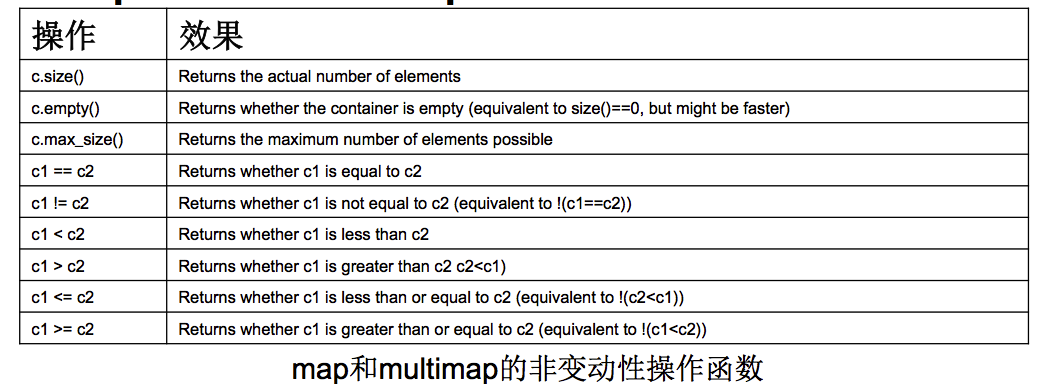
非变动性操作函数
- 运算符重载
- 下标运算符

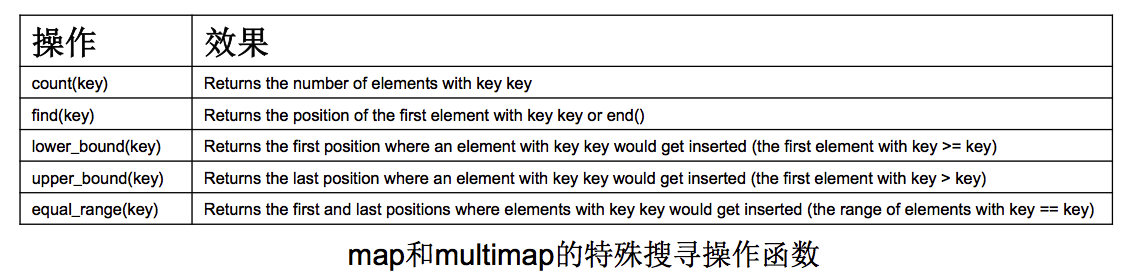
- 查找操作函数
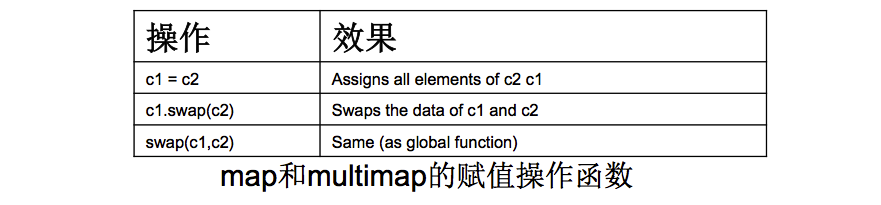
- 赋值操作
- 迭代器操作
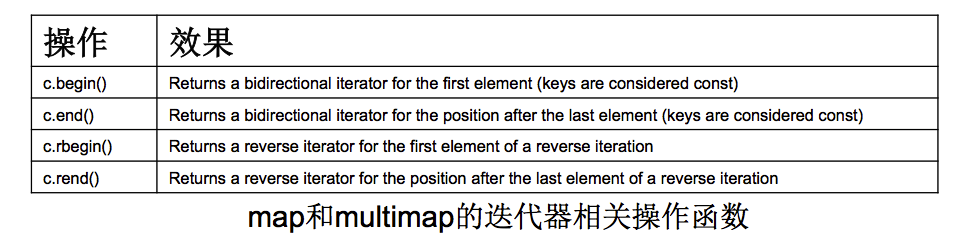
- 运算符重载
-
插入删除操作
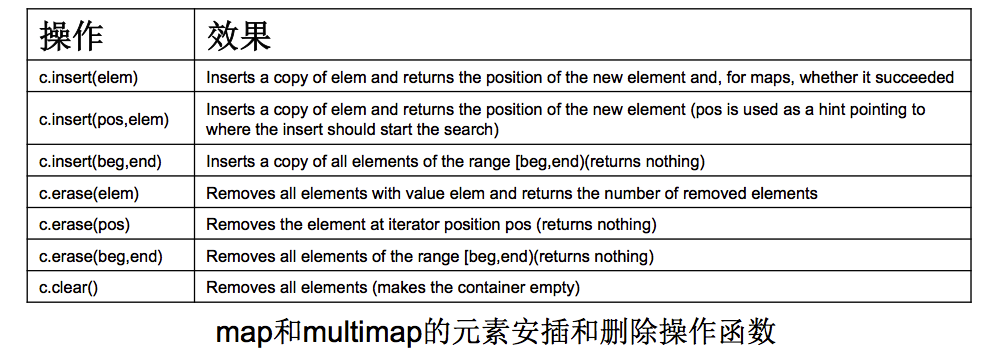
-
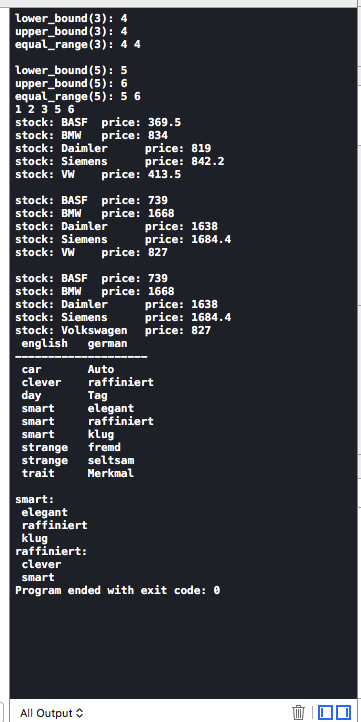
范例如下
#include <iostream> #include <map> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; int main () { #pragma mark - 基本使用 map<int,string> c; c.insert(make_pair(1,"1")); c.insert(make_pair(2,"2")); c.insert(make_pair(4,"4")); c.insert(make_pair(5,"5")); c.insert(make_pair(6,"6")); cout << "lower_bound(3): " << c.lower_bound(3)->second << endl; cout << "upper_bound(3): " << c.upper_bound(3)->first << endl; cout << "equal_range(3): " << (c.equal_range(3).first)->first << " " << (c.equal_range(3).second)->first << endl; cout << endl; cout << "lower_bound(5): " << c.lower_bound(5)->first << endl; cout << "upper_bound(5): " << c.upper_bound(5)->first << endl; cout << "equal_range(5): " << (c.equal_range(5).first)->first << " " << (c.equal_range(5).second)->first << endl; c.insert(c.lower_bound(3), make_pair(3, "3")); // c.erase(4); c.erase(c.find(4)); map<int,string>::iterator i; for (i = c.begin(); i!=c.end(); i++) { cout<<i->first<<" "; } cout<<endl; #pragma mark- 实例1:将map当做关联数组 typedef map<string,float> StringFloatMap; StringFloatMap stocks; // create empty container //insert some elements stocks["BASF"] = 369.50; stocks["VW"] = 413.50; stocks["Daimler"] = 819.00; stocks["BMW"] = 834.00; stocks["Siemens"] = 842.20; //print all elements StringFloatMap::iterator pos; for (pos = stocks.begin(); pos != stocks.end(); ++pos) { cout << "stock: " << pos->first << " " << "price: " << pos->second << endl; } cout << endl; //boom (all prices doubled) for (pos = stocks.begin(); pos != stocks.end(); ++pos) { pos->second *= 2; } //print all elements for (pos = stocks.begin(); pos != stocks.end(); ++pos) { cout << "stock: " << pos->first << " " << "price: " << pos->second << endl; } cout << endl; /*rename key from "VW" to "Volkswagen" *-only provided by exchanging element */ stocks["Volkswagen"] = stocks["VW"]; stocks.erase("VW"); //print all elements for (pos = stocks.begin(); pos != stocks.end(); ++pos) { cout << "stock: " << pos->first << " " << "price: " << pos->second << endl; } #pragma mark - 实例2:将multimap当做字典 typedef multimap<string,string> StrStrMMap; //create empty dictionary StrStrMMap dict; //insert some elements in random order dict.insert(make_pair("day","Tag")); dict.insert(make_pair("strange","fremd")); dict.insert(make_pair("car","Auto")); dict.insert(make_pair("smart","elegant")); dict.insert(make_pair("trait","Merkmal")); dict.insert(make_pair("strange","seltsam")); dict.insert(make_pair("smart","raffiniert")); dict.insert(make_pair("smart","klug")); dict.insert(make_pair("clever","raffiniert")); //print all elements StrStrMMap::iterator pos1; cout.setf (ios::left, ios::adjustfield); cout << ' ' << setw(10) << "english " << "german " << endl; cout << setfill('-') << setw(20) << "" << setfill(' ') << endl; for (pos1 = dict.begin(); pos1 != dict.end(); ++pos1) { cout << ' ' << setw(10) << pos1->first.c_str() << pos1->second << endl; } cout << endl; //print all values for key "smart" string word("smart"); cout << word << ": " << endl; for (pos1 = dict.lower_bound(word); pos1 != dict.upper_bound(word); ++pos1) { cout << " " << pos1->second << endl; } //print all keys for value "raffiniert" word = ("raffiniert"); cout << word << ": " << endl; for (pos1 = dict.begin(); pos1 != dict.end(); ++pos1) { if (pos1->second == word) { cout << " " << pos1->first << endl; } }}
-
运行截图